SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1438-1455.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.05.20240040
• Research paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Xin-yan1,2)( ), ZENG Xian-wei1), LI Meng-ya1), WEI Ding-jun1), CUI Jin1)
), ZENG Xian-wei1), LI Meng-ya1), WEI Ding-jun1), CUI Jin1)
Received:2024-04-03
Revised:2024-07-26
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-11-11
李新艳1,2)( ), 曾宪伟1), 李蒙亚1), 卫定军1), 崔瑾1)
), 曾宪伟1), 李蒙亚1), 卫定军1), 崔瑾1)
作者简介:李新艳, 女, 1986年生, 2025年9月于宁夏大学获水文学及水资源专业博士学位, 高级工程师, 主要从事地电阻率与遥感水文学研究, E-mail: lixinyan905@163.com。
基金资助:LI Xin-yan, ZENG Xian-wei, LI Meng-ya, WEI Ding-jun, CUI Jin. APPARENT RESITIVITY VARIATION AT KEPING SEISMIC STATION BEFORE THE MODERATE EARTHQUAKES IN SOUTH TIANSHAN AREA, XINJIANG[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(5): 1438-1455.
李新艳, 曾宪伟, 李蒙亚, 卫定军, 崔瑾. 柯坪地电阻率在新疆南天山地震带中强地震前的响应[J]. 地震地质, 2025, 47(5): 1438-1455.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.dzdz.ac.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.05.20240040
