地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 435-454.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.02.008
陈鲲1)( ), 高孟潭1), 俞言祥1), 徐伟进1), 杜义2), 李雪靖1), 陆东华1)
), 高孟潭1), 俞言祥1), 徐伟进1), 杜义2), 李雪靖1), 陆东华1)
修回日期:2022-12-09
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-05-18
作者简介:陈鲲, 男, 1976年生, 2013年于中国地震局地球物理研究所获固体地球物理博士学位, 研究员, 主要从事地震区划、地震危险性分析及地震动强度图等方面的研究, E-mail: Chenkun-6620@163.com。
基金资助:
CHEN Kun1)( ), GAO Meng-tan1), YU Yan-xiang1), XU Wei-jin1), DU Yi2), LI Xue-jin1), LU Dong-hua1)
), GAO Meng-tan1), YU Yan-xiang1), XU Wei-jin1), DU Yi2), LI Xue-jin1), LU Dong-hua1)
Revised:2022-12-09
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-05-18
摘要:
文中采用蒙特卡罗随机抽样方法, 研发了一套融合传统二维潜在震源区(下文简称“潜源”)和三维断层源的概率地震危险性算法。该算法不仅适用于传统的区域面源, 同时还能考虑地震的破裂尺度并兼容三维断层源的概率地震危险性计算。文中研发的算法可高效实现断层源地震事件集的三维模拟, 并将地震破裂尺度引入到概率地震危险性计算中, 显著提高了近断层地区地震危险性计算的合理性。为了提高程序的执行效率, 算法采用预先在平面潜源中充填网格点的方式随机模拟地震事件在潜源内的均匀分布。对于椭圆衰减的地震危险性计算, 算法采用了预先构建不同震级、距离及不同场点与潜源长轴方向夹角下的短轴距的三维矩阵, 通过查表和插值方式直接获得相应场点的短轴距, 避免了循环迭代逼近短轴距计算效率低下的问题。分别利用五代图的概率地震危险性程序和文中研发的算法, 计算了湖南长-株-潭(长沙-株洲-湘潭)城市群所处的中强地震活动环境的区域地震危险性以及近断层源的常德、株洲2个场点在不同概率水平下(重现期分别为50a、475a和2 475a)的地震危险性。比较研究表明, 五代图的程序低估了三维断层源附近的地震危险性, 且随着概率水平的降低, 低估的程度越来越高。最后, 利用太平洋地震工程中心(Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, PEER)验证概率地震危险性程序的算例(数据集1案例10)验证了文中算法的可靠性。
中图分类号:
