SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 363-377.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.02.006
• Research paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Xiao-shan1,3)( ), WAN Yong-ge2,3),*(
), WAN Yong-ge2,3),*( )
)
Received:2020-12-23
Revised:2021-05-15
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-06-14
Contact:
WAN Yong-ge
通讯作者:
万永革
作者简介:王晓山, 男, 1980年生, 博士, 高级工程师, 主要研究方向为地震定位、 震源机制与应力场反演及地震活动性等方面研究, E-mail: pragueboy@163.com。
基金资助:CLC Number:
WANG Xiao-shan, WAN Yong-ge. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE CRUSTAL STRESS FIELD AND ITS DIRECTION CONVERGENCE BEFORE THE WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(2): 363-377.
王晓山, 万永革. 汶川地震前震中周围地壳应力场及应力方向集中的特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 363-377.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.dzdz.ac.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.02.006
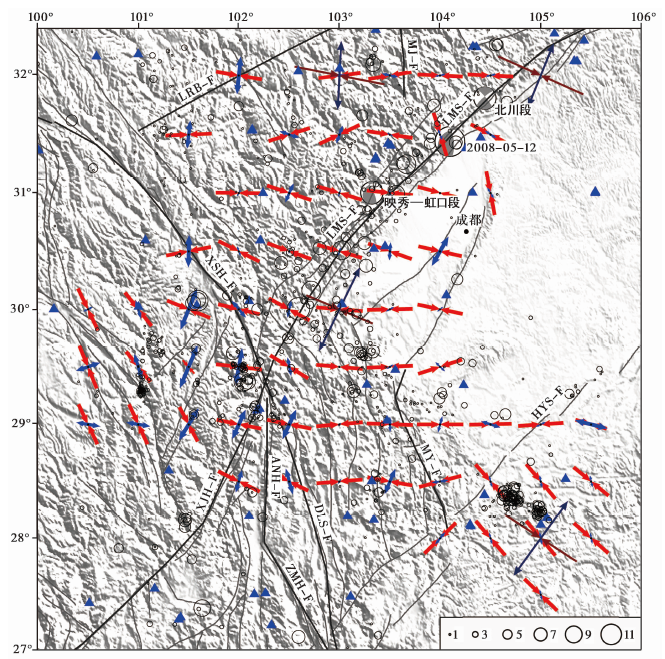
Fig. 1 The earthquakes(circles)and stations(blue triangles)used in this study and the P(Red quivers) and T(blue quivers)directions of the composite focal mechanisms obtained in this study.
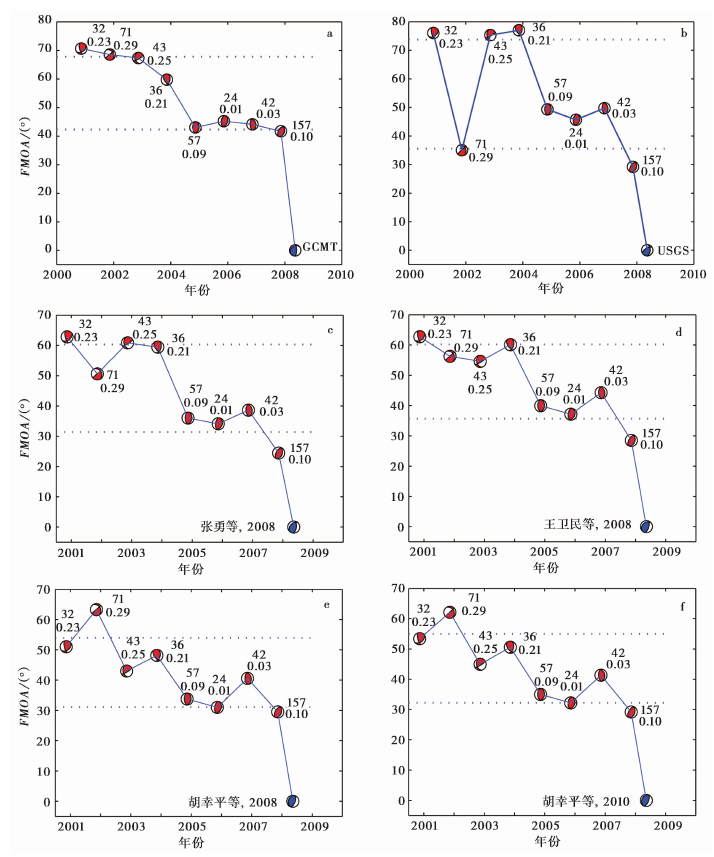
Fig. 3 The FMOAs of the composite focal mechanisms(beach balls with red color filled) to Wenchuan earthquake focal mechanism(blue color filled)vs. time(the same below).