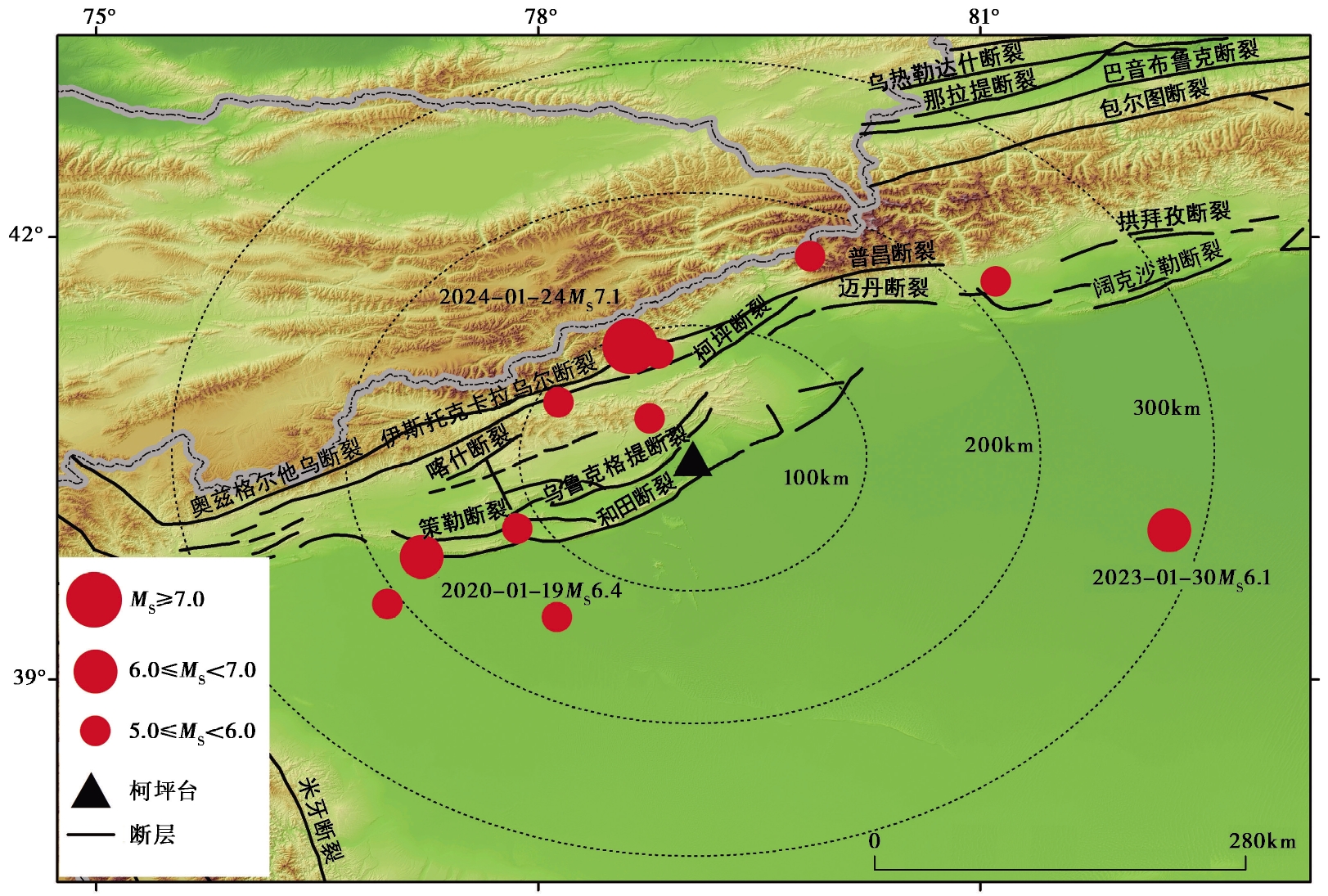
Fig. 1 Distribution of fault zones and moderate-strong earthquakes(from 2018 to January 2024, delete foreshocks and aftershocks) around Keping station.

Fig. 1 Distribution of fault zones and moderate-strong earthquakes(from 2018 to January 2024, delete foreshocks and aftershocks) around Keping station.
| 序号 | 日期 | 地点 | 震中距 /km | 震级 /MS | 震源 深度 /km | 节面Ⅰ | 节面Ⅱ | P轴 | 来源 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 走向 /(°) | 倾向 /(°) | 滑动角 /(°) | 走向 /(°) | 倾向 /(°) | 滑动角 /(°) | 方位 /(°) | 倾角 /(°) | |||||||
| 1 | 2018-09-04 | 新疆伽师 | 208 | 5.5 | 25.5 | 140 | 87 | -174 | 50 | 84 | -3 | 5 | 7 | USGS |
| 2 | 2019-10-27 | 新疆乌什 | 84 | 5 | 11 | 58 | 34 | 76 | 254 | 57 | 99 | 164 | 1 | CENC |
| 3 | 2020-01-19 | 新疆伽师 | 174 | 6.4 | 19.5 | 221 | 20 | 72 | 60 | 71 | 96 | 145 | 26 | USGS |
| 4 | 2020-05-09 | 新疆柯坪 | 43 | 5.2 | 20 | 72 | 53 | 55 | 301 | 49 | 127 | 184 | 6 | CENC |
| 5 | 2021-03-24 | 新疆拜城 | 223 | 5.4 | 11 | 341 | 75 | 180 | 71 | 90 | 15 | 205 | 6 | CENC |
