SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 627-648.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.02.20240156
Previous Articles Next Articles
NIE Wen-yu1)( ), FAN Xi-wei1),*(
), FAN Xi-wei1),*( ), LI Hua-yue1,2), QI Yuan-meng1), LIU Min1)
), LI Hua-yue1,2), QI Yuan-meng1), LIU Min1)
Received:2024-12-09
Revised:2025-03-14
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-06-07
聂文钰1)( ), 范熙伟1),*(
), 范熙伟1),*( ), 李华玥1,2), 齐远猛1), 刘敏1)
), 李华玥1,2), 齐远猛1), 刘敏1)
通讯作者:
* 范熙伟, 男, 1986年生, 研究员, 博士生导师, 现主要研究方向为地震应急与减灾, E-mail: fanxiwei@ies.ac.cn。
作者简介:聂文钰, 女, 1998年生, 现为中国地震局地质研究所第四纪地质学专业在读博士研究生, 主要从事地震灾害风险评估研究, E-mail: niewenyu0528@163.com。
基金资助:NIE Wen-yu, FAN Xi-wei, LI Hua-yue, QI Yuan-meng, LIU Min. EARTHQUAKE CASUALTY RISK ANALYSIS UNDER THE RECURRENCE SCENARIO OF THE 1902 ARTUX MS8¼ EARTHQUAKE: A CASE STUDY OF KASHGAR AND ARTUX[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(2): 627-648.
聂文钰, 范熙伟, 李华玥, 齐远猛, 刘敏. 1902年阿图什MS8¼地震重现下的人员伤亡风险分析——以喀什市和阿图什市为例[J]. 地震地质, 2025, 47(2): 627-648.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.dzdz.ac.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.02.20240156
| 破坏等级 | 地震烈度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅷ | Ⅸ | Ⅹ | Ⅺ | |
| 基本完好 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 轻微破坏 | 12 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| 中等破坏 | 16 | 14 | 0 | 0 |
| 严重破坏 | 27 | 25 | 20 | 0 |
| 毁坏 | 38 | 50 | 80 | 100 |
Table1 Building vulnerability matrix for civil structures in the study area (unit: %)
| 破坏等级 | 地震烈度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅷ | Ⅸ | Ⅹ | Ⅺ | |
| 基本完好 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 轻微破坏 | 12 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| 中等破坏 | 16 | 14 | 0 | 0 |
| 严重破坏 | 27 | 25 | 20 | 0 |
| 毁坏 | 38 | 50 | 80 | 100 |
| 破坏等级 | 地震烈度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅷ | Ⅸ | Ⅹ | Ⅺ | |
| 基本完好 | 21 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| 轻微破坏 | 23 | 20 | 5 | 0 |
| 中等破坏 | 34 | 28 | 20 | 10 |
| 严重破坏 | 16 | 21 | 30 | 30 |
| 毁坏 | 6 | 19 | 45 | 60 |
Table2 Building vulnerability matrix for brick and wood structures in the study area(unit: %)
