地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 735-752.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.03.008
王江1,2)( ), 陈志3),*(
), 陈志3),*( ), 张帆2), 张志相2), 张素欣1,2)
), 张帆2), 张志相2), 张素欣1,2)
收稿日期:2022-11-30
修回日期:2023-02-16
出版日期:2023-06-20
发布日期:2023-07-18
通讯作者:
* 陈志, 男, 1983年生, 研究员, 主要研究方向为活动构造带流体地球化学特征及其成因机理, E-mail: 作者简介:王江, 男, 1984年生, 2010年于桂林理工大学获矿物学、 岩石学、 矿床学专业硕士学位, 高级工程师, 主要从事地震地下流体、 构造地球化学监测与研究, E-mail: wang.jiang@msn.com。
基金资助:
WANG Jiang1,2)( ), CHEN Zhi3),*(
), CHEN Zhi3),*( ), ZHANG Fan2), ZHANG Zhi-xiang2), ZHANG Su-xin1,2)
), ZHANG Fan2), ZHANG Zhi-xiang2), ZHANG Su-xin1,2)
Received:2022-11-30
Revised:2023-02-16
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-07-18
摘要:
文中基于对野外流动观测数据的分析处理, 初步研究了雄安新区主要断裂带土壤气体的Rn与CO2脱气特征及其对区域环境的影响。经观测分析发现, 新区3条地震剖面上方的土壤气体浓度高值异常区域与深部断裂的分布高度吻合, 展现出沿断裂带集中脱气的现象。受局部生物活动影响, 个别断裂区段土壤气体Rn和CO2可能存在不同的补给来源, 导致个别区段的Rn和CO2浓度高值异常区域不一致, 以及Rn和CO2浓度与通量测值之间较弱的相关性。计算结果显示, 新区主要断裂带存在强脱气特征, 各剖面土壤气体Rn通量平均值的变化范围为71.44~335.35mBq/m2·s, CO2通量平均值的变化范围为25.96~78.23g/m2·d; Rn浓度强度平均值的变化范围为0.91~2.30, CO2浓度强度平均值的变化范围为1.13~2.61, 与国内外其他典型断裂带及地震带的土壤气体脱气强度相当。结合室内气体环境污染综合防治标准对雄安新区主要断裂带释放气体的环境效应进行评估, 结果表明, 新区容城断裂的氡气释放最高值达675mBq/m2·s, 牛东断裂2条分支的最高值分别达395.70mBq/m2·s和334.84mBq/m2·s, 有必要对建在容城断裂和牛东断裂带上方的建筑物进行综合防氡处理。CO2释放量的初步估算结果表明, 新区主要断裂带的CO2脱气对大气的日贡献量约为1 622.56t, 年贡献量高达0.59×106t, 其对区域环境的影响应予以重视。文中的研究成果对于新区城市规划、 环境治理及断裂带释放气体环境影响的综合评估具有重要的科学意义。
王江, 陈志, 张帆, 张志相, 张素欣. 雄安新区主要断裂带土壤气体的Rn与CO2脱气特征[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 735-752.
WANG Jiang, CHEN Zhi, ZHANG Fan, ZHANG Zhi-xiang, ZHANG Su-xin. PRELIMINARY STUDY ON CHARACTERISTICS OF SOIL GAS Rn AND CO2 DEGASSING IN THE MAIN FAULT ZONES OF XIONG'AN NEW AREA[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(3): 735-752.
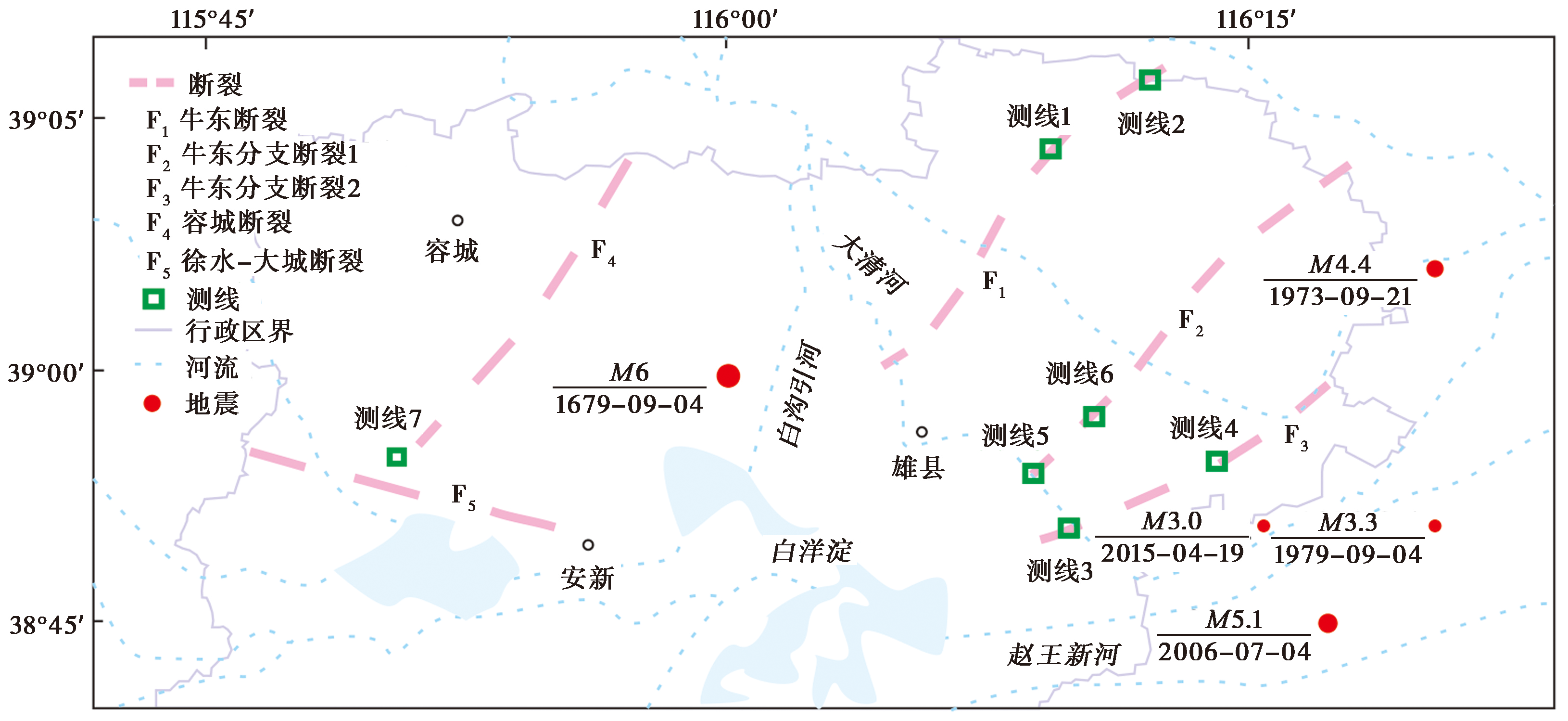
图 2 雄安新区断裂带的土壤气体测线分布图(改自王江等, 2022)
Fig. 2 Distribution of soil gas observation lines in the fault zone within Xiong'an New Area (adapted after WANG Jiang et al., 2022).