| 6 | 2022-07-03 | 新疆阿合奇 | 95 | 5.2 | 12 | 45 | 55 | 98 | 212 | 36 | 79 | 164 | 3 | CENC |
| 7 | 2022-10-16 | 新疆巴楚 | 147 | 5.1 | 17 | 196 | 74 | 3 | 105 | 87 | 164 | 151 | 9 | ① |
| 8 | 2023-01-30 | 新疆沙雅 | 281 | 6.1 | 40.5 | 257 | 79 | 29 | 155 | 62 | 167 | 20 | 11 | USGS |
| 9 | 2023-02-27 | 新疆温宿 | 174 | 5.1 | 10 | 245 | 61 | 1 | 155 | 89 | 158 | 202 | 14 | ① |
| 10 | 2023-12-19 | 新疆阿图什 | 114 | 5.5 | 8 | 65 | 85 | 90 | 245 | 5 | 90 | 134 | 18 | CENC |
| 11 | 2024-01-23 | 新疆乌什 | 97 | 7.1 | 35.5 | 235 | 45 | 42 | 113 | 62 | 126 | 178 | 10 | USGS |
Table 1 The seismic source parameters of earthquakes with MS≥5.0(delete foreshocks and aftershocks) around Keping station
| 序号 | 日期 | 地点 | 震中距 /km | 震级 /MS | 震源 深度 /km | 节面Ⅰ | 节面Ⅱ | P轴 | 来源 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 走向 /(°) | 倾向 /(°) | 滑动角 /(°) | 走向 /(°) | 倾向 /(°) | 滑动角 /(°) | 方位 /(°) | 倾角 /(°) | |||||||
| 1 | 2018-09-04 | 新疆伽师 | 208 | 5.5 | 25.5 | 140 | 87 | -174 | 50 | 84 | -3 | 5 | 7 | USGS |
| 2 | 2019-10-27 | 新疆乌什 | 84 | 5 | 11 | 58 | 34 | 76 | 254 | 57 | 99 | 164 | 1 | CENC |