陈鲲, 高孟潭, 俞言祥, 徐伟进, 杜义, 李雪靖, 陆东华. 融合三维断层源和二维潜在震源区的随机抽样概率地震危险性分析算法研发[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 435-454.
CHEN Kun, GAO Meng-tan, YU Yan-xiang, XU Wei-jin, DU Yi, LI Xue-jin, LU Dong-hua. PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS ALGORITHM INTEGRATING THREE-DIMENSIONAL FAULT SOURCES AND POTENTIAL SEISMIC SOURCE ZONE USING RANDOM SAMPLING[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(2): 435-454.
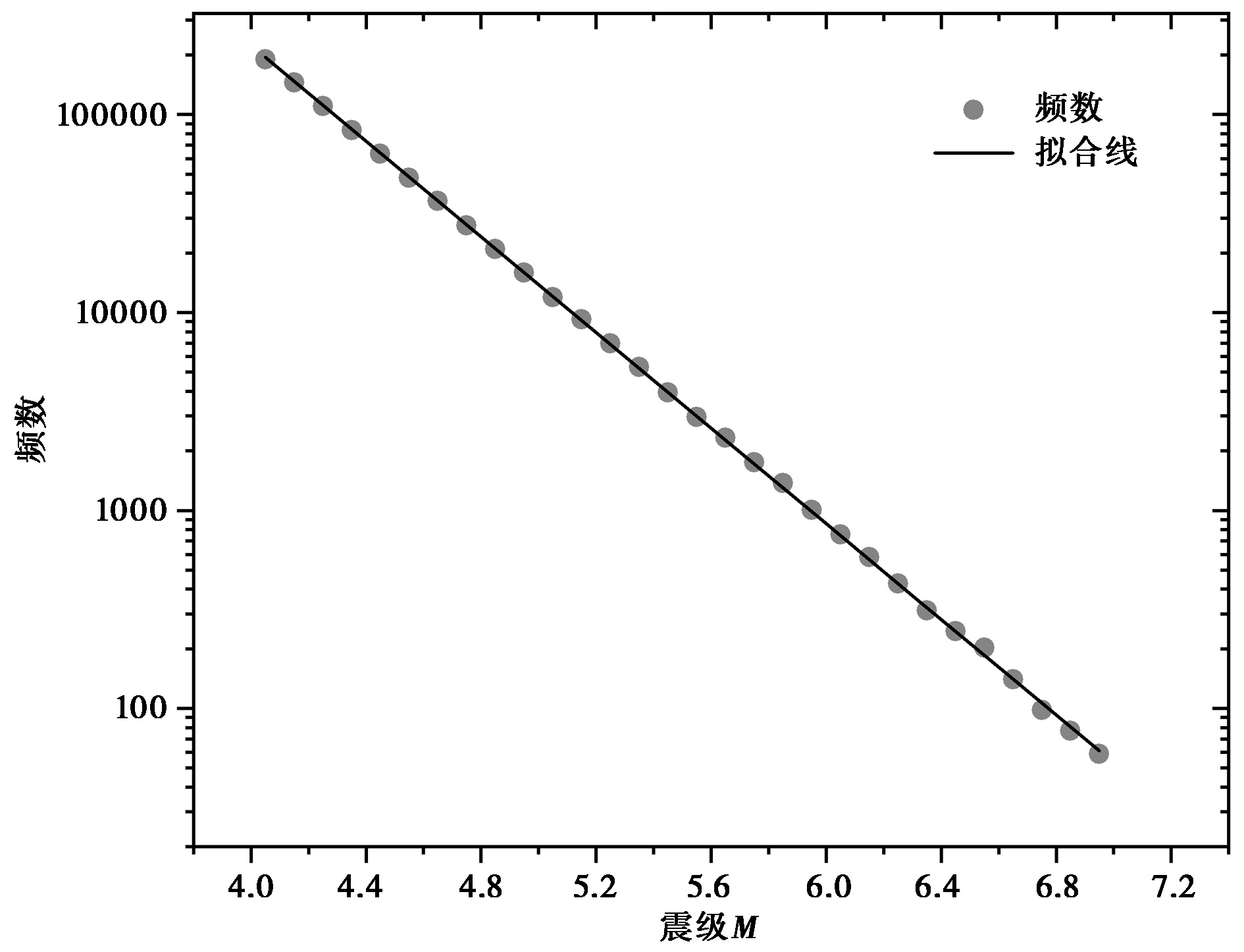
图3 用长江中下游地震带模拟地震目录的震级-频度(G-R)统计(模拟时长247 500a)
Fig. 3 Statistics of the magnitude frequency for simulated earthquakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Changjian River seismic belt(simulation duration 247 500 years).
| 地表形迹坐标 | 宽度/km | 倾角/(°) | 顶面埋深/km |
|---|---|---|---|
| 29.47°N, 112.00°E; 29.33°N, 111.91°E; 29.25°N, 111.83°E | 60 | 60 | 0 |
| 29.15°N, 111.76°E; 29.04°N, 111.73°E; 28.99°N, 111.70°E |
表1 太阳山断裂的三维断层源参数
Table1 3D fault source parameters of the Taiyangshan fault
| 地表形迹坐标 | 宽度/km | 倾角/(°) | 顶面埋深/km |
|---|---|---|---|
| 29.47°N, 112.00°E; 29.33°N, 111.91°E; 29.25°N, 111.83°E | 60 | 60 | 0 |
| 29.15°N, 111.76°E; 29.04°N, 111.73°E; 28.99°N, 111.70°E |

图6 用本文研发算法模拟的三维断层源的地震目录空间分布图
Fig. 6 Spatial distribution map of earthquake catalogs of 3D fault sources simulated by the algorithm developed in this paper.