| 破坏等级 | 地震烈度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅷ | Ⅸ | Ⅹ | Ⅺ | |
| 基本完好 | 21 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| 轻微破坏 | 23 | 20 | 5 | 0 |
| 中等破坏 | 34 | 28 | 20 | 10 |
| 严重破坏 | 16 | 21 | 30 | 30 |
| 毁坏 | 6 | 19 | 45 | 60 |
| 破坏等级 | 地震烈度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅷ | Ⅸ | Ⅹ | XI | |
| 基本完好 | 24 | 16 | 5 | 0 |
| 轻微破坏 | 37 | 32 | 15 | 10 |
| 中等破坏 | 22 | 24 | 20 | 15 |
| 严重破坏 | 11 | 16 | 30 | 25 |
| 毁坏 | 6 | 12 | 30 | 50 |
Table3 Building vulnerability matrix for brick and concrete structures in the study area(unit: %)
| 破坏等级 | 地震烈度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅷ | Ⅸ | Ⅹ | XI | |
| 基本完好 | 24 | 16 | 5 | 0 |
| 轻微破坏 | 37 | 32 | 15 | 10 |
| 中等破坏 | 22 | 24 | 20 | 15 |
| 严重破坏 | 11 | 16 | 30 | 25 |
| 毁坏 | 6 | 12 | 30 | 50 |
| 破坏等级 | 地震烈度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅷ | Ⅸ | Ⅹ | XI | |
| 基本完好 | 39 | 27 | 8 | 0 |
| 轻微破坏 | 47 | 34 | 22 | 15 |
| 中等破坏 | 9 | 27 | 45 | 30 |
| 严重破坏 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| 毁坏 | 0 | 2 | 10 | 35 |
Table4 Building vulnerability matrix for reinforced concrete structures in the study area(unit: %)
| 破坏等级 | 地震烈度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅷ | Ⅸ | Ⅹ | XI | |
| 基本完好 | 39 | 27 | 8 | 0 |
| 轻微破坏 | 47 | 34 | 22 | 15 |
| 中等破坏 | 9 | 27 | 45 | 30 |
| 严重破坏 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| 毁坏 | 0 | 2 | 10 | 35 |
| 破坏等级 | 地震烈度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅷ | Ⅸ | Ⅹ | XI | |
| 基本完好 | 71 | 20 | 5 | 0 |
| 轻微破坏 | 23 | 45 | 26 | 15 |
| 中等破坏 | 5 | 25 | 32 | 20 |
| 严重破坏 | 1 | 10 | 20 | 25 |
| 毁坏 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 40 |
Table5 Building vulnerability matrix for the Anju structures in the study area(unit: %)
| 破坏等级 | 地震烈度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅷ | Ⅸ | Ⅹ | XI | |
| 基本完好 | 71 | 20 | 5 | 0 |
| 轻微破坏 | 23 | 45 | 26 | 15 |
| 中等破坏 | 5 | 25 | 32 | 20 |
| 严重破坏 | 1 | 10 | 20 | 25 |
| 毁坏 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 40 |
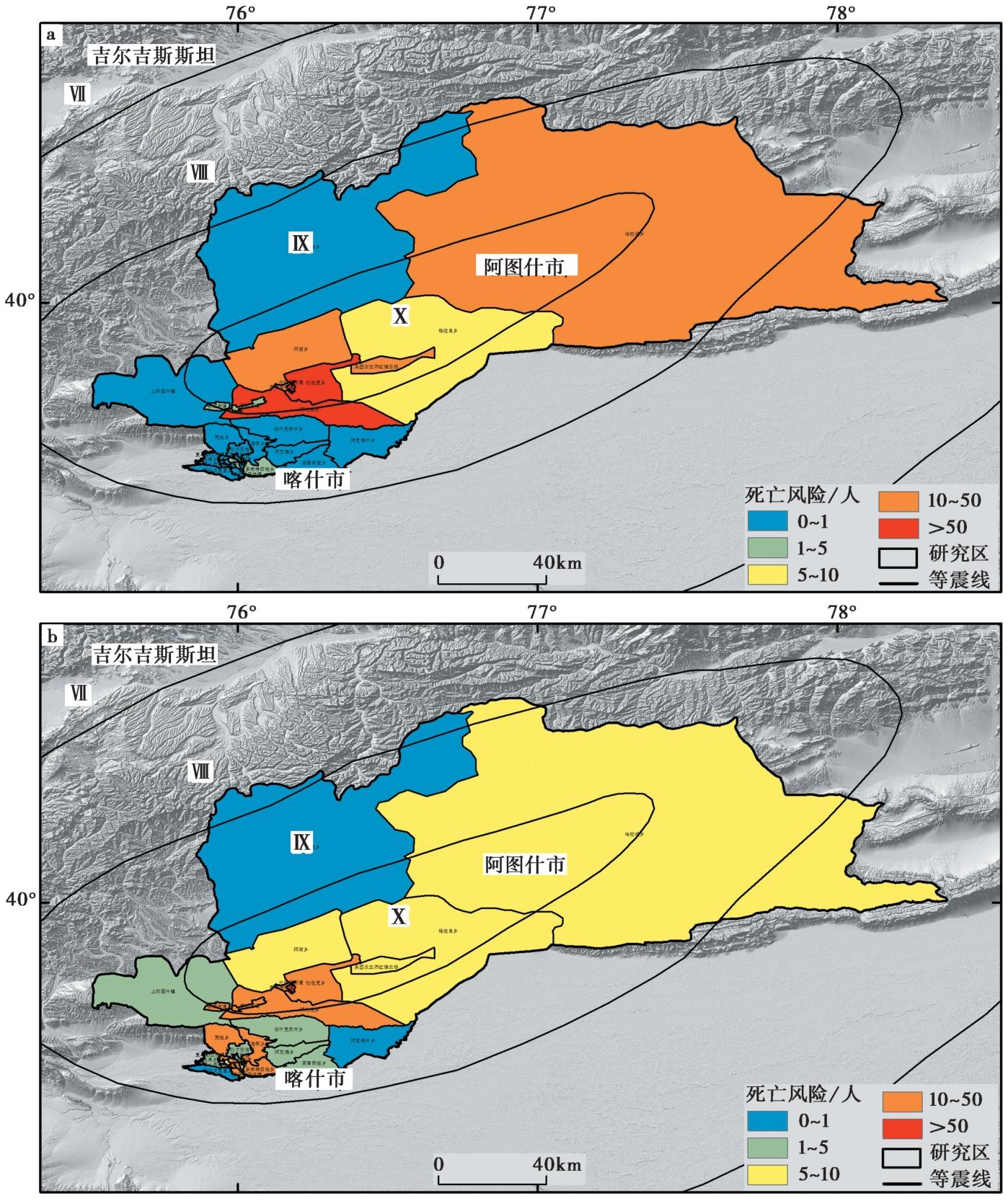
Fig. 9 Comparison of earthquake fatality risk assessment result between based on census data and based on population heatmap data under the Artux MS8¼ earthquake scenario.