| 断裂 | 测线 | 年份 | Rn/mBq·m-2·s-1 | CO2/g·m-2·d-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 均值 | 最大值 | 均值 | |||
| F1 | 1 | 2020 | 132.65 | 99.05 | 13.97 | 13.88 |
| 1 | 2021 | 87.15 | 43.82 | 44.61 | 42.97 | |
| 2 | 2020 | 42.10 | 38.55 | 59.97 | 40.65 | |
| 2 | 2021 | 258.00 | 253.27 | 88.53 | 85.04 | |
| F3 | 3 | 2020 | 82.96 | 82.96 | 30.65 | 29.76 |
| 3 | 2021 | 334.84 | 195.50 | 41.00 | 29.14 | |
| 4 | 2020 | 268.96 | 156.42 | 101.61 | 79.62 | |
| 4 | 2021 | 129.03 | 105.07 | 46.56 | 35.02 | |
| F2 | 5 | 2020 | 351.38 | 177.97 | 19.31 | 14.66 |
| 5 | 2021 | 169.60 | 100.85 | 41.33 | 37.25 | |
| 6 | 2020 | 395.70 | 395.70 | 74.22 | 55.40 | |
| 6 | 2021 | 59.04 | 49.82 | 44.38 | 42.18 | |
| F4 | 7 | 2020 | 342.26 | 237.40 | 62.82 | 42.34 |
| 7 | 2021 | 675.06 | 433.30 | 131.16 | 114.12 |
表 1 雄安新区土壤气体测线通量的观测结果
Table 1 Results of soil gas flux profiles in Xiong'an New Area
| 断裂 | 测线 | 年份 | Rn/mBq·m-2·s-1 | CO2/g·m-2·d-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 均值 | 最大值 | 均值 | |||
| F1 | 1 | 2020 | 132.65 | 99.05 | 13.97 | 13.88 |
| 1 | 2021 | 87.15 | 43.82 | 44.61 | 42.97 | |
| 2 | 2020 | 42.10 | 38.55 | 59.97 | 40.65 | |
| 2 | 2021 | 258.00 | 253.27 | 88.53 | 85.04 | |
| F3 | 3 | 2020 | 82.96 | 82.96 | 30.65 | 29.76 |
| 3 | 2021 | 334.84 | 195.50 | 41.00 | 29.14 | |
| 4 | 2020 | 268.96 | 156.42 | 101.61 | 79.62 | |
| 4 | 2021 | 129.03 | 105.07 | 46.56 | 35.02 | |
| F2 | 5 | 2020 | 351.38 | 177.97 | 19.31 | 14.66 |
| 5 | 2021 | 169.60 | 100.85 | 41.33 | 37.25 | |
| 6 | 2020 | 395.70 | 395.70 | 74.22 | 55.40 | |
| 6 | 2021 | 59.04 | 49.82 | 44.38 | 42.18 | |
| F4 | 7 | 2020 | 342.26 | 237.40 | 62.82 | 42.34 |
| 7 | 2021 | 675.06 | 433.30 | 131.16 | 114.12 |
| 断裂 | Rn/mBq·m-2·s-1 | CO2/g·m-2·d-1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020年均值 | 2021年均值 | 2期均值 | 2020年均值 | 2021年均值 | 2期均值 | |
| F1 | 68.80 | 148.54 | 108.67 | 27.26 | 128.01 | 77.64 |
| F2 | 286.84 | 75.34 | 181.09 | 35.03 | 39.72 | 37.38 |