| 序号 | 走向/(°) | 倾角/(°) | 滑动角/(°) | FMOAmin/(°) | FMOAlimit/(°) | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 231 | 25 | 138 | 41.7 | 42.3 | GCMT |
| 2 | 238 | 59 | 128 | 29.2 | 35.6 | USGS |
| 3 | 225 | 39 | 120 | 24.4 | 31.4 | 张勇等, |
| 4 | 229 | 32 | 118 | 28.5 | 35.7 | 王卫民等, |
| 5 | 202 | 27 | 90 | 29.5 | 31.1 | 胡幸平等, |
| 6 | 208 | 27 | 96 | 29.2 | 32.2 | 胡幸平, |
Table1 The FMOAs of the composite focal mechanisms to Wenchuan earthquake focal mechanism and their mean value subtracting its standard deviation value
| 序号 | 走向/(°) | 倾角/(°) | 滑动角/(°) | FMOAmin/(°) | FMOAlimit/(°) | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 231 | 25 | 138 | 41.7 | 42.3 | GCMT |
| 2 | 238 | 59 | 128 | 29.2 | 35.6 | USGS |
| 3 | 225 | 39 | 120 | 24.4 | 31.4 | 张勇等, |
| 4 | 229 | 32 | 118 | 28.5 | 35.7 | 王卫民等, |
| 5 | 202 | 27 | 90 | 29.5 | 31.1 | 胡幸平等, |
| 6 | 208 | 27 | 96 | 29.2 | 32.2 | 胡幸平, |
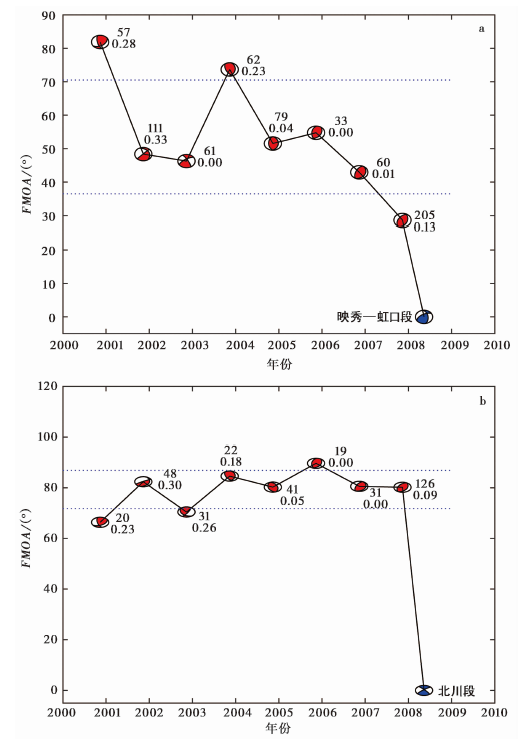
Fig. 4 The FMOAs of the composite focal mechanisms to the focal mechanisms which represent the Yingxiu-Hongkou segment(a)and the Beichuan segment(b)vs. time.