| 3 | 2020-01-19 | 新疆伽师 | 174 | 6.4 | 19.5 | 221 | 20 | 72 | 60 | 71 | 96 | 145 | 26 | USGS |
| 4 | 2020-05-09 | 新疆柯坪 | 43 | 5.2 | 20 | 72 | 53 | 55 | 301 | 49 | 127 | 184 | 6 | CENC |
| 5 | 2021-03-24 | 新疆拜城 | 223 | 5.4 | 11 | 341 | 75 | 180 | 71 | 90 | 15 | 205 | 6 | CENC |
| 6 | 2022-07-03 | 新疆阿合奇 | 95 | 5.2 | 12 | 45 | 55 | 98 | 212 | 36 | 79 | 164 | 3 | CENC |
| 7 | 2022-10-16 | 新疆巴楚 | 147 | 5.1 | 17 | 196 | 74 | 3 | 105 | 87 | 164 | 151 | 9 | ① |
| 8 | 2023-01-30 | 新疆沙雅 | 281 | 6.1 | 40.5 | 257 | 79 | 29 | 155 | 62 | 167 | 20 | 11 | USGS |
| 9 | 2023-02-27 | 新疆温宿 | 174 | 5.1 | 10 | 245 | 61 | 1 | 155 | 89 | 158 | 202 | 14 | ① |
| 10 | 2023-12-19 | 新疆阿图什 | 114 | 5.5 | 8 | 65 | 85 | 90 | 245 | 5 | 90 | 134 | 18 | CENC |
| 11 | 2024-01-23 | 新疆乌什 | 97 | 7.1 | 35.5 | 235 | 45 | 42 | 113 | 62 | 126 | 178 | 10 | USGS |
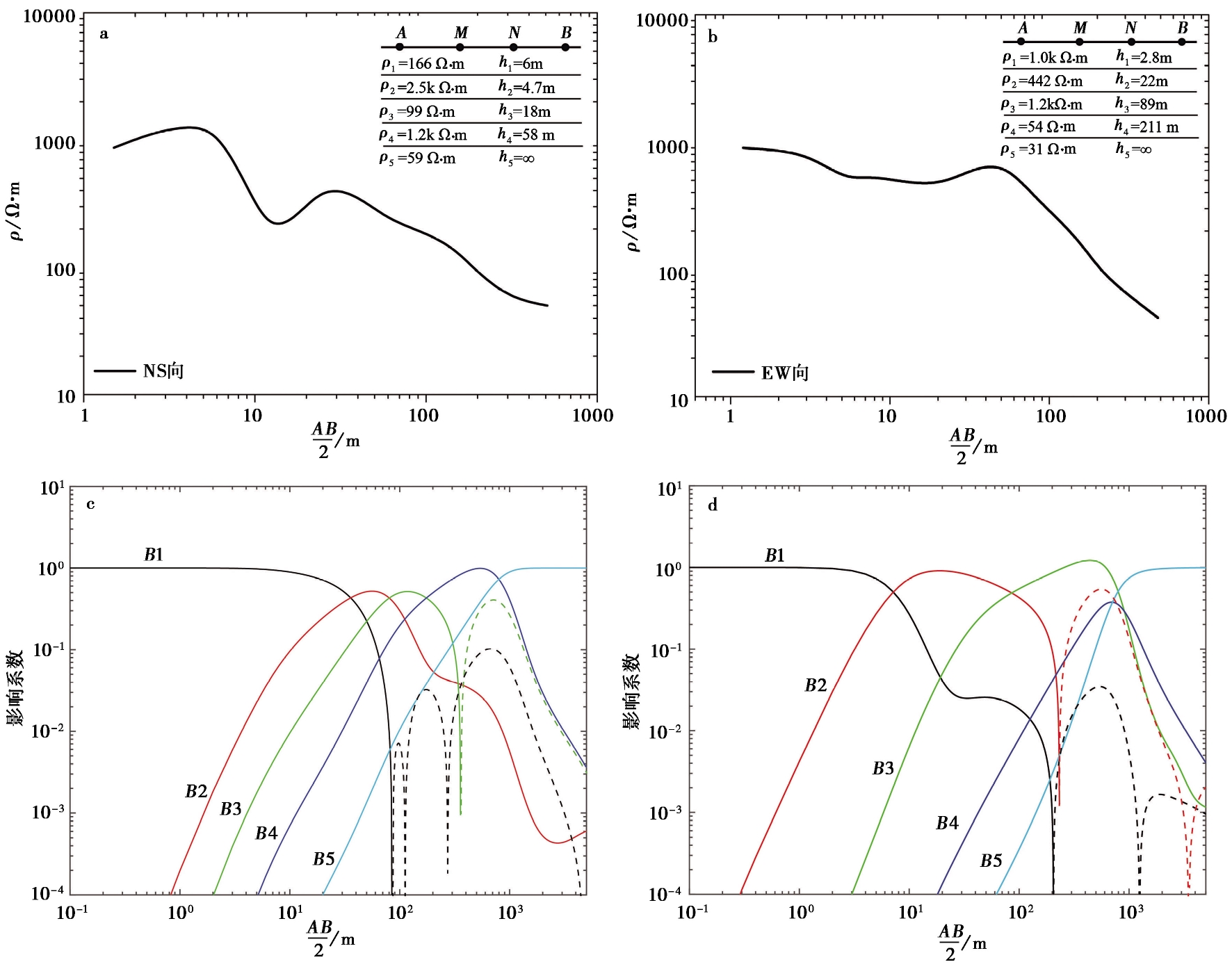
Fig. 3 The electrical sounding curve(Fig. 3a represents EW direction and 3b represents NS direction) and sensitivity coefficients(Fig. 3c represents the EW direction and 3d represents the NS direction) of the Keping station.