| F3 | 119.69 | 150.28 | 134.99 | 54.69 | 32.68 | 43.69 |
| F4 | 237.40 | 433.30 | 335.35 | 42.34 | 114.12 | 78.23 |
表 2 雄安新区主要断裂的土壤气体通量计算结果
Table 2 Results of fault soil gas flux calculation in Xiong'an New Area
| 断裂 | Rn/mBq·m-2·s-1 | CO2/g·m-2·d-1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020年均值 | 2021年均值 | 2期均值 | 2020年均值 | 2021年均值 | 2期均值 | |
| F1 | 68.80 | 148.54 | 108.67 | 27.26 | 128.01 | 77.64 |
| F2 | 286.84 | 75.34 | 181.09 | 35.03 | 39.72 | 37.38 |
| F3 | 119.69 | 150.28 | 134.99 | 54.69 | 32.68 | 43.69 |
| F4 | 237.40 | 433.30 | 335.35 | 42.34 | 114.12 | 78.23 |
| 土壤气体 | 断裂 | 测线 | 年份 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 异常界 | 异常均值 | 背景值 | 浓度强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rn/kBq·m-3 | F1 | 1 | 2020 | 7.97 | 15.33 | 12.86 | 14.57 | 19.87 | 0.73 |
| 1 | 2021 | 11.71 | 24.50 | 19.34 | 21.95 | 19.87 | 1.10 | ||
| 2 | 2020 | 11.45 | 23.67 | 18.62 | 23.67 | 19.87 | 1.19 | ||
| 2 | 2021 | 30.89 | 61.57 | 51.27 | 61.53 | 19.87 | 3.10 | ||
| F3 | 3 | 2020 | 14.89 | 35.50 | 25.34 | 35.50 | 19.87 | 1.79 | |
| 3 | 2021 | 15.63 | 36.59 | 26.54 | 32.21 | 19.87 | 1.62 | ||
| 4 | 2020 | 36.85 | 52.09 | 50.46 | 52.09 | 19.87 | 2.62 | ||
| 4 | 2021 | 29.07 | 39.91 | 36.55 | 33.14 | 19.87 | 1.67 | ||
| F2 | 5 | 2020 | 21.98 | 40.02 | 32.63 | 36.51 | 19.87 | 1.84 | |
| 5 | 2021 | 26.22 | 4.76 | 35.43 | 30.98 | 19.87 | 1.56 | ||
| 6 | 2020 | 26.50 | 45.80 | 40.73 | 44.70 | 19.87 | 2.25 | ||
| 6 | 2021 | 19.38 | 46.76 | 31.52 | 46.76 | 19.87 | 2.35 | ||
| F4 | 7 | 2020 | 13.68 | 49.74 | 28.55 | 39.22 | 19.87 | 1.97 | |
| 7 | 2021 | 11.94 | 43.32 | 24.73 | 41.20 | 19.87 | 2.07 | ||
| CO2/% | F1 | 1 | 2020 | 0.72 | 1.16 | 0.96 | 1.07 | 1.14 | 0.94 |
| 1 | 2021 | 0.81 | 1.70 | 1.27 | 1.50 | 1.14 | 1.32 | ||
| 2 | 2020 | 0.74 | 1.63 | 1.28 | 1.57 | 1.14 | 1.37 | ||
| 2 | 2021 | 0.93 | 1.90 | 1.35 | 1.90 | 1.14 | 1.67 | ||
| F3 | 3 | 2020 | 1.39 | 3.95 | 2.39 | 3.36 | 1.14 | 2.94 | |
| 3 | 2021 | 1.16 | 3.20 | 1.96 | 2.60 | 1.14 | 2.28 | ||