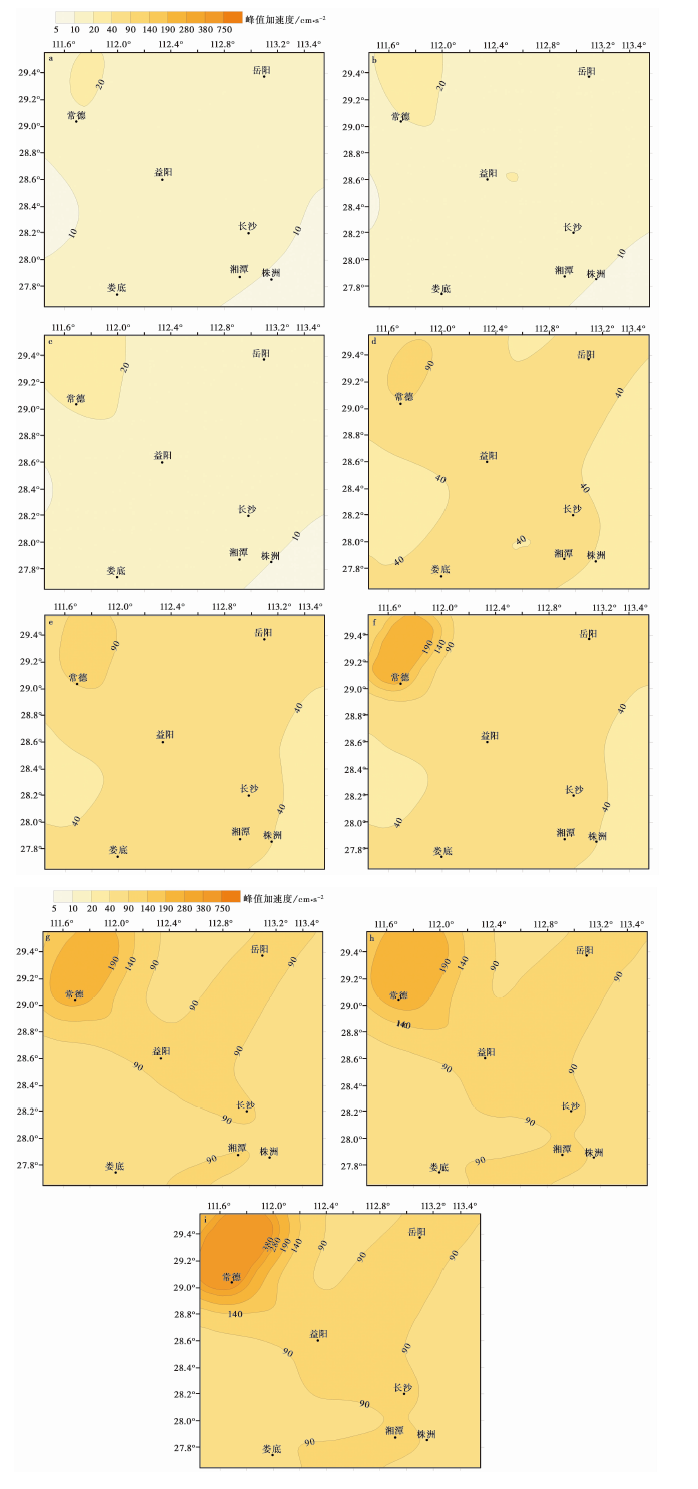
图7 研究区不同方案、不同概率水平下的地震动峰值加速度分布 a 50a超越概率63%(方案1); b 50a超越概率63%(方案2); c 50a超越概率63%(方案3); d 50a超越概率10%(方案1); e 50a超越概率10%(方案2); f 50a超越概率10%(方案3); g 50a超越概率2%(方案1); h 50a超越概率2%(方案2); i 50a超越概率2%(方案3).
Fig. 7 Distribution of ground motion peak acceleration with different probability levels for different schemes in the study area.
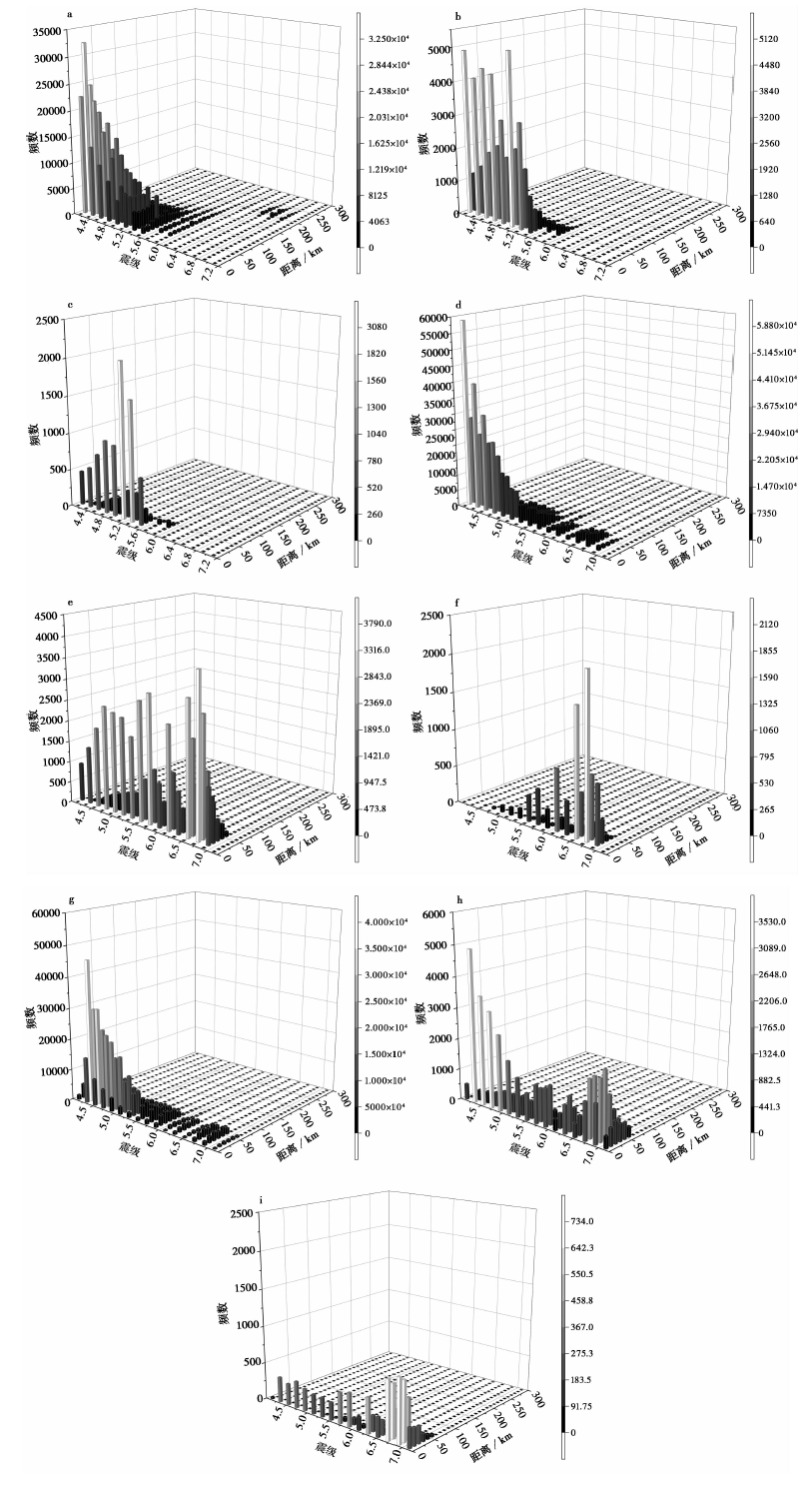
