SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (6): 1667-1687.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.06.20240015
Previous Articles Next Articles
CAI Ming-gang1)( ), PENG Bai1), LU Ren-qi1),*(
), PENG Bai1), LU Ren-qi1),*( ), ZHANG Yang1,2), LIU Guan-shen1), XU Fang1), TAO Wei1), ZHANG Jin-yu1), HAO Chong-tao1)
), ZHANG Yang1,2), LIU Guan-shen1), XU Fang1), TAO Wei1), ZHANG Jin-yu1), HAO Chong-tao1)
Received:2024-01-30
Revised:2024-09-19
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-31
蔡明刚1)( ), 彭白1), 鲁人齐1),*(
), 彭白1), 鲁人齐1),*( ), 张扬1,2), 刘冠伸1), 徐芳1), 陶玮1), 张金玉1), 郝重涛1)
), 张扬1,2), 刘冠伸1), 徐芳1), 陶玮1), 张金玉1), 郝重涛1)
通讯作者:
*鲁人齐, 男, 1982年生, 研究员, 博士生导师, 主要从事地震构造解析与三维建模研究, E-mail: lurenqi@ies.ac.cn。
作者简介:蔡明刚, 男, 1977年生, 2011年于中国地震局地质研究所获固体地球物理学博士学位, 助理研究员, 主要从事活动断层探测研究, E-mail: caimg@ies.ac.cn。
基金资助:CAI Ming-gang, PENG Bai, LU Ren-qi, ZHANG Yang, LIU Guan-shen, XU Fang, TAO Wei, ZHANG Jin-yu, HAO Chong-tao. GEOMETRIC STRUCTURAL FEATURE OF THE TANGDONG FAULT IN THE SOUTHEASTERN MARGIN OF TAIHANG MOUNTAIN: BASED ON SHALLOW SEISMIC EXPLORATION AND 3D MODELING[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(6): 1667-1687.
蔡明刚, 彭白, 鲁人齐, 张扬, 刘冠伸, 徐芳, 陶玮, 张金玉, 郝重涛. 太行山东南缘汤东断裂浅层几何结构特征--基于浅层地震勘探与三维建模[J]. 地震地质, 2025, 47(6): 1667-1687.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.dzdz.ac.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.06.20240015
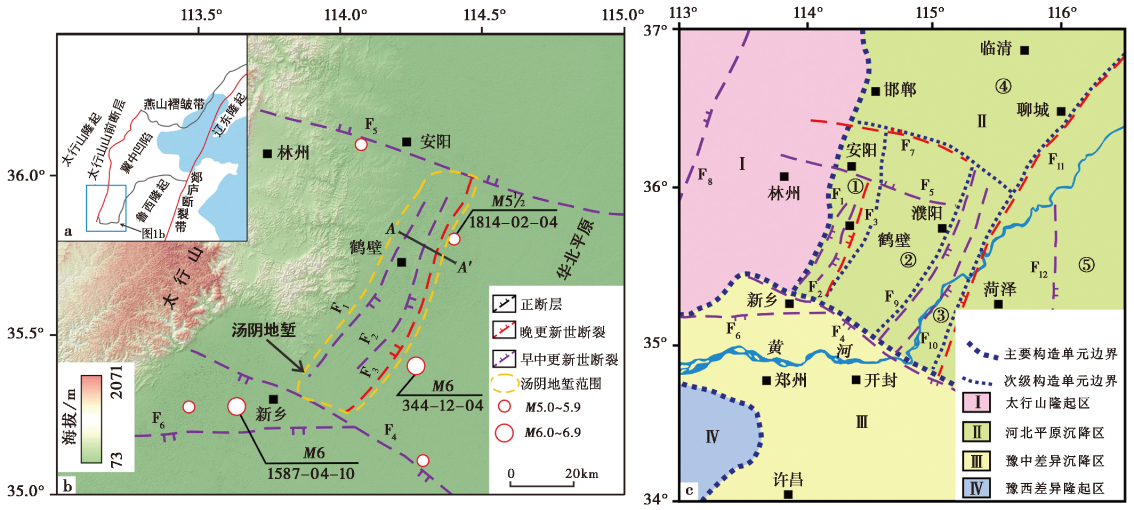
Fig. 1 Topography, geomorphology, and tectonic division map of active fault detection target area in Hebi City(Fig. 1c modified from WANG Zhi-shuo, 2017).