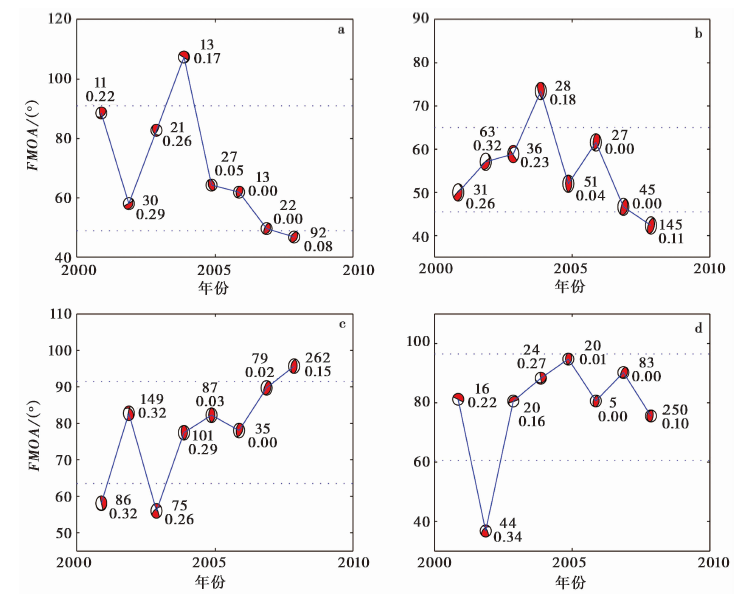
Fig. 5 The FMOAs of the composite focal mechanisms(beach balls with red color filled) to the focal mechanism which represents the stress field direction obtained by Wan(2010)vs. time. a (32°N, 105°E); b (32°N, 103°E); c (30°N, 103°E); d (28°N, 105°E)
| [1] | 陈颙. 1978. 用震源机制一致性作为描述地震活动性的新参数[J]. 地球物理学报, 19(2): 142-159. |
| CHEN Yong. 1978. Consistence of focal mechanism as a new parameter in describing seismic activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 19(2): 142-159. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 刁桂苓, 于利民, 李钦祖. 1994. 强震前后震源区应力场变化一例[J]. 地震学报, 16(2): 64-69. |
| DIAO Gui-ling, YU Li-min, LI Qin-zu. 1994. Variation of stress field in the source region around a strong shock: An example[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 16(2): 64-69. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 胡召齐, 朱光, 刘国生, 等. 2009. 川东“侏罗山式”褶皱带形成时代: 不整合面的证据[J]. 地质评论, 55(1): 32-42. |
| HU Shao-qi, ZHU Guang, LIU Guo-sheng,et al. 2009. The folding time of the eastern Sichuan Jura-type fold belt: Evidence from unconformity[J]. Geological Review, 55(1): 32-42. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 胡幸平. 2010. 汶川地震序列震源机制及其动力学解释[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地壳应力研究所. |
| HU Xing-ping. 2010. Focal mechanism solutions of Wenchuan earthquake sequence and its dynamic explanation[D]. Institute of Crustal Dynamics, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 胡幸平, 俞春泉, 陶开, 等. 2008. 利用P波初动资料求解汶川地震及其强余震震源机制解[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(6): 1711-1718. |
| HU Xing-ping, YU Chun-quan, TAO Kai,et al. 2008. Focal mechanism solutions of Wenchuan earthquake and its strong aftershocks obtained from initial P wave polarity analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(6): 1711-1718. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] |
雷建设, 赵大鹏, 徐锡伟, 等. 2018. 龙门山断裂带深部细结构与2008年汶川地震发震机理[J]. 科学通报, 63(19): 1906-1916. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00415.
DOI |
| LEI Jian-she, ZHAO Da-peng, XU Xi-wei,et al. 2018. Deep structure of the Longmenshan fault zone and mechanism of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(19): 1906-1916. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 李钦祖, 王泽皋, 贾云年, 等. 1973. 由单台小地震资料所得2个区域的应力场[J]. 地球物理学报, 16(1): 49-61. |
| LI Qin-zu, WANG Ze-gao, JIA Yun-nian,et al. 1973. Stress field obtained for two regions from weak earthquake data recorded at a single station[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 16(1): 49-61. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 牟磊育, 赵仲和, 张伟, 等. 2006. 用INGLADA与GEIGER方法实现近震精定位[J]. 中国地震, 22(3): 294-302. |
| MOU Lei-yu, ZHAO Zhong-he, ZHANG Wei,et al. 2006. Using the INGLADA and GEIGER method to realize regional earthquake location accurately[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 22(3): 294-302. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 沈正康, 王敏, 甘卫军, 等. 2003. 中国大陆现今构造应变率场及其动力学成因研究[J]. 地学前缘, 10(S1): 93-100. |
| SHEN Zheng-kang, WANG Min, GAN Wei-jun,et al. 2003. Contemporary tectonic strain rate field of Chinese continent and its geodynamic implications[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(S1): 93-100. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 孙若昧, 刘福田, 刘建华. 1991. 四川地区的地震层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 34(6): 708-716. |
| SUN Ruo-mei, LIU Fu-tian, LIU Jian-hua. 1991. Seismic tomography in Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 34(6): 708-716. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 万永革. 2001. “地震静态应力触发”问题的研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所. |
| WAN Yong-ge. 2001. Research on “seismic static stress triggering” problem[D]. Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 万永革. 2008. 美国Landers地震和Hector Mine地震前震源机制与主震机制一致现象的研究[J]. 中国地震, 24(3): 216-225. |
| WAN Yong-ge. 2008. Study on consistency of focal mechanism of mainshock and that of preshocks in Landers and Hector Mine earthquake in United States[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 24(3): 216-225. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] |
万永革. 2019. 同一地震多个震源机制中心解的确定[J]. 地球物理学报, 62(12): 4718-4728. doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0553.