图8 株洲、常德不同方案、不同震级-距离档的地震对不同概率水平下峰值加速度危险性的贡献 a 超越概率63%(株洲, 方案2); b 超越概率10%(株洲, 方案2); c 超越概率2%(株洲, 方案2); d 超越概率63%(常德, 方案2); e 超越概率10%(常德, 方案2); f 超越概率2%(常德, 方案2); g 超越概率63%(常德, 方案3); h 超越概率10%(常德, 方案3); i 超越概率2%(常德, 方案3)
Fig. 8 Contribution of different magnitude-distance bins to PGA hazard with different probability levels in Zhuzhou and Changde.
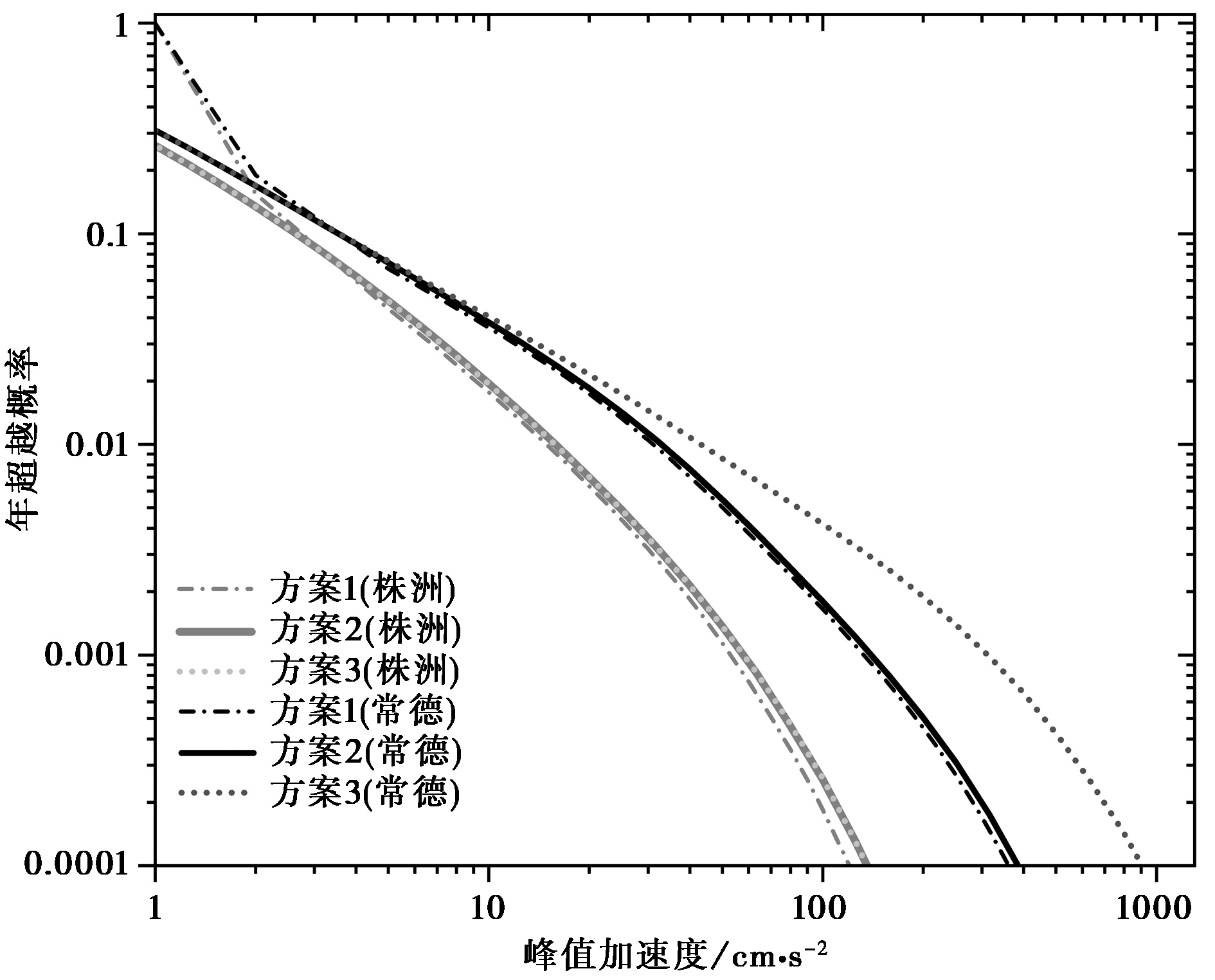