| [1] |
安基文, 徐敬海, 聂高众, 等. 2015. 高精度承灾体数据支撑的地震灾情快速评估[J]. 地震地质, 37(4): 1225-1241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.04.022.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [2] |
陈飞. 2016. 地震灾害人员伤亡评估方法研究及程序实现[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
谷国梁, 安立强, 朱宏, 等. 2021. 城市地震压埋人员分布评估研究: 以天津市区为例[J]. 地震工程学报, 43(6): 1352-1360.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
谷国梁, 王晓蕾, 李雅静, 等. 2016. 天津市面向震害快速评估的房屋和人口空间化研究[J]. 地震, 36(2): 149-158.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
何玉林, 黎大虎, 范开红, 等. 2002. 四川省房屋建筑易损性研究[J]. 中国地震, 18(1): 52-58.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
姜鹏飞, 张桂欣, 陈相兆, 等. 2022. 京津冀地区再现三河-平谷8.0级地震的人员伤亡分析[J]. 世界地震工程, 38(4): 1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
李媛媛, 苏国峰, 翁文国, 等. 2014. 地震人员伤亡评估方法研究[J]. 灾害学, 29(2): 223-227.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
聂高众, 高建国, 马宗晋, 等. 2002. 中国未来10-15年地震灾害的风险评估[J]. 自然灾害学报, 11(1): 68-73.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
聂高众, 夏朝旭, 范熙伟, 等. 2021. 基于历史地震数据的建筑物致死性水平研究[J]. 地质科学, 56(4): 1250-1266.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
聂文钰. 2023. 考虑建筑物功能类型的精细化地震灾害风险评估[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
谭明, 常想德, 孙静, 等. 2014. 2014年2月12日新疆于田7.3级地震抗震安居(安居富民)房破坏比初步分析[J]. 内陆地震, 28(2): 97-103.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
田丽莉. 2012. 地震灾害人员伤亡影响因素分析及人员伤亡估算公式[D]. 北京: 首都经济贸易大学.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
温和平, 胡伟华, 谭明, 等. 2017. 新疆2次破坏性地震的房屋震害初步分析[J]. 内陆地震, 31(4): 325-333.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
温和平, 唐丽华, 孙甲宁, 等. 2021. 新疆地区地震灾害风险初步研究: 以阿图什市为例[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
温和平, 唐丽华, 姚远, 等. 2023. 新疆阿图什市城市地震灾害风险初步研究[J]. 内陆地震, 37(3): 224-231.
DOI |
|
DOI |
|
| [16] |
吴星宇, 李雪, 吴桂桔. 2021. 川滇地区城市地震风险变化分析[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 18(3): 391-399.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
闫佳琦, 陈相兆, 孙柏涛. 2021. 地震人员伤亡评估方法及损失评估系统综述[J]. 工程力学, 38(12): 1-16.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
尹之潜. 1991. 地震灾害损失预测研究[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 11(4): 87-96.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
尹之潜. 1996. 地震灾害及损失预测方法[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
袁海红, 高晓路, 戚伟. 2016. 城市地震风险精细化评估: 以北京海淀区为例[J]. 地震地质, 38(1): 197-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.01.015.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [21] |
张桂欣, 孙柏涛, 陈相兆, 等. 2018. 北京市建筑抗震能力分类及地震灾害风险分析[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 38(3): 223-229.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
郑山锁, 张睿明, 陈飞, 等. 2019. 地震人员伤亡评估理论及应用研究[J]. 世界地震工程, 35(1): 87-96.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
PMID |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
FEMAFederal Emergency Management Agency. 1999. HAZUS99 earthquake loss estimation methodology, technical manual[R]. Washington, DC, United States: Federal Emergency Management Agency.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
NIBSNational Institute of Building Sciences, FEMAFederal Emergency Management Agency. 2003. Multi-hazard loss estimation methodology, earthquake model, HAZUS®MH technical manual[R]. Washington, DC: Federal Emergency Management Agency.
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||