| 测道 | 时段 | 土壤水分与地电阻率 | 土壤温度与地电阻率 | 拟合残差 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| swvl1 | swvl2 | swvl3 | swvl4 | stl1 | stl2 | stl3 | stl4 | 偏度 | 峰度 | RMSE | ||
| NS | P1 | -0.09 | 0.67* | -0.43* | -0.62* | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.88* | 0.86* | 0.49 | -0.63 | 0.17 |
| P2 | -0.42* | 0.72* | -0.53* | -0.47* | 0.76 | 0.82* | 0.90* | 0.81 | ||||
| P3 | -0.15 | -0.24 | -0.52* | -0.53* | 0.82 | 0.88* | 0.94* | 0.80 | ||||
| EW | P1 | -0.19 | 0.68* | -0.37* | -0.64* | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.93* | 0.89* | -0.58 | -0.39 | 0.19 |
| P2 | -0.35* | 0.78* | -0.40* | -0.41* | 0.81 | 0.86* | 0.91* | 0.76 | ||||
| P3 | -0.19 | -0.20 | -0.55* | -0.66* | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.93* | 0.90* | ||||
Table2 Correlation coefficient between apparent resistivity vs. soil water content and apparent resistivity vs. soil temperature, and the statistical characteristics and errors of fitting residue
| 测道 | 时段 | 土壤水分与地电阻率 | 土壤温度与地电阻率 | 拟合残差 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| swvl1 | swvl2 | swvl3 | swvl4 | stl1 | stl2 | stl3 | stl4 | 偏度 | 峰度 | RMSE | ||
| NS | P1 | -0.09 | 0.67* | -0.43* | -0.62* | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.88* | 0.86* | 0.49 | -0.63 | 0.17 |
| P2 | -0.42* | 0.72* | -0.53* | -0.47* | 0.76 | 0.82* | 0.90* | 0.81 | ||||
| P3 | -0.15 | -0.24 | -0.52* | -0.53* | 0.82 | 0.88* | 0.94* | 0.80 | ||||
| EW | P1 | -0.19 | 0.68* | -0.37* | -0.64* | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.93* | 0.89* | -0.58 | -0.39 | 0.19 |
| P2 | -0.35* | 0.78* | -0.40* | -0.41* | 0.81 | 0.86* | 0.91* | 0.76 | ||||
| P3 | -0.19 | -0.20 | -0.55* | -0.66* | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.93* | 0.90* | ||||
| [1] |
邓起东, 冯先月, 张培震, 等. 2000. 天山活动构造[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2002. 中国活动构造基本特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 32(12): 1020-1030.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
杜学彬. 2010. 在地震预报中的两类视电阻率变化[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 40(10): 1321-1330.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
杜学彬, 李宁, 叶青, 等. 2007. 强地震附近视电阻率各向异性变化的原因[J]. 地球物理学报, 50(6): 1802-1810.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
杜学彬, 刘君, 崔腾发, 等. 2015. 2次近距离大震前成都台视电阻率重现性、 相似性和各向异性变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(2): 576-588.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
杜学彬, 马占虎, 叶青, 等. 2006. 与强地震有关的视电阻率各向异性变化[J]. 地球物理学进展, 21(1): 93-100.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
杜学彬, 叶青, 马占虎, 等. 2008. 强地震附近电阻率对称四极观测的探测深度[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(6): 1943-1949.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
金安忠. 1981. 地电阻率正常变化的初步研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 24(1): 92-106.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李金, 蒋海昆, 魏芸芸, 等. 2021. 2020年1月19日伽师6.4级地震发震构造的初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 43(2): 357-376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.02.007.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
李新艳, 解滔, 曾宪伟, 等. 2024. 断层虚位错模式揭示的2022年1月8日青海门源 MS6.9 地震前的地电阻率变化[J]. 地震学报, 46(2): 292-306.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
毛先进, 段炜, 杨玲英, 等. 2021. 分层均匀结构地电阻率影响系数一个重要特性普适性的证明[J]. 地震研究, 44(1): 129-132.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
钱复业, 赵玉林, 许同春. 1987. 地电阻率季节干扰变化分析[J]. 地震学报, 9(3): 289-302.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