DOI |
| WAN Yong-ge. 2019. Determination of center of several focal mechanisms of the same earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 62(12): 4718-4728. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 万永革, 盛书中, 程万正, 等. 2012. 考虑到时误差的地震定位算法及其在四川地区2001-2008 年地震定位的应用[J]. 地震地质, 34(1): 1-10. |
| WAN Yong-ge, SHENG Shu-zhong, CHENG Wan-zheng,et al. 2012. Earthquake location method with arrival time uncertainty considered and its application to location of earthquakes from 2001-2008 in Sichuan area[J]. Seismology and Geology, 34(1): 1-10. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 万永革, 吴逸民, 盛书中, 等. 2011. P波极性数据所揭示的台湾地区三维应力结构的初步结果[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(11): 2809-2818. |
| WAN Yong-ge, WU Yi-min, SHENG Shu-zhong,et al. 2011. Preliminary result of Taiwan 3-D stress field from P wave polarity data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(11): 2809-2818. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 王俊国, 刁桂苓. 2005. 千岛岛弧大震前哈佛大学矩心矩张量(CMT)解一致性的预测意义[J]. 地震学报, 27(2): 178-183. |
| WANG Jun-guo, DIAO Gui-ling. 2005. Consistent CMT solutions from Harvard University before great earthquakes in Kurile Islands and its significance for earthquake prediction[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 27(2): 178-183. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 王卫民, 赵连锋, 李娟, 等. 2008. 四川汶川8.0级地震震源过程[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(5): 1403-1410. |
| WANG Wei-min, ZHAO Lian-feng, LI Juan,et al. 2008. Rupture process of the MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake of Sichuan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(5): 1403-1410. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 谢富仁, 崔效锋, 赵建涛. 2003. 全球应力场与构造分析[J]. 地学前缘, 10(S1): 22-30. |
| XIE Fu-ren, CUI Xiao-feng, ZHAO Jian-tao. 2003. Analysis of global tectonic stress field[J]. Earth Science Frontier, 10(S1): 22-30. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 许忠淮, 刘玉芬, 张郢珍. 1979. 京津唐张地区地震应力场的方向特征[J]. 地震学报, 1(2): 121-132. |
| XU Zhong-huai, LIU Yu-fen, ZHANG Ying-zhen. 1979. On the characteristic of direction of the earthquake stress field around the Beijing area[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 1(2): 121-132. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 许忠淮, 阎明, 赵仲和. 1983. 由多个小地震推断的华北地区构造应力场的方向[J]. 地震学报, 5(3): 268-279. |
| XU Zhong-huai, YAN Ming, ZHAO Zhong-he. 1983. Evaluation of the direction of tectonic stress in North China from recorded data of a large number of small earthquakes[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 5(3): 268-279. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 杨蓉, 尊珠桑姆, 许长海, 等. 2010. 四川盆地东部华蓥山断裂滑动分析与古应力重建[J]. 内蒙古石油化工, 36(4): 97-100. |
| YANG Rong, ZUNZHU Sang-mu, XU Chang-hai,et al. 2010. Fault sliding analysis and paleostress reconstruction of Huayingshan faults to East Sichuan Basin[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry, 36(4): 97-100. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 曾融生, 孙为国. 1992. 青藏高原及其邻区的地震活动性和震源机制以及高原物质东流的讨论[J]. 地震学报, 11(S1): 531-563. |
|
ZENG Rong-sheng, SUN Wei-guo. 1992. Discuss on seismicity and focal mechanism in Tibet and its adjacent areas and matters of plateau flow to east[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 11(S1): 531-563. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [23] | 张勇, 冯万鹏, 许力生, 等. 2008. 2008 年汶川大地震的时空破裂过程[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 38(10): 1186-1194. |
| ZHANG Yong, FENG Wan-peng, XU Li-sheng,et al. 2008. Spatio-temporal rupture process of the 2008 great Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 38(10): 1186-1194. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] |
Becker T W, Lowry A R, Faccenna C,et al. 2015. Western US intermountain seismicity caused by changes in the upper mantle flow[J]. Nature, 524(7566): 458-461.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Feng G C, Hetland E A, Ding X,et al. 2010. Coseismic fault slip of the 2008 MW7.9 Wenchuan earthquake estimated from InSAR and GPS measurements[J]. Geophysics Research Letter, 37: L01302. doi: 10.1029/2009GL041213.