图9 常德、株洲不同方案的地震动峰值加速度超越概率曲线的对比
Fig. 9 Comparison of mean-hazard curves of ground motion peak acceleration in Changde and Zhuzhou for different schemes.
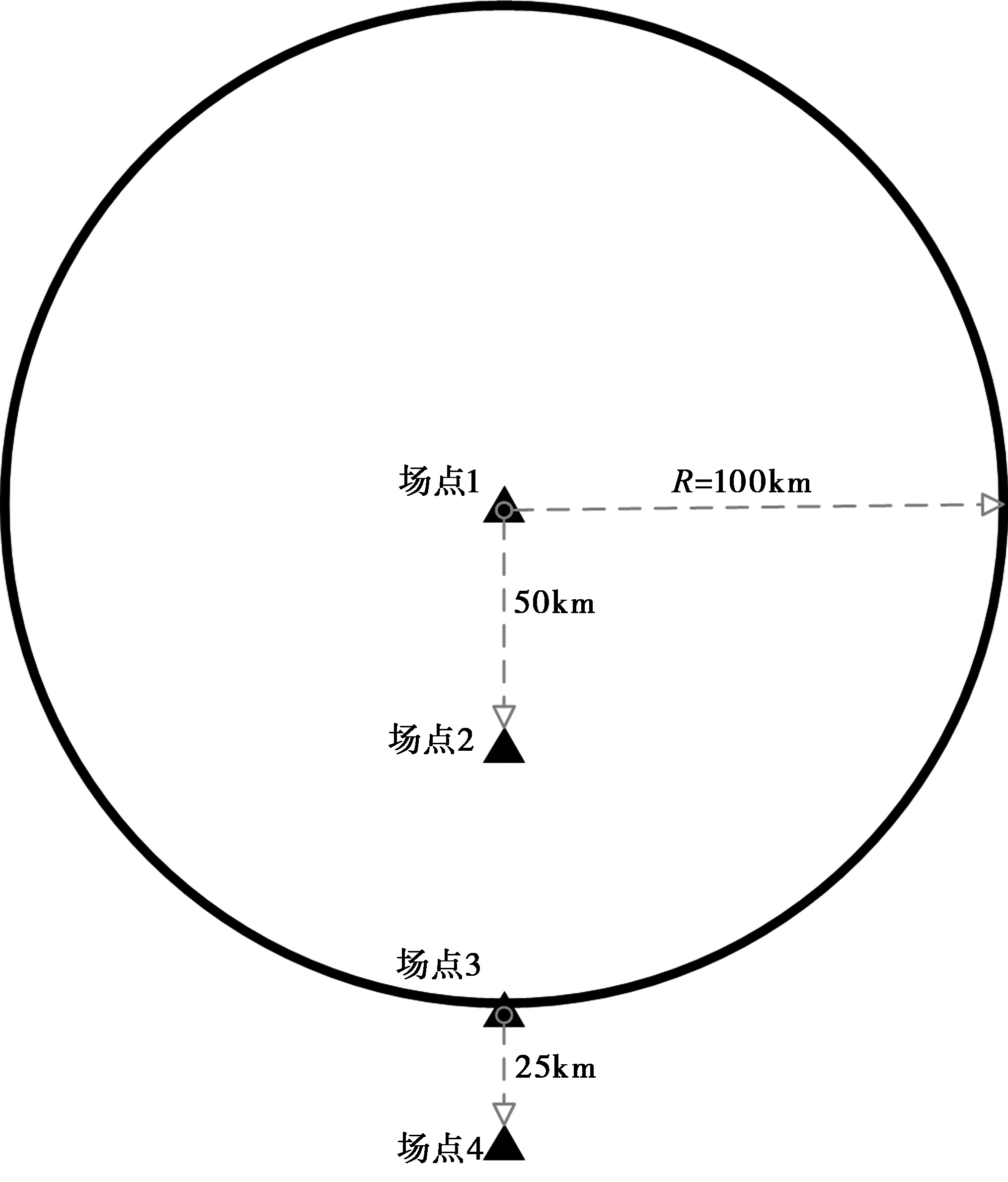
图10 太平洋工程地震中心验证概率地震危险性算例的示意图(数据集1、案例10)
Fig. 10 Schematic diagram of Validation Example of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard analysis in PEER(Set 1, Case 10).
