SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (3): 969-983.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.03.20250014
Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Qing-xu1)( ), RONG Mian-shui1),*(
), RONG Mian-shui1),*( ), ZHANG Bin2), WANG Ji-xin2), KONG Xiao-shan1), LI Xiao-jun1)
), ZHANG Bin2), WANG Ji-xin2), KONG Xiao-shan1), LI Xiao-jun1)
Received:2025-01-23
Revised:2025-02-21
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-08-13
赵庆旭1)( ), 荣棉水1),*(
), 荣棉水1),*( ), 张斌2), 王继鑫2), 孔小山1), 李小军1)
), 张斌2), 王继鑫2), 孔小山1), 李小军1)
通讯作者:
*荣棉水, 男, 1982年生, 教授, 主要从事强震和环境振动作用下的场地效应研究, E-mail: rongmianshui@bjut.edu.cn。
作者简介:赵庆旭, 男, 1997年生, 现为北京工业大学建筑工程学院土木工程专业在读博士研究生, 主要从事人工智能在地震动场地效应中的应用研究, E-mail: QingxuZhao@emails.bjut.edu.cn。
基金资助:ZHAO Qing-xu, RONG Mian-shui, ZHANG Bin, WANG Ji-xin, KONG Xiao-shan, LI Xiao-jun. RAPID ESTIMATION OF PARAMETERS FOR THE M6.8 EARTH-QUAKE ON JANUARY 7, 2025 IN DINGRI(XIZANG, CHINA) BASED ON DATA-DRIVEN METHODS[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 969-983.
赵庆旭, 荣棉水, 张斌, 王继鑫, 孔小山, 李小军. 基于数据驱动模型的2025年1月7日西藏定日6.8级地震参数快速估算[J]. 地震地质, 2025, 47(3): 969-983.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.dzdz.ac.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.03.20250014
| 台站名称 | 仪器类型 | 北纬/(°) | 东经/(°) | 震源距/km | P波到时/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB001 | 强震仪 | 29.10 | 89.20 | 183.60 | 57.59 |
| DS002 | 强震仪 | 28.90 | 88.00 | 70.38 | 36.61 |
| DX001 | 强震仪 | 29.44 | 88.20 | 127.66 | 46.45 |
| RKZ | 强震仪 | 29.26 | 88.80 | 156.65 | 52.65 |
| D0001 | 烈度仪 | 29.30 | 87.20 | 92.50 | 40.80 |
| D0003 | 烈度仪 | 30.07 | 86.90 | 182.31 | 58.26 |
| D0004 | 烈度仪 | 28.37 | 87.70 | 30.12 | 31.52 |
| D0005 | 烈度仪 | 28.24 | 88.40 | 97.99 | 42.14 |
| D0007 | 烈度仪 | 29.09 | 87.60 | 67.75 | 35.78 |