| 项 | 类别 | 参数 |
|---|---|---|
| 设备型号 | 仪器型号 | Geode DZ200 |
| 震源型号 | M18/612HD | |
| 检波器主频/Hz | 60 | |
| 震源激发 | 扫描频率/Hz | 10~120或8~90 |
| 扫描长度/s | 12 | |
| 最大出力/kN | 225 | |
| 记录 | 采样间隔/ms | 0.5 |
| 记录长度/ms | 2000 | |
| 观测系统 | 探测方向 | WE或EW |
| 道间距/m | 2 | |
| 炮间距/m | 6或8 | |
| 接收道数 | 240 | |
| 偏移距范围/m | 10~488或0~318 | |
| 覆盖次数 | 40或30 |
Table1 Shallow seismic data acquisition and observation system parameters
| 项 | 类别 | 参数 |
|---|---|---|
| 设备型号 | 仪器型号 | Geode DZ200 |
| 震源型号 | M18/612HD | |
| 检波器主频/Hz | 60 | |
| 震源激发 | 扫描频率/Hz | 10~120或8~90 |
| 扫描长度/s | 12 | |
| 最大出力/kN | 225 | |
| 记录 | 采样间隔/ms | 0.5 |
| 记录长度/ms | 2000 | |
| 观测系统 | 探测方向 | WE或EW |
| 道间距/m | 2 | |
| 炮间距/m | 6或8 | |
| 接收道数 | 240 | |
| 偏移距范围/m | 10~488或0~318 | |
| 覆盖次数 | 40或30 |
| 断裂 | 测线名称 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 | L8 | L9 | L10 | |
| F3-2 | √ | × | √ | √ | √ | × | × | × | √ | |
| F3-1 | × | × | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
Table2 T1 interface of the east and west branches of the Tangdong Fault
| 断裂 | 测线名称 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 | L8 | L9 | L10 | |
| F3-2 | √ | × | √ | √ | √ | × | × | × | √ | |
| F3-1 | × | × | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| [1] |
柴炽章, 孟广魁, 杜鹏, 等. 2006. 隐伏活动断层的多层次综合探测: 以银川隐伏活动断层为例[J]. 地震地质, 28(4): 536-546.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
方盛明, 张先康, 刘保金, 等. 2002. 探测大城市活断层的地球物理方法[J]. 地震地质, 24(4): 606-613.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
顾勤平, 康清清, 许汉刚, 等. 2013. 薄覆盖层地区隐伏断层及其上断点探测的地震方法技术: 以废黄河断层为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(5): 1609-1618.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
顾勤平, 许汉刚, 赵启光. 2015. 厚覆盖层地区隐伏活断层探测的地震方法技术: 以桥北镇-宿迁断层为例[J]. 物探与化探, 39(2): 408-415.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
顾勤平, 杨浩, 赵启光, 等, 2019. 金坛-如皋断裂北东段浅层地震勘探新证据[J]. 地震地质, 41(3): 743-758. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.03.013.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [6] |
韩慕康, 赵景珍. 1980. 河南汤阴地堑的地震地质特征与地震危险性[J]. 地震地质, 2(4): 47-58.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
韩慕康, 朱世龙, 赵景珍, 等. 1983. 太行山东麓断裂带南段第四纪构造应力场的地貌表现[J]. 地理学报, 38(4): 348-357.