| 4 | 2020 | 1.58 | 2.32 | 2.12 | 2.27 | 1.14 | 1.99 | ||
| 4 | 2021 | 0.88 | 1.11 | 1.04 | 1.11 | 1.14 | 0.97 | ||
| F2 | 5 | 2020 | 1.48 | 2.45 | 2.31 | 2.42 | 1.14 | 2.12 | |
| 5 | 2021 | 2.21 | 3.56 | 2.83 | 1.71 | 1.14 | 1.50 | ||
| 6 | 2020 | 1.50 | 2.31 | 2.14 | 2.24 | 1.14 | 1.96 | ||
| 6 | 2021 | 1.17 | 2.46 | 1.66 | 2.46 | 1.14 | 2.16 | ||
| F4 | 7 | 2020 | 0.70 | 1.94 | 1.24 | 1.70 | 1.14 | 1.49 | |
| 7 | 2021 | 0.64 | 1.39 | 0.99 | 1.17 | 1.14 | 1.03 |
表 3 雄安新区土壤气体的浓度强度统计表
Table 3 Statistics of intensity of soil gas concentration in Xiong'an New Area
| 土壤气体 | 断裂 | 测线 | 年份 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 异常界 | 异常均值 | 背景值 | 浓度强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rn/kBq·m-3 | F1 | 1 | 2020 | 7.97 | 15.33 | 12.86 | 14.57 | 19.87 | 0.73 |
| 1 | 2021 | 11.71 | 24.50 | 19.34 | 21.95 | 19.87 | 1.10 | ||
| 2 | 2020 | 11.45 | 23.67 | 18.62 | 23.67 | 19.87 | 1.19 | ||
| 2 | 2021 | 30.89 | 61.57 | 51.27 | 61.53 | 19.87 | 3.10 | ||
| F3 | 3 | 2020 | 14.89 | 35.50 | 25.34 | 35.50 | 19.87 | 1.79 | |
| 3 | 2021 | 15.63 | 36.59 | 26.54 | 32.21 | 19.87 | 1.62 | ||
| 4 | 2020 | 36.85 | 52.09 | 50.46 | 52.09 | 19.87 | 2.62 | ||
| 4 | 2021 | 29.07 | 39.91 | 36.55 | 33.14 | 19.87 | 1.67 | ||
| F2 | 5 | 2020 | 21.98 | 40.02 | 32.63 | 36.51 | 19.87 | 1.84 | |
| 5 | 2021 | 26.22 | 4.76 | 35.43 | 30.98 | 19.87 | 1.56 | ||
| 6 | 2020 | 26.50 | 45.80 | 40.73 | 44.70 | 19.87 | 2.25 | ||
| 6 | 2021 | 19.38 | 46.76 | 31.52 | 46.76 | 19.87 | 2.35 | ||
| F4 | 7 | 2020 | 13.68 | 49.74 | 28.55 | 39.22 | 19.87 | 1.97 | |
| 7 | 2021 | 11.94 | 43.32 | 24.73 | 41.20 | 19.87 | 2.07 | ||
| CO2/% | F1 | 1 | 2020 | 0.72 | 1.16 | 0.96 | 1.07 | 1.14 | 0.94 |
| 1 | 2021 | 0.81 | 1.70 | 1.27 | 1.50 | 1.14 | 1.32 | ||
| 2 | 2020 | 0.74 | 1.63 | 1.28 | 1.57 | 1.14 | 1.37 | ||
| 2 | 2021 | 0.93 | 1.90 | 1.35 | 1.90 | 1.14 | 1.67 | ||
| F3 | 3 | 2020 | 1.39 | 3.95 | 2.39 | 3.36 | 1.14 | 2.94 | |