钱复业, 赵玉林, 于谋明, 等. 1982. 地震前地电阻率的异常变化[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 12(9): 831-839.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
钱家栋, 陈有发, 金安忠. 1985. 地电阻率法在地震预报中的应用[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
钱家栋, 张学民, 王亚璐, 等. 2018. 2008年汶川 MS8.0 地震前成都台NE向地电阻率趋势异常的数值模拟[J]. 地震, 38(2): 107-116.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
饶文, 刘海洋, 张治广, 等. 2021. 柯坪地电阻率台年变特征及成因分析[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 42(1): 61-68.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
田勤俭, 丁国瑜, 郝平. 2006. 南天山及塔里木北缘构造带西段地震构造研究[J]. 地震地质, 28(2): 213-223.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
王同利, 崔博闻, 叶青, 等. 2020. 九寨沟 MS7.0 地震地电阻率变化时空演化分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(6): 2345-2356.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
汪志亮, 郑大林, 余素荣. 2002. 地震地电阻率前兆异常现象[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
吴传勇. 2016. 西南天山北东东走向断裂的晚第四纪活动特征及在天山构造变形中的作用[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
吴玮莹, 单新建, 屈春燕, 等. 2022. 联合空基与地基观测数据揭示2017年新疆精河 MW6.3 地震震前多参数时空关联及可能的物理机制[J]. 地球物理学报, 65(9): 3335-3350.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
解滔, 韩盈, 于晨. 2023. 2021-2022年川滇地区4次MS≥6.0地震前井下地电阻率观测的异常变化[J]. 地震地质, 45(6): 1370-1384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.06.007.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
解滔, 卢军. 2020a. 含裂隙介质中的视电阻率各向异性变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(4): 1675-1694.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
解滔, 卢军, 杜学彬. 2022a. 自适应变化幅度方法提取直流视电阻率中短期异常[J]. 中国地震, 38(1): 52-60.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
解滔, 薛艳, 卢军. 2022b. 中国MS≥7.0地震前视电阻率变化及其可能原因[J]. 地球物理学报, 65(8): 3064-3077.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
解滔, 于晨, 王亚丽, 等. 2020b. 基于断层虚位错模式讨论2008年汶川 MS8.0 地震前视电阻率变化[J]. 中国地震, 36(3): 492-501.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
解滔, 于晨, 王亚丽, 等. 2022c. 2013年岷县-漳县 MS6.6 地震前通渭台的视电阻率变化[J]. 地震地质, 44(3): 701-717. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.03.009.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
徐世浙. 1985. 视电阻率年变的定量计算[J]. 地震学报, 7(4): 422-427.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
徐锡伟, 张先康, 冉勇康, 等. 2006. 南天山地区巴楚-伽师地震(MS6.8)发震构造初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 28(2): 161-178.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
严宇红, 沈永平, 李宇安, 等. 2007. 新疆天山南麓柯坪河水文特性与洪水分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 29(5): 824-829.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
张金铸, 陆阳泉. 1983. 不同三轴应力条件下岩石电阻率变化的试验研究[J]. 地震学报, 5(4): 440-445.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
张志斌, 赵晓成, 任林. 2020. 新疆天山中段的震源机制解与构造应力场特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 42(3): 595-611. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.03.004.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
赵国泽, 张学民, 蔡军涛, 等. 2022. 中国地震电磁研究现状和发展趋势[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 52(8): 1499-1515.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
赵和云, 钱家栋. 1982. 地电阻率法中勘探深度和探测范围的理论讨论和计算[J]. 西北地震学报, 4(1): 40-56.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
赵玉林, 卢军, 李正南, 等. 1996. 唐山地震应变-电阻率前兆及虚错动模式[J]. 地震学报, 18(1): 78-82.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
赵玉林, 卢军, 张洪魁, 等. 2001. 电测量在中国地震预报中的应用[J]. 地震地质, 23(2): 277-285.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
赵玉林, 钱复业, 杨体成, 等. 1983. 原地电阻率变化的实验[J]. 地震学报, 5(2): 217-225.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [1] | YANG Jian-wen, JIN Ming-pei, LI Qing, LI Zhen-ling, YE Beng, LI Jian, ZHANG Ying-feng. COSEISMIC DEFORMATION FIELD AND SLIP MODELS OF JANUARY 23, 2024 MS7.1 WUSHI EARTHQUAKE, XINJIANG, CHINA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(5): 1382-1395. |