DOI |
|
DOI |
|
| [8] |
韩竹军, 徐杰, 冉勇康, 等. 2003. 华北地区活动地块与强震活动[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 108-118.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
何登发, 单帅强, 张煜颖, 等. 2018. 雄安新区的三维地质结构: 来自反射地震资料的约束[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 48(9): 1207-1222.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
河南省地质矿产局. 1989. 河南省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 280-292.
|
|
Bureau of Geology and Mineral of Henan Province. 1989. Regional Geology of Henan Province[M]. Geological Publishing House, Beijing: 280-292 (in Chinese).
|
|
| [11] |
花鑫升, 酆少英, 姬计法, 等. 2020. 用地震反射剖面研究汤阴地堑上地壳结构与断裂特征[J]. 震灾防御技术, 15(4): 811-820.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
花鑫升, 石金虎, 谭雅丽, 等. 2018. 浅层地震勘探资料揭示汤东断裂特征[J]. 震灾防御技术, 13(2): 276-283.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
李彦宝, 冉勇康. 2011. 汤东断裂晚第四纪活动性钻孔联合剖面探测[C]//中国地球物理学会主编. 中国地球物理学会第二十七届年会论文集. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社: 174.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
刘保金, 柴炽章, 酆少英, 等. 2008. 第四纪沉积区断层及其上断点探测的地震方法技术: 以银川隐伏活动断层为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(5): 1475-1483.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
刘保金, 何宏林, 石金虎, 等. 2012. 太行山东缘汤阴地堑地壳结构和活动断裂探测[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(10): 3266-3276.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
刘尧兴, 周庆, 荆智国, 等, 2001. 豫北地区新构造活动特征及中长期地震预报研究[M]. 西安: 西安地图出版社: 82-84.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
彭白, 苏鹏, 鲁人齐, 等. 2022. 浅层人工地震和地质雷达在城市活动断层探测中的联合应用: 以鹤壁市汤东断裂为例[J]. 震灾防御技术, 17(2): 269-277.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
秦晶晶, 石金虎, 张毅, 等. 2018. 郯庐断裂带合肥段五河-合肥断裂构造特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(11): 4475-4485.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [19] |
任青芳, 张先康. 1998. 汤阴地堑及邻区的壳幔结构与地震危险性[J]. 中国地震, 14(2): 157-166.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
王金艳, 鲁人齐, 张浩, 等. 2020. 郯庐断裂带江苏段新生界三维地质构造建模[J]. 地震学报, 42(2): 216-230.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
王志铄. 2017. 河南省地震构造特征[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 7-23.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
许汉刚, 范小平, 冉勇康, 等. 2016. 郯庐断裂带宿迁段F5断裂浅层地震勘探新证据[J]. 地震地质, 38(1): 31-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.01.003.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [23] |
徐杰, 高战武, 宋长青, 等. 2000. 太行山山前断裂带的构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 22(2): 111-122.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
徐增波, 刘保金, 姬计法, 等. 2019. 太行山南端浅层速度结构成像和隐伏断裂探测[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 39(1): 88-92.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
杨承先. 1984. 邯郸、 汤阴断陷地质结构及其活动性[J]. 地震地质, 6(3): 59-66.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
于慎谔, 赵俊香, 杨承先. 2012. 太行东断裂的性状与分布[J]. 中国地震, 28(1): 78-87.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
张成科, 赵金仁, 任青芳, 等. 1994. 豫北及其外围地区地壳上地幔结构研究[J]. 地震地质, 16(3): 243-253.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
DOI URL |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
DOI URL |
| [31] |
DOI URL |
| [32] |
DOI URL |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
DOI URL |
| [37] |
DOI URL |
| [38] |
DOI URL |
| [39] |
DOI URL |
| [40] |
DOI URL |
| [1] | TIAN Yi-ming, YANG Zhuo-xin, WANG Zhi-shuo, SHI Jin-hu, ZHANG Yang, TAN Ya-li, ZHANG Jian-zhi, SONG Wei, JI Tong-yu. A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF THE SHALLOW EXPLORATION AND QUATERNARY ACTIVITIES OF THE FENGQIU SEGMENT OF THE XINXIANG-SHANGQIU FAULT [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(1): 139-152. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||