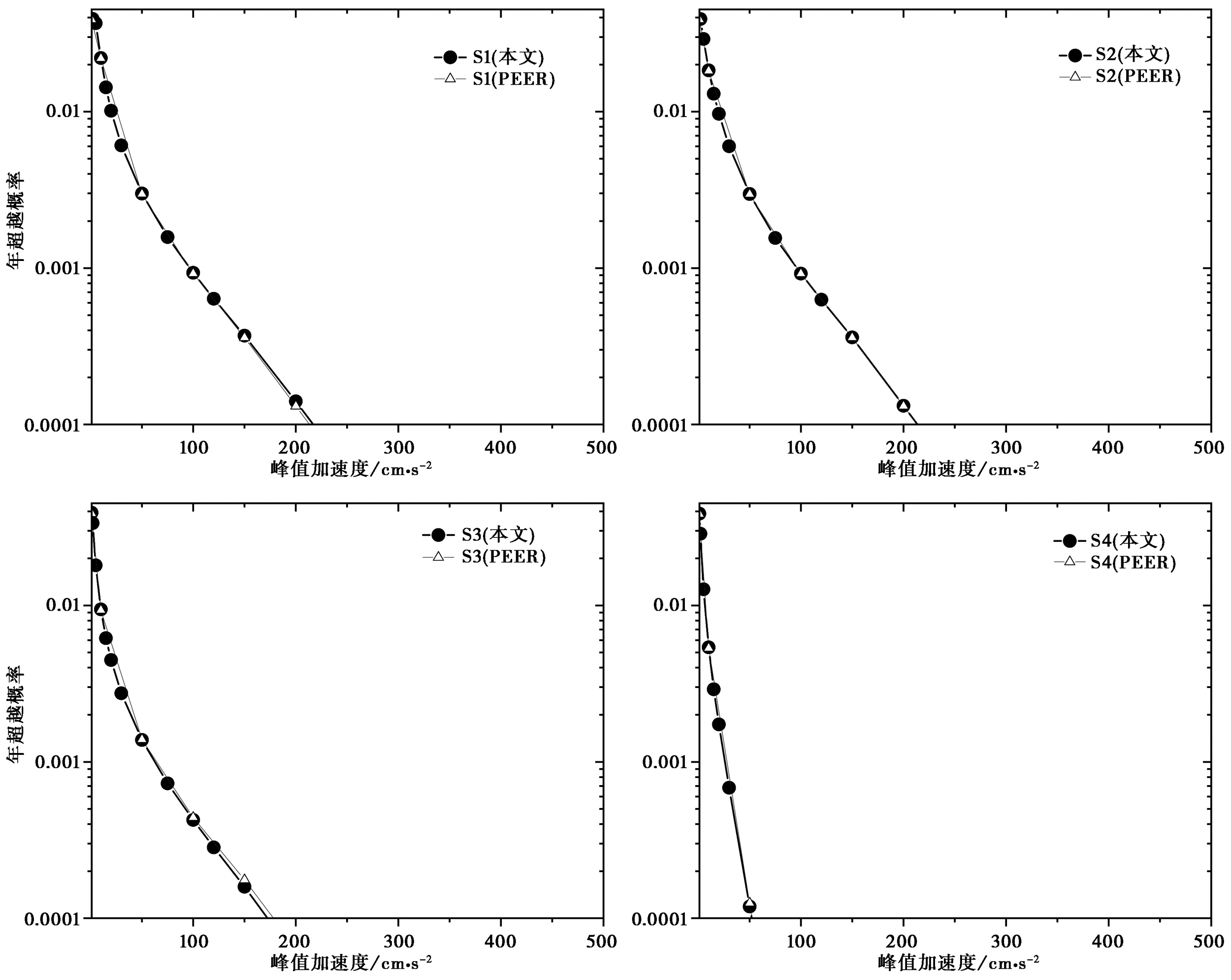
图11 太平洋地震工程中心概率地震危险性算例验证(数据集1, 案例10)
Fig. 11 Verification of Probabilistic seismic hazard calculation example in Pacific Earthquake Engineering Center(Set 1, Case 10).