DOI |
| [26] |
Gao Y, Wang P D, Zheng S H,et al. 1998. Temporal changes in shear-wave splitting at an isolated swarm of small earthquakes in 1992 near Dongfang, Hainan Island, southern China[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 135(1): 102-112.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Gephart J W, Forsyth D W. 1984. An improved method for determining the regional stress tensor using earthquake focal mechanism data: Application to the San Fernando earthquake sequence[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89(B11): 9305-9320.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Kagan Y Y. 1991. 3-D rotation of double-couple earthquake sources[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 106(3): 709-716.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Lei J S, Li Y, Xie F R,et al. 2014. Pn anisotropic tomography and dynamics under eastern Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 119(3): 2174-2198.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Lei J S, Zhao D P. 2016. Teleseismic P-wave tomography and mantle dynamics beneath eastern Tibet[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 17(5): 1861-1884.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Lei J S, Zhao D P, Xu X W,et al. 2019. Is there a big mantle wedge under eastern Tibet?[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 292: 100-113.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Michael A J. 1984. Determination of stress from slip data: Faults and folds[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89(B13): 11517-11526.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Mooney W D, Laske G, Masters G. 1998. CRUST 5.1: A global crustal model at 5°×5°[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 103(B1): 727-747.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Mooney W D, Ritsema J, Hwang Y K. 2012. Crustal seismicity and the earthquake catalog maximum moment magnitude(Mcmax)in stable continental regions(SCRs): Correlation with the seismic velocity of the lithosphere[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 357-358: 78-83.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Robinson R, McGinty P J. 2000. The enigma of the Arthur’s Pass, New Zealand, earthquake: 2. The aftershock distribution and its relation to regional and induced stress fields[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105(B7): 16139-16150.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Shen Z K, Jackson D, Ge B. 1996. Crustal deformation across and beyond the Los Angeles Basin from geodetic measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 101(B12): 27957-27980.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Shen Z K, Sun J B, Zhang P Z,et al. 2009. Slip maxima at fault junctions and rupturing of barriers during the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2(10): 718-724.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Tong X P, Sandwell D T, Fialko Y. 2010. Coseismic slip model of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake derived from joint inversion of interferometric synthetic aperture radar, GPS, and field data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115: B04314. doi: 10.1029/2009JB006625.
DOI |
| [39] |
Wan Y G. 2010. Contemporary tectonic stress field in China[J]. Earthquake Science, 23(4): 377-386.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Wan Y G, Shen Z K. 2010. Coulomb failure stress changes on faults caused by the 2008 MW7.9 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 491(1-4): 105-118.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Wan Y G, Shen Z K, Bürgmann R,et al. 2017. Fault geometry and slip distribution of the 2008 MW7.9 Wenchuan, China earthquake, inferred from GPS and InSAR measurements[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 208(2): 748-766.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Wan Y G, Sheng S Z. 2009. Seismological evidence for the convergence of crustal stress orientation before large earthquakes[J]. Earthquake Science, 22(6): 623-629.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Wan Y G, Sheng S Z, Huang J C,et al. 2016. The grid search algorithm of tectonic stress tensor based on focal mechanism data and its application in the boundary zone of China, Vietnam and Laos[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 27(5): 777-785.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Wessel P, Smith W M F. 1998. New improved version of generic mapping tools released[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 79(47): 579.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Xu Z H, Wang S Y, Huang Y R,et al. 1992. Tectonic stress field of China inferred from a large number of small earthquakes[J]. Journal Geophysical Research, 97(B8): 11867-11877.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Zoback M D. 1992. First and second order patterns of stress in the lithosphere: The World Stress Map Project[J]. Journal Geophysical Research, 97(B8): 11703-11728.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Zoback M L, Zoback M D, Adams J,et al. 1989. Global patterns of tectonic stress[J]. Nature, 341:291-298.