| 3 | 2021 | 1.16 | 3.20 | 1.96 | 2.60 | 1.14 | 2.28 | ||
| 4 | 2020 | 1.58 | 2.32 | 2.12 | 2.27 | 1.14 | 1.99 | ||
| 4 | 2021 | 0.88 | 1.11 | 1.04 | 1.11 | 1.14 | 0.97 | ||
| F2 | 5 | 2020 | 1.48 | 2.45 | 2.31 | 2.42 | 1.14 | 2.12 | |
| 5 | 2021 | 2.21 | 3.56 | 2.83 | 1.71 | 1.14 | 1.50 | ||
| 6 | 2020 | 1.50 | 2.31 | 2.14 | 2.24 | 1.14 | 1.96 | ||
| 6 | 2021 | 1.17 | 2.46 | 1.66 | 2.46 | 1.14 | 2.16 | ||
| F4 | 7 | 2020 | 0.70 | 1.94 | 1.24 | 1.70 | 1.14 | 1.49 | |
| 7 | 2021 | 0.64 | 1.39 | 0.99 | 1.17 | 1.14 | 1.03 |
| 断裂 | Rn浓度强度 | CO2浓度强度 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020年均值 | 2021年均值 | 2期均值 | 2020年均值 | 2021年均值 | 2期均值 | |
| F1 | 0.96 | 2.10 | 1.53 | 1.16 | 1.49 | 1.33 |
| F2 | 2.20 | 1.64 | 1.92 | 2.47 | 1.63 | 2.05 |
| F3 | 2.04 | 1.96 | 2.00 | 2.04 | 1.83 | 1.94 |
| F4 | 1.97 | 2.07 | 2.02 | 1.49 | 1.03 | 1.26 |
表 4 雄安新区主要断裂带的土壤气体浓度强度结果
Table 4 Results of intensity of soil gas concentration of fault zones within Xiong'an New Area
| 断裂 | Rn浓度强度 | CO2浓度强度 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020年均值 | 2021年均值 | 2期均值 | 2020年均值 | 2021年均值 | 2期均值 | |
| F1 | 0.96 | 2.10 | 1.53 | 1.16 | 1.49 | 1.33 |
| F2 | 2.20 | 1.64 | 1.92 | 2.47 | 1.63 | 2.05 |
| F3 | 2.04 | 1.96 | 2.00 | 2.04 | 1.83 | 1.94 |
| F4 | 1.97 | 2.07 | 2.02 | 1.49 | 1.03 | 1.26 |
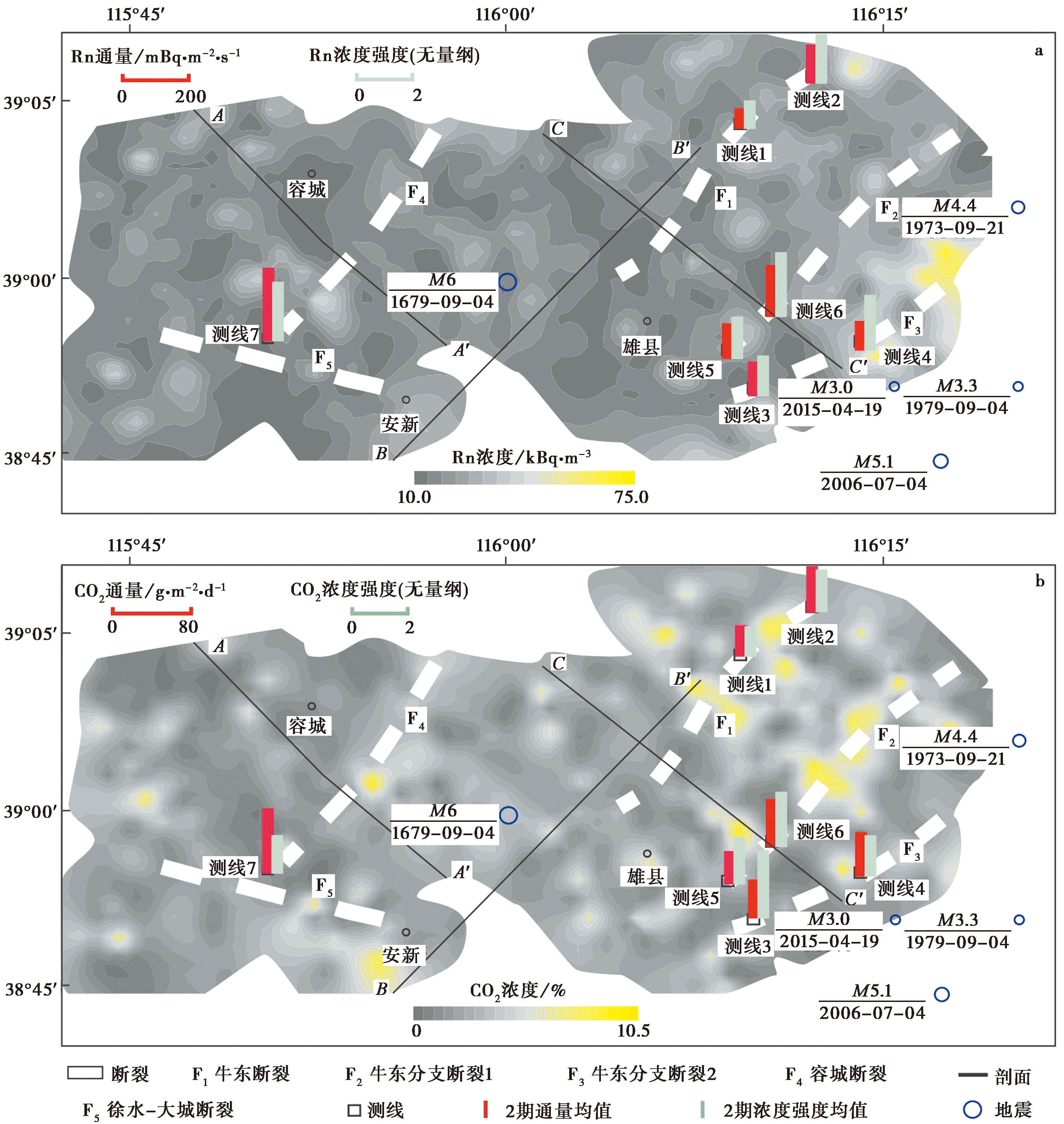
图 4 雄安新区主要断裂的土壤气体通量、 浓度强度(改自王江等, 2022)及地震剖面(改自何登发等, 2018) a 土壤气体Rn的通量与浓度强度; b 土壤气体CO2的通量与浓度强度
Fig. 4 Soil gas flux, concentration intensity(adapted after WANG Jiang et al., 2022), and seismic profile (adapted after HE Deng-fa et al., 2018)within the main fault zones in the Xiong'an New Area.
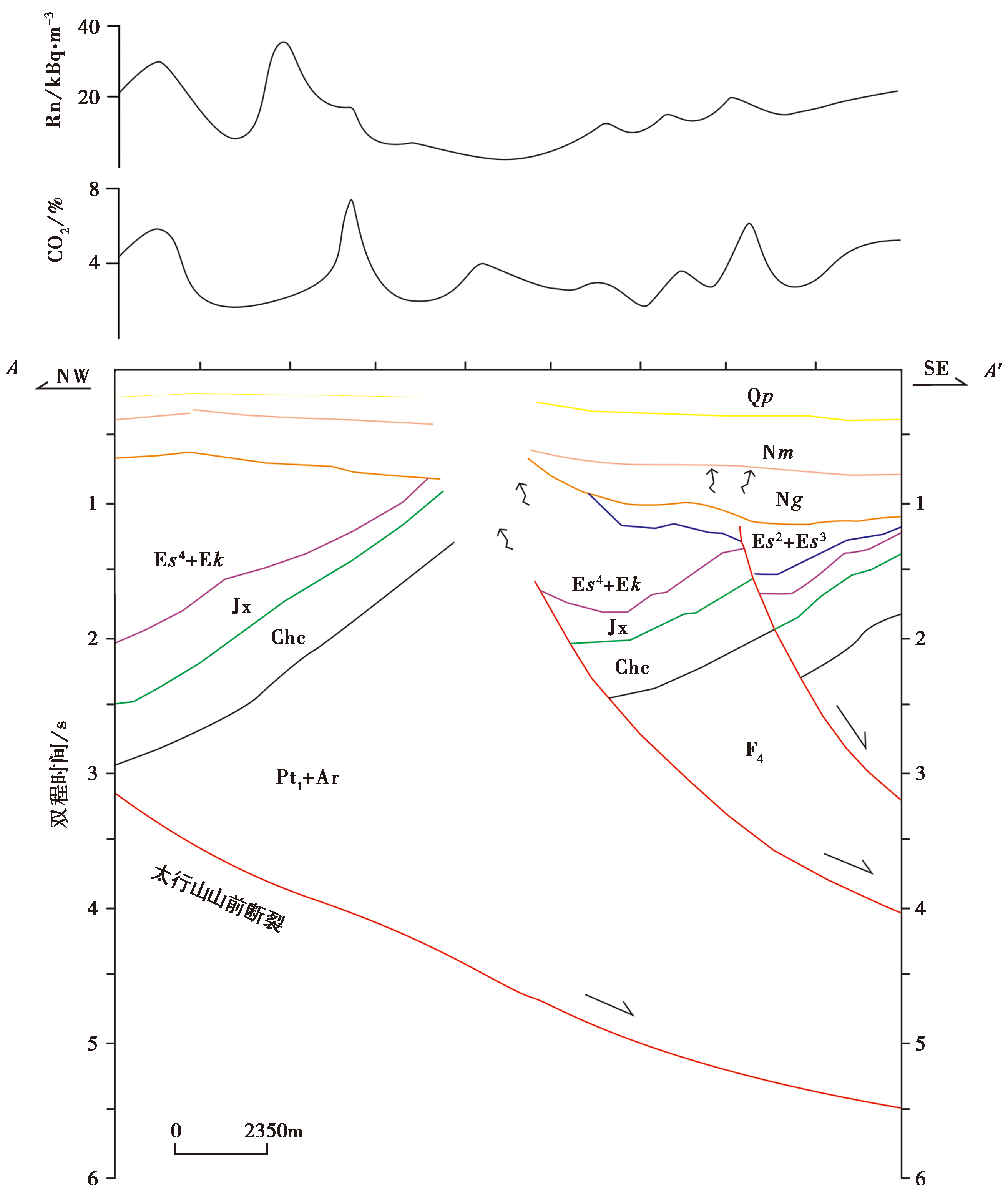
图 5 NW-SE向AA'剖面上的断层展布及土壤气体Rn、 CO2的浓度 土壤气体浓度曲线来自文献(王江等, 2022); 地震剖面来自文献(何登发等, 2018)。Qp 第四系平原组; Nm 新近系明化镇组; Ng 新近系馆陶组; Es2 古近系沙二段; Es3 古近系沙三段; Es4 古近系沙四段; Ek 古近系孔店组; Jx 中元古界蓟县系; Chc 中元古界长城系; Pt1+Ar 太古界—古元古界
Fig. 5 Fault distribution and soil gas Rn, CO2 concentration in NW-SE trending AA' profile of the Xiong'an New Area.