| D0009 | 烈度仪 | 29.68 | 89.00 | 199.94 | 58.61 |
Table 1 Basic information of selected stations
| 台站名称 | 仪器类型 | 北纬/(°) | 东经/(°) | 震源距/km | P波到时/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB001 | 强震仪 | 29.10 | 89.20 | 183.60 | 57.59 |
| DS002 | 强震仪 | 28.90 | 88.00 | 70.38 | 36.61 |
| DX001 | 强震仪 | 29.44 | 88.20 | 127.66 | 46.45 |
| RKZ | 强震仪 | 29.26 | 88.80 | 156.65 | 52.65 |
| D0001 | 烈度仪 | 29.30 | 87.20 | 92.50 | 40.80 |
| D0003 | 烈度仪 | 30.07 | 86.90 | 182.31 | 58.26 |
| D0004 | 烈度仪 | 28.37 | 87.70 | 30.12 | 31.52 |
| D0005 | 烈度仪 | 28.24 | 88.40 | 97.99 | 42.14 |
| D0007 | 烈度仪 | 29.09 | 87.60 | 67.75 | 35.78 |
| D0009 | 烈度仪 | 29.68 | 89.00 | 199.94 | 58.61 |
| 台站名称 | 仪器烈度 (速报结果) | 仪器烈度 (本文计算结果) | PGA /cm·s-2 | PGV /cm·s-1 | PGD /cm | SA(0.3) /cm·s-2 | SA(1.0) /cm·s-2 | SA(3.0) /cm·s-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB001 | 2.9 | 2.90 | 3.14 | 1.34 | 0.87 | 6.34 | 4.11 | 7.45 |
| DS002 | 5.5 | 5.54 | 40.30 | 3.64 | 2.18 | 124.01 | 20.35 | 12.53 |
| DX001 | 4.8 | 4.83 | 17.32 | 4.11 | 3.53 | 39.55 | 10.31 | 8.53 |
| RKZ | 3.6 | 3.61 | 4.30 | 2.51 | 1.82 | 7.97 | 8.35 | 9.73 |
| D0001 | 6.1 | 6.10 | 62.59 | 6.79 | 5.81 | 125.47 | 51.87 | 16.06 |
| D0003 | 4.2 | 4.24 | 7.39 | 4.55 | 3.71 | 17.51 | 12.31 | 9.77 |
| D0004 | 7.3 | 7.28 | 114.76 | 14.86 | 5.21 | 285.08 | 170.17 | 28.06 |
| D0005 | 4.6 | 4.62 | 20.72 | 2.24 | 1.45 | 59.53 | 7.81 | 7.01 |
| D0007 | 8.0 | 8.02 | 396.02 | 28.29 | 8.29 | 1066.71 | 277.97 | 79.00 |
| D0009 | 4.1 | 4.09 | 16.27 | 1.29 | 1.00 | 68.47 | 6.52 | 5.11 |
Table2 Instrumental intensity and ground motion parameters of selected stations
| 台站名称 | 仪器烈度 (速报结果) | 仪器烈度 (本文计算结果) | PGA /cm·s-2 | PGV /cm·s-1 | PGD /cm | SA(0.3) /cm·s-2 | SA(1.0) /cm·s-2 | SA(3.0) /cm·s-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB001 | 2.9 | 2.90 | 3.14 | 1.34 | 0.87 | 6.34 | 4.11 | 7.45 |