| [1] | 陈鲲, 高孟潭. 2015. 中国大陆地区一般建设工程抗地震倒塌风险研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 36(1): 23-29. |
| CHEN Kun, GAO Meng-tan. 2015. Controlling seismic collapse risk of general construction projects in China mainland[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 36(1): 23-29. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 高孟潭. 1986. 地震危险性分析方法概述[J]. 国际地震动态, (11): 10-13. |
| GAO Meng-tan. 1986. An outline of the analytic methods for Seismic risk assessment[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology, (11): 10-13. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 高孟潭. 2015. 《中国地震动参数区划图》宣贯教材(GB 18306-2015)[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 中国质检出版社. |
| GAO Meng-tan. 2015. Chinese Ground Motion Intensity Measures Zoning Map Publicity Materials(GB 18306-2015)[M]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. Zhijian Publishing House. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 汪素云, 俞言祥, 高阿甲, 等. 2000. 中国分区地震动衰减关系的确定[J]. 中国地震, 16(2): 99-106. |
| WANG Su-yun, YU Yan-xiang, GAO A-jia, et al. 2000. Development of attenuation relations for ground motion in China[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 16(2): 99-106. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 徐伟进, 高孟潭, 左惠强. 2020. 地震巨灾模型中的随机地震事件集模拟[J]. 地震工程学报, 42(4): 1024-1034. |
| XU Wei-jin, GAO Meng-tan, ZUO Hui-qiang. 2020. Simulations of stochastic seismic event set using the earthquake catastrophe model[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 42(4): 1024-1034. | |
| [6] | 俞言祥, 李山有, 肖亮. 2013. 为新区划图编制所建立的地震动衰减关系[J]. 震灾防御技术, 8(1): 24-33. |
| YU Yan-xiang, LI Shan-you, XIAO Liang. 2013. Development of ground motion attenuation relations for the new seismic hazard map of China[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 8(1): 24-33. | |
| [7] | 章在墉, 陈达生. 1982. 二滩水电站坝区场地地震危险性分析[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 2(3): 1-15. |
|
ZHANG Zai-yong, CHEN Da-sheng. 1982. Seismic hazard analysis of the Ertan dam site[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2(3): 1-15.
DOI URL |
|
| [8] |
Bazzurro P, Cornell C A. 1999. Disaggregation of seismic hazard[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 89(2): 501-520.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Bender B, Perkins D M. 1987. SEISRISK Ⅲ: A computer program for seismic hazard estimation[R]. US Geological Survey Bulletin, 1772:48. |
| [10] |
Cornell C A. 1968. Engineering seismic risk analysis[J]. Bulletin of Seismological Society of America, 58(5): 1583-1606.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Ebel J E, Kafka A L. 1999. A Monte Carlo approach to seismic hazard analysis[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 89(4): 854-866.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Field E H, Jordan T H, Cornell C A. 2003. Open SHA: A developing community-modeling environment for seismic hazard analysis[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 74(4): 406-419.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Hong H P, Goda K. 2006. A comparison of seismic-hazard and risk deaggregation[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 96(6): 2021-2039. |
| [14] | McGuire R K. 1976. Fortran computer program for seismic risk analysis[R]. US Geological Survey. Open-File Report: 76-67. |
| [15] | McGuire R K. 1978. FRISK: Computer program for seismic risk analysis using faults as earthquake sources[R]. US Geological Survey. Open-File Report: 78-1007. |
| [16] | McGuire R K. 2004. Seismic hazard and risk analysis[R]. Earthquake Engineering Research Institute, Report MNO-10: 240. |
| [17] | McGuire R K. 2008. Probabilistic seismic hazard analysis: early history[J]. Earthquake Engineering& Structural Dynamics, 37(3): 329-338. |
| [18] | Musson R M W. 1999. Determination of design earthquakes in seismic hazard analysis through Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 3(4): 463-474. |
| [19] | Musson R M W. 2000. The use of Monte Carlo simulations for seismic hazard assessment in the UK[J]. Annali Di Geofisica, 43(1): 1-9. |