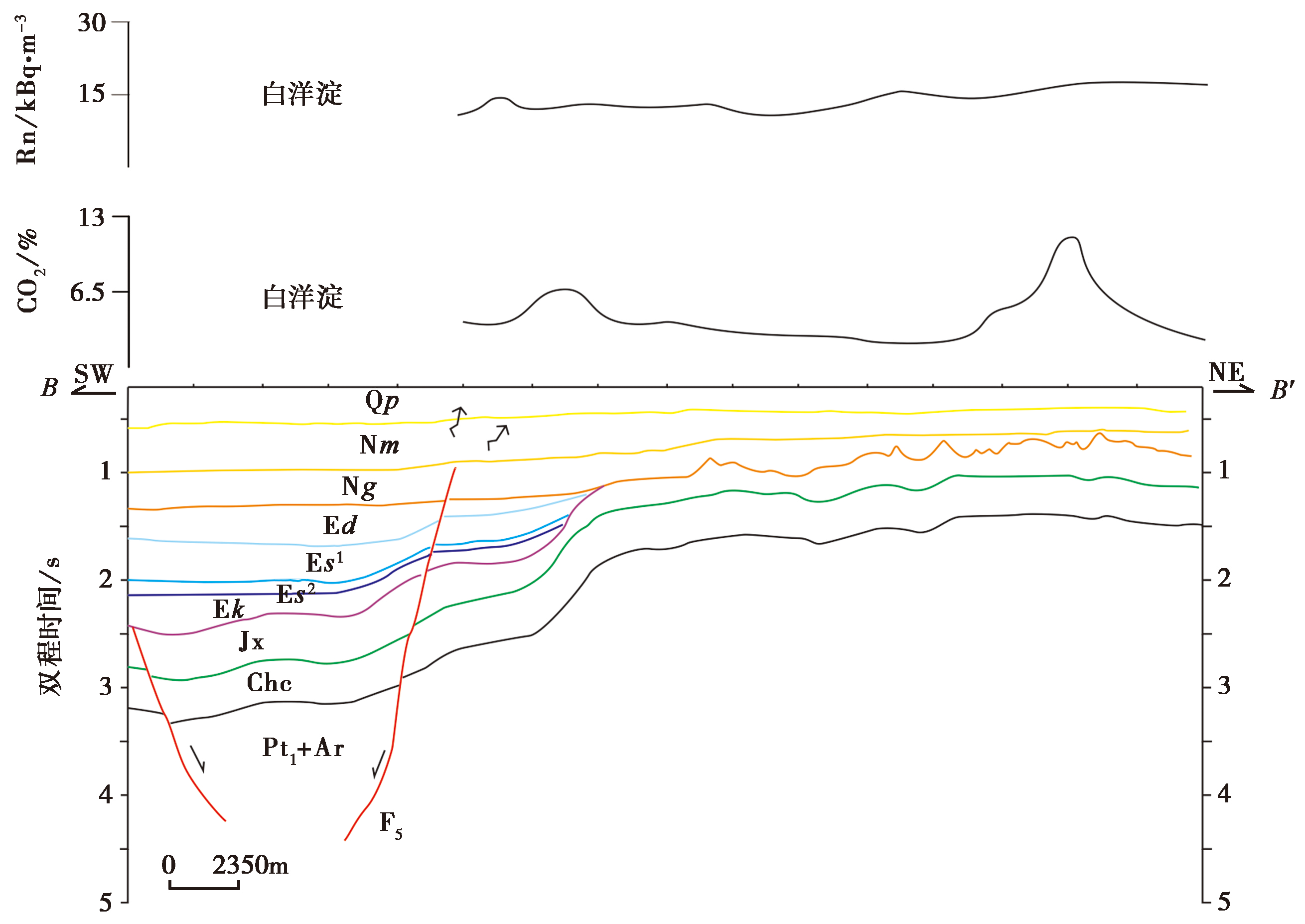
图 6 SW-NE向BB' 剖面上的断层展布及土壤气体Rn、 CO2的浓度 土壤气体浓度曲线来自文献(王江等, 2022); 地震剖面来自文献(何登发等, 2018)。Qp 第四系平原组; Nm 新近系明化镇组; Ng 新近系馆陶组; Ed 古近系东营组; Es1 古近系沙一段; Es2 古近系沙二段; Ek 古近系孔店组; Jx 中元古界蓟县系; Chc 中元古界长城系; Pt1+Ar 太古界—古元古界
Fig. 6 The fault distribution and soil gas Rn, CO2 concentration in SW-NE trending BB' profile of the Xiong'an New Area.