| [2] | ZHANG Li-qiong, LI Na, GAO Shu-de, JIANG Jia-jia. APPARENT RESITIVITY VARIATION OBSERVED FROM EARTH RESITIVITY STATIONS BEFORE THE JISHISHAN MS6.2 EARTHQUAKE IN 2023 [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(4): 1244-1261. |
| [3] | XIE Tao, HAN Ying, YU Chen. APPARENT RESISTIVITY ABNORMAL CHANGES OF BOREHOLE MONITORING BEFORE FOUR MS≥6.0 EARTHQUAKES IN SICHUAN-YUNNAN AREA FROM 2021 TO 2022 [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(6): 1370-1384. |
| [4] | XIE Tao, YU Chen, WANG Ya-li, LI Mei, WANG Zhong-ping, YAO Li, LU Jun. APPARENT RESITIVITY VARIATION OF TONGWEI SEISMIC STATION BEFORE THE MINXIAN-ZHANGXIAN MS6.6 EARTHQUAKE IN 2013 [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(3): 701-717. |
| [5] | XIE Tao, LU Jun. THE EFFECTS OF LATERAL INHOMOGENEITY ON ANISOTROPIC CHANGES OF APPARENT RESISTIVITY AND THE DEPTH OF RESISTIVITY CHANGES BEFORE EARTHQUAKES [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2020, 42(5): 1172-1187. |
| [6] | XIE Tao, LU Jun, YAN Wei. THE MECHANISM OF DIURNAL VARIATION IN CONSECUTIVE APPARENT RESISTIVITY OBSERVATION [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2019, 41(6): 1464-1480. |
| [7] | WANG Qing-lin, SUN Huai-feng, ZHU Cheng-lin, ZHANG Ji-hong, TANG Ting-mei. DEEP TECTONIC STRESS CHANGE BASED ON LONG-TERM APPARENT RESISTIVITY TIME SERIES: A CASE STUDY FROM NORTH SECTION OF YISHU FAULT ZONE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2017, 39(1): 147-157. |
| [8] | XIE Tao, LU Jun. APPARENT RESISTIVITY TEMPORAL VARIATION CHARAC-TERISTICS AFFECTED BY THE FIXED DISTURBANCE SOURCE ON SURFACE OF MEASURING AREA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2016, 38(4): 922-936. |
| [9] | AN Zhang-hui, ZHAN Yan, CHEN Xiao-bin, JIANG Feng, GAO Yue. SHIFTING SELF-CORRELATION METHOD INITIALY USED IN THE APPARENT RESISTIVITY OBSERVATION DATA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2016, 38(4): 1019-1029. |
| [10] | XIE Tao, LU Jun. three-dimensional sensitivity coefficients of apparent resistivity and preliminary application [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2015, 37(4): 1125-1135. |
| [11] | SUN Wei-huai, TANG Ji, ZHANG Ping, YANG Xue-hui. RESEARCH ON THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ANOMALIES IN ELF ELECTROMAGNETIC OBSERVATIONS IN YUNNAN PROVINCE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2012, (3): 488-499. |
| [12] | QIN Qing-yan, LUO Wei, ZHANG Wei. THE INFLUENCE OF THE EARTH'S CURVATURE ON THE LONG-PERIOD MAGNETOTELLURIC SOUNDING METHOD [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2012, (3): 456-466. |
| [13] | WANG Li-feng, ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Guo-ze, WANG Ji-jun, XIAO Qi-bin, MO Qing-yun, GAO Peng-fei, ZHANG Yuan-han, WEI Yong-fu. THE RESISTIVITY VARIATION IN WATER LOADING OF LONGTAN RESERVOIR IN GUANGXI,CHINA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2010, 32(4): 586-594. |
| [14] | ZHAO Fu-yuan, YAN Liang-jun, HE Zhan-xiang, CHEN Xiao-bin. THE SOLUTION FOR THE ALL-TIME APPARENT RESISTIVITY IN TIME DOMAIN WITH LONG GROUND WIRE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2010, 32(3): 473-481. |
| [15] | ZHOU Lei, YAN Liang-jun, HE Zhan-xiang, CHEN Xiao-bin. A PRIMARY STUDY ON THE FREQUENCY DOMAIN SOUNDING METHOD IN NEAR FIELD WITH LONG GROUNDED WIRE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2010, 32(3): 465-472. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||