| DS002 | 5.5 | 5.54 | 40.30 | 3.64 | 2.18 | 124.01 | 20.35 | 12.53 |
| DX001 | 4.8 | 4.83 | 17.32 | 4.11 | 3.53 | 39.55 | 10.31 | 8.53 |
| RKZ | 3.6 | 3.61 | 4.30 | 2.51 | 1.82 | 7.97 | 8.35 | 9.73 |
| D0001 | 6.1 | 6.10 | 62.59 | 6.79 | 5.81 | 125.47 | 51.87 | 16.06 |
| D0003 | 4.2 | 4.24 | 7.39 | 4.55 | 3.71 | 17.51 | 12.31 | 9.77 |
| D0004 | 7.3 | 7.28 | 114.76 | 14.86 | 5.21 | 285.08 | 170.17 | 28.06 |
| D0005 | 4.6 | 4.62 | 20.72 | 2.24 | 1.45 | 59.53 | 7.81 | 7.01 |
| D0007 | 8.0 | 8.02 | 396.02 | 28.29 | 8.29 | 1066.71 | 277.97 | 79.00 |
| D0009 | 4.1 | 4.09 | 16.27 | 1.29 | 1.00 | 68.47 | 6.52 | 5.11 |
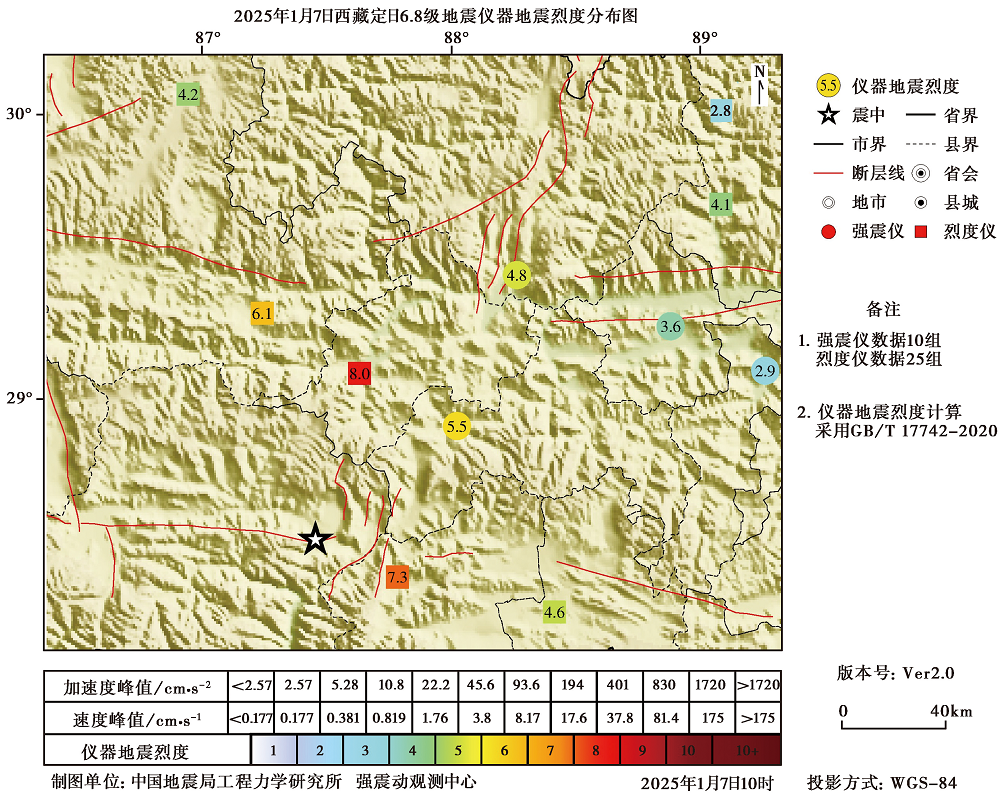
Fig. 6 Distribution map of instrumental intensity for the Dingri M6.8 earthquake(Cited from the Strong Motion Observation Center, Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration).
| [1] |
金星. 2024. 地震预警与烈度速报-风险与控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
金星, 张红才, 李军, 等. 2012. 地震预警震级确定方法研究[J]. 地震学报, 34(5): 593-610.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
刘辰, 李小军, 景冰冰, 等. 2019. 地震预警PGV-Pd关系参数的距离分段特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 62(4): 1413-1426.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [4] |
马美帅, 王延伟, 汪祚赚, 等. 2022. 基于累积绝对位移值的震级估算方法[J]. 自然灾害学报, 31(2): 93-101.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
赵庆旭, 王延伟, 莫红艳, 等. 2024. 基于多输入高斯过程回归的震级快速估算方法[J]. 地震学报, 46(5): 806-824.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
中国地震局. 2020. 中国地震烈度表GB/T 17742-2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
China Earthquake Administration. 2020. The Chinese seismic intensity scale, GB/T 17742-2020[S]. Standards Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese).