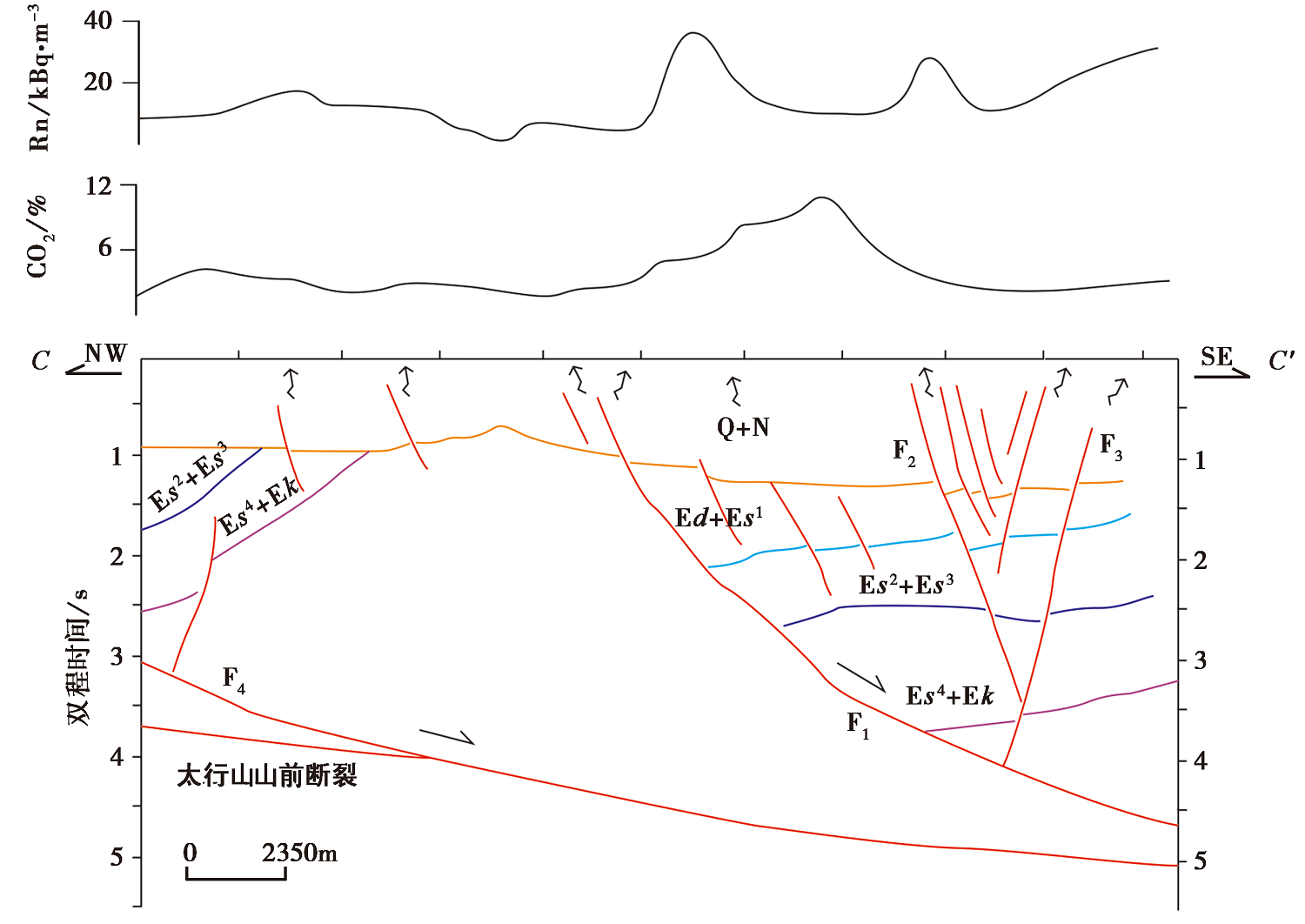
图 7 NW-SE向CC'剖面上的断层展布及土壤气体Rn、 CO2的浓度 土壤气体浓度曲线来自文献(王江等, 2022); 地震剖面来自文献(何登发等, 2018)。Qp 第四系平原组; Nm 新近系明化镇组; Ng 新近系馆陶组; Ed 古近系东营组; Es1 古近系沙一段; Es2 古近系沙二段; Ek 古近系孔店组; Jx 中元古界蓟县系; Chc 中元古界长城系; Pt1+Ar 太古界—古元古界
Fig. 7 The fault distribution and soil gas Rn, CO2 concentration in NW-SE trending CC' profile of the Xiong'an New Area.