DOI URL |
| [1] | SONG Dong-mei, WANG Hui, SHAN Xin-jian, WANG Bin, CUI Jian-yong. A NOVEL EXTRACTION METHOD OF PRE-EARTHQUAKE GRACE GRAVITY ANOMALY INFORMATION BASED ON MAXIMUM SHEAR STRAIN [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(6): 1539-1556. |
| [2] | CHEN Li-juan, CHEN Xue-zhong, LI Yan-e, GONG Li-wen. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN DECREASING AMPLITUDE OF b-VALUE AND THE SEISMOGENIC ZONE OF THE WENCHUAN MS8.0 EARTHQUAKE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(4): 1046-1058. |
| [3] | GUO Shu-song, ZHU Yi-qing, XU Yun-ma, LIU Fang, ZHAO Yun-feng, ZHANG Guo-qing, ZHU Hui. GRAVITY EVIDENCE OF META-INSTABLE STATE BEFORE THE 2008 WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(6): 1368-1380. |
| [4] | CUI Hua-wei, ZHENG Jian-chang, ZHANG Zheng-shuai, LI Dong-mei, CHAI Guang-bin. FITTING THE FAULT PLANE PARAMETERS WITH SMALL EARTHQUAKES AND THE CHARACTERISTICS OF STRESS FIELD OF CHANGDAO AREA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2020, 42(6): 1432-1445. |
| [5] | LAN Jian, CHEN Xiao-li. EVOLUTION CHARACTERISTICS OF LANDSLIDES TRIGGERED BY 2008 MS8.0 WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE IN YINGXIU AREA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2020, 42(1): 125-146. |
| [6] | ZHU Chuan-hua, SHAN Xin-jian, ZHANG Guo-hong, JIAO Zhong-hu, ZHANG Ying-feng, LI Yan-chuan, QIAO Xin. TWO DIMENSIONAL MODEL ON RELATION BETWEEN THERMAL ANOMALY BEFORE WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE AND TECTONIC STRESS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2019, 41(6): 1497-1510. |
| [7] | SONG Dong-mei, XIANG Liang, SHAN Xin-jian, YIN Jing-yuan, WANG Bin, CUI Jian-yong. THE METHOD OF CONSTRUCTING IONOSPHERIC TEC BACKGROUND FIELD BASED ON SVR MODEL [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2019, 41(6): 1511-1528. |
| [8] | WANG Hui, CAO Jian-ling, XU Hua-chao. PRELIMINARY APPLICATION OF FOCAL MECHANISM SOLUTIONS OF SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZE EARTHQUAKES TO FAULT STABILITY ANALYSIS IN THE SOUTHEASTERN TIBETAN PLATEAU [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2019, 41(3): 633-648. |
| [9] | MA Si-yuan, XU Chong, WANG Tao, LIU Jia-mei. APPLICATION OF TWO SIMPLIFIED NEWMARK MODELS TO THE ASSESSMENT OF LANDSLIDES TRIGGERED BY THE 2008 WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2019, 41(3): 774-788. |
| [10] | XU Zhi-ping, WANG Fu-yun, JIANG Lei, ZHAO Yan-na, YANG Li-pu, TANG Lin. THE THREE DIMENSIONAL DENSITY STRUCTURE OF CRUST AND UPPER MANTLE IN THE CENTRAL-SOUTHERN PART OF LONGMENSHAN [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2019, 41(1): 84-98. |
| [11] | YIN De-yu, LIU Qi-fang, LIU Chang, JI Xin-yang. ESTIMATING THE WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE RUPTURE PROCESS USING NEAR FIELD STRONG MOTION RECORDS AND COSEISMIC DISPLACEMENTS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2018, 40(3): 698-717. |
| [12] | ZHAO You-jia, ZHANG Guo-hong, ZHANG Ying-feng, SHAN Xin-jian, QU Chun-yan. TWO-DIMENSIONAL WHOLE CYCLE SIMULATION OF SPONTANE-OUS RUPTURE OF THE 2008 WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE USING THE CONTINUOUS-DISCRETE ELEMENT METHOD [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2018, 40(1): 12-26. |
| [13] | LIU Yuan-zheng, MA Jin, MA Wen-tao, JIANG Tong. INFLUENCE OF PRESSURE HEAD CHANGE AND ITS CHANGE RATE ON RESERVOIR TRIGGERED SEISMICITY -A CASE STUDY OF ZIPINGPU RESERVOIR [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2017, 39(3): 437-450. |
| [14] | YAO Lu, MA Sheng-li, WANG Yu, HE Hong-lin, CHEN Jian-ye, YANG Xiao-song, SHIMAMOTO Toshihiko. THE VITRINITE REFLECTANCE OF FAULT ROCKS FROM THE WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE FAULT ZONE: CONSTRAINTS ON FRICTIONAL PROPERTIES OF THE FAULT DURING THE EARTHQUAKE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2016, 38(4): 817-829. |
| [15] | WEI Ben-yong, SU Gui-wu. ASSESSMENT ON INDIRECT ECONOMIC LOSS OF WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE DISASTER BASED ON INPUT-OUTPUT ANALYSIS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2016, 38(4): 1082-1094. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||