|
|
| [7] |
PMID |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [1] | ZHI Long-xiang, ZHAO Xu. RESEARCH ON EARLY AFTERSHOCKS OF THE 2025 DINGRI M6.8 EARTHQUAKE BASED ON THE DEEP-LEARNING-BASED SINGLE-STATION LOCATION METHOD [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 820-834. |
| [2] | MENG Rui, ZHANG Yuan-fan, XIE Xiao-feng, NIE Zhi-xi, WANG Zhen-jie, SHAN Xin-jian. RESEARCH ON RAPID ESTIMATION METHOD OF EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE BASED ON STRONG-MOTION RECORDS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(5): 1219-1232. |
| [3] | XU Zhi-ping, ZHANG Yang, YANG Li-pu, XU Shun-qiang, JIANG Lei, TANG Lin, LIN Ji-yan. STUDY ON THE DEEP STRUCTURAL CHARACTERISTIC OF MAIN ACTIVE FAULTS IN HENAN PROVINCE AND ITS ADJACENT AREAS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(6): 1521-1538. |
| [4] | YAO Wen-qian, WANG Zi-jun, LIU-ZENG Jing, LIU Xiao-li, HAN Long-fei, SHAO Yan-xiu, WANG Wen-xin, XU Jing, QIN Ke-xin, GAO Yun-peng, WANG Yan, LI Jin-yang, ZENG Xian-yang. DISCUSSION ON COSEISMIC SURFACE RUPTURE LENGTH OF THE 2021 MW7.4 MADOI EARTHQUAKE, QINGHAI, CHINA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(2): 541-559. |
| [5] | QI Yu-ping, LONG Feng, LIN Sheng-jie, XIAO Ben-fu, ZHAO Xiao-yan, WANG Pei-ling, FENG Jian-gang. A STUDY ON THE EARTHQUAKE SEQUENCE TYPE IN THE MIDDLE SECTION OF THE NORTH-SOUTH SEISMIC BELT AND ITS SURROUNDING REGIONS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2021, 43(1): 177-196. |
| [6] | XIE Zhuo-juan, LI Shan-you, LÜ Yue-jun, XU Wei-jin, ZHANG Yu-ling, LIU Wen-xin. UNIFIED EARTHQUAKE CATALOG FOR CHINA’S SEAS AND ADJACENT REGIONS AND ITS COMPLETENESS ANALYSIS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2020, 42(4): 993-1019. |
| [7] | WU Guo, ZHOU Qing, RAN Hong-liu. THE MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESTIMATION OF b-VALUE IN MAGNITUDE-FREQUENCY RELATION AND ANALYSIS OF ITS INFLUENCING FACTORS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2019, 41(1): 21-43. |
| [8] | LEI Dong-ning, LIU Jie, LIU Zhu-mei, HE Yu-lin, QIAO Yue-qiang. DISCUSSION ON THE SEISMOGENIC STRUCTURE OF THE 2016 MENYUAN M6.4 EARTHQUAKE IN MENYUAN, QINGHAI [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2018, 40(1): 107-120. |
| [9] | XU Xi-wei, WU Xi-yan, YU Gui-hua, TAN Xi-bin, LI Kang. SEISMO-GEOLOGICAL SIGNATURES FOR IDENTIFYING M≥7.0 EARTHQUAKE RISK AREAS AND THEIR PREMILIMARY APPLICATION IN MAINLAND CHINA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2017, 39(2): 219-275. |
| [10] | WU Wei-wei, SU Jin-rong, WEI Ya-ling, WU Peng, LI Jun, SUN Wei. DISCUSSION ON ATTENUATION CHARACTERISTICS, SITE RESPONSE AND MAGNITUDE DETERMINATION IN SICHUAN [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2016, 38(4): 1005-1018. |
| [11] | CAO Hui-jing, CUI Xiao-feng, FAN Wen-jie. ESTIMATING THE MAGNITUDE OF TECTONIC STRESS BASED ON THE FRICTION CRITERIA OF FAULT AND ANALYSING THE PARAMETERS' INFLUENCE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2016, 38(2): 386-396. |
| [12] | WU Fu-yao, RAN Yong-kang, CHEN Li-chun, LI An. DISTRIBUTION OF 3 EARTHQUAKE RUPTURE ZONES IN ESATERN TIENSHAN AND ITS RELATIONSHIP WITH 2 HISTORICAL EARTHQUAKES [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2016, 38(1): 77-90. |
| [13] | TANG Mao-yun, LIU Jing, SHAO Yan-xiu, WANG Peng, YUAN Zhao-de. analysis about the minimum magnitude earthquake associated with surface ruptures [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2015, 37(4): 1193-1214. |
| [14] | CHEN Kun, YU Yan-xiang, GAO Meng-tan, KANG Chuan-chuan. RESEARCH ON METHOD OF ESTIMATING GROUND MOTION PARAMETERS IN WESTERN CHINA USING INTENSITY DATA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2014, 36(4): 1043-1052. |
| [15] | FENG Wei, JIANG Li-xin, YANG Tian-qing, LI Yang, ZHENG Tong-yan. A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS BETWEEN INSTRUMENTAL INTENSITY AND SURVEY SPOT INTENSITY OF LUSHAN M7.0 EARTHQUAKE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2014, 36(1): 222-229. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||