| 断裂 | CO2平均通量/g·m-2·d-1 | 断裂长度/km | 破碎带宽度/m | 面积/m2 | 日贡献量/t | 年贡献量/t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 77.64 | 59 | 200 | 1.18×107 | 916.15 | 0.33×106 |
| F2 | 37.38 | 27 | 125 | 3.37×106 | 125.81 | 0.05×106 |
| F3 | 43.39 | 17 | 150 | 2.56×106 | 111.22 | 0.04×106 |
| F4 | 78.23 | 30 | 200 | 6.00×106 | 469.38 | 0.17×106 |
表 5 雄安新区主要断裂带土壤气体CO2脱气对大气的贡献量
Table 5 Contribution of soil gas CO2 degassing from the main fault zones to the atmosphere in Xiong'an New Area
| 断裂 | CO2平均通量/g·m-2·d-1 | 断裂长度/km | 破碎带宽度/m | 面积/m2 | 日贡献量/t | 年贡献量/t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 77.64 | 59 | 200 | 1.18×107 | 916.15 | 0.33×106 |
| F2 | 37.38 | 27 | 125 | 3.37×106 | 125.81 | 0.05×106 |
| F3 | 43.39 | 17 | 150 | 2.56×106 | 111.22 | 0.04×106 |
| F4 | 78.23 | 30 | 200 | 6.00×106 | 469.38 | 0.17×106 |
| [1] |
丁志华, 崔月菊, 唐杰. 2022. 2020年7月12日唐山5.1级地震前高光谱多参数异常特征分析[J]. 中国地震, 38(3): 494-502.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
杜建国, 宇文欣, 李圣强, 等. 1998. 八宝山断裂带逸出氡的地球化学特征及其映震效能[J]. 地震, 18(2): 155-162.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
杜乐天. 2005. 地球排气作用的重大意义及研究进展[J]. 地质论评, 51(2): 174-180.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
冯希杰. 1988. 中国大陆北西-北北西向断裂系统与强震[J]. 西安地质学院学报, 10(3): 47-55.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
高程达, 孙向阳, 曹吉鑫, 等. 2008. 土壤二氧化碳通量原位测定方法及装置[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 30(2): 102-105.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
高战武, 徐杰, 赵铁虎, 等. 2016. 渤海海域主要新构造活动断裂带[J]. 中国地震, 32(4): 595-606.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
何登发, 崔永谦, 张煜颖, 等. 2017. 渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷古潜山的构造成因类型[J]. 岩石学报, 33(4): 1338-1356.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
何登发, 单帅强, 张煜颖, 等. 2018. 雄安新区的三维地质结构: 来自反射地震资料的约束[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学(D辑): 1207-1222.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
胡秋韵, 高俊, 马峰, 等. 2020. 雄安新区容城凸起区地热可采资源量动态预测[J]. 地质学报, 94(7): 2013-2025.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
蒋海昆, 付虹, 杨马陵. 2018. 中国震例(2007-2010)[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
劳海港. 2010. 冀中坳陷潜山类型及其演化特征研究[D]. 山东: 中国石油大学.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
李弘, 俞建宝, 吕慧, 等. 2017. 雄县地热田重磁响应及控热构造特征研究[J]. 物探与化探, 41(2): 242-248.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
李静, 陈志, 陆丽娜, 等. 2018. 夏垫活动断裂CO2、 Rn、 Hg脱气对环境的影响[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 37(4): 629-638.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
李祖武. 1992. 中国东部北北西(北西)向构造系与地震活动关系的讨论[J]. 地壳形变与地震, 12(2): 47-53.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
刘兆飞, 李营, 陈志, 等. 2019. 吉兰泰断陷盆地周缘断裂带气体释放及其对断层活动性的指示意义[J]. 地震学报, 41(5): 613-632.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
商世杰, 丰成君, 谭成轩, 等. 2019. 雄安新区附近主要隐伏断裂第四纪活动性研究[J]. 地球学报, 40(6): 836-846.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
邵永新, 杨绪连, 李一兵. 2007. 海河隐伏活断层探测中土壤气氡和气汞测量及其结果[J]. 地震地质, 29(3): 627-636.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
孙冬胜, 刘池阳, 杨明慧, 等. 2004. 渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷中区中新生代复合伸展构造[J]. 地质论评, 50(5): 484-491.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
滕吉文. 2001. 地球内部物质、 能量交换与资源和灾害[J]. 地学前缘, 8(3): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
王华林, 陈锦太, 耿杰, 等. 1991. 胜利油田及邻近地区断裂活动性研究[J]. 西北地震学报, 13(1): 78-84.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
王基华, 王亮, 孙凤民, 等. 1996. 隐伏断层活动性分段的汞地球化学标志初探[J]. 地震地质, 18(4): 409-412.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
王江, 陈志, 张帆, 等. 2022. 基于土壤气体地球化学的雄安新区活动断裂空间展布及活动性探讨[J]. 地震研究, 45(2): 264-274.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
王江, 李营, 陈志. 2017. 口泉断裂断层气地球化学变化特征及断层活动性[J]. 地震, 37(1): 39-51.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
徐锡伟, 郭婷婷, 刘少卓, 等. 2016. 活动断层避让相关问题的讨论[J]. 地震地质, 38(3): 477-502. doi: 10.3969/j.Issn.0253-4967.2016.03.001.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [25] |
杨江, 李营, 陈志, 等. 2019. 唐山断裂带南西段和北东段土壤气Rn和CO2浓度特征[J]. 地震, 39(3): 61-70.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
杨明慧, 刘池阳, 孙冬胜, 等. 2002. 冀中坳陷的伸展构造系统及其构造背景[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 26(2): 113-120.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
杨晓松, 陈建业, 段庆宝, 等. 2014. 地震断层带流体作用的岩石化学-物理响应: 来自矿物学、 岩石化学、 岩石物理学的启示[J]. 地震地质, 36(3): 862-881. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.024.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [28] |
赵元鑫, 李营, 陈志, 等. 2022. 唐山断裂带气体组分变异函数空间分布特征[J]. 地震, 42(1): 18-32.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
郑国东, 赵文斌, 陈志, 等. 2021. 中国地质源温室气体释放近十年研究概述[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 40(6): 1250-1271.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
周晓成, 柴炽章, 雷启云, 等. 2013. 银川隐伏断层带土壤气中H2的地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 33(1): 147-149.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
周晓成, 杜建国, 陈志, 等. 2012. 地震地球化学研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 31(4): 340-346.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
周晓成, 杜建国, 王传远, 等. 2007. 西藏拉萨市土壤气中氡、 汞环境地球化学特征[J]. 环境科学, 28(3): 659-663.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
周晓成, 孙凤霞, 陈志, 等. 2017. 汶川 MS8.0 地震破裂带CO2、 CH4、 Rn和Hg脱气强