| [20] | Musson R M W. 2004. Objective validation of seismic hazard source models[C]. Proceedings of the thirteenth World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Vancouver, Paper No. 2492. |
| [21] |
Musson R M W. 2012. PSHA validated by quasi observational means[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 83(1): 130-134.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Ordaz M, Martinelli F, D’Amico V, et al. 2013. CRISIS2008: A flexible tool to perform probabilistic seismic hazard assessment[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 84(3): 495-504.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Pagani M, Marcellini A. 2007. Seismic-hazard disaggregation: A fully probabilistic methodology[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 97(5): 1688-1701.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Pagani M, Monelli D, Weatherill G, et al. 2014. OpenQuake engine: An open hazard(and risk)software for the global earthquake model[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 85(3): 692-702.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Patricia T, Ivan W, Norman A, et al. 2010. Verification of probabilistic seismic hazard analysis computer programs[R]. Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center Report 2010/106. |
| [26] | Petersen M D, Eeri M, Shumway A M, et al. 2020. The 2018 update of the US National Seismic Hazard Model: Overview of model and implications[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 36(1): 5-41. |
| [27] | Petersen M D, Frankel A D, Harmsen S C, et al. 2008. Documentation for the 2008 update of the United States National Seismic Hazard Maps[R]. US Geological Survey Open-File Report 2008-1128: 61. |
| [28] |
Powers P M, Clayton B S, Altekruse J M. 2022. Nshmp-haz: National Seismic Hazard Model Project hazard applications and web services[CP]. US Geological Survey Software Release. doi: 10.5066/P9STF5GK.
DOI |
| [29] | Robinson D, Fulford G, Dhu T. 2005. EQRM: Geoscience Australia’s Earthquake Risk Model: Technical Manual: Version 3.0[R]. Geoscience Australia Record 2005-01:148. |
| [30] |
Sadigh K, Chang C Y, Egan J A, et al. 1997. Attenuation relationships for shallow crustal earthquakes based on California strong motion data[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 68(1): 180-189.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Weatherill G, Burton P W. 2010. An alternative approach to probabilistic seismic hazard analysis in the Aegean region using Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Tectonophysics, 492(1): 253-278.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Wells D L, Coppersmith K J. 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area and surface displacement[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(4): 974-1002. |
| [1] | 冉洪流. 中国西部走滑型活动断裂的地震破裂参数与震级的经验关系[J]. 地震地质, 2011, 33(3): 577-585. |
| [2] | 肖和平. 湘东地区断裂活动性及潜在震源区划分研究[J]. 地震地质, 2009, 31(3): 488-500. |
| [3] | 张永庆, 谢富仁, 王峰. 乌鲁木齐地区活动断裂强震复发概率模型研究[J]. 地震地质, 2007, 29(4): 776-786. |
| [4] | 何仲太, 马保起, 卢海峰. 大青山山前活动断裂带分段与潜在震源区划分[J]. 地震地质, 2007, 29(4): 765-775. |
| [5] | 周庆, 虢顺民, 向宏发. 滇西北地区潜在震源区的划分原则和方法[J]. 地震地质, 2004, 26(4): 761-771. |
| [6] | 周本刚. 论发震构造特性在潜在震源区参数确定中的应用[J]. 地震地质, 2004, 26(4): 750-760. |
| [7] | 韩竹军, 张裕明, 于贵华. 如何确定对场地地震危险性贡献量最大的潜在震源区[J]. 地震地质, 1999, 21(4): 443-451. |
| [8] | 张裕明. 几个术语的含义及地震构造区最大潜在地震评价[J]. 地震地质, 1993, 15(4): 375-380. |
| [9] | 蒋秀琴, 王国新, 李东春. 用模式识别方法划分辽宁及其邻区的潜在震源区[J]. 地震地质, 1993, 15(1): 51-56. |
| [10] | 王绳祖. 青藏高原中部地区潜在震源发震概率的构造物理方法研究[J]. 地震地质, 1993, 15(1): 1-20. |
| [11] | 张裕明. 在确定潜在震源区中地震和地质资料的应用[J]. 地震地质, 1992, 14(3): 275-278. |
| [12] | 王绳祖. 浅源强震的判据和发震概率[J]. 地震地质, 1990, 12(2): 131-140. |
| [13] | 金学申, 戴英华, 马桂花, 康吉成, 冯会云, 赵军. 综合概率法及其在表征潜在震源区时空不均匀性上的应用[J]. 地震地质, 1989, 11(4): 63-70. |
| [14] | 叶洪, 窦毅强. 图象识别方法在工程地震学中的应用[J]. 地震地质, 1988, 10(4): 89-97. |
| [15] | 许建东, 张裕明. 判定潜在震源区的活断层模糊综合评判模型[J]. 地震地质, 1988, 10(4): 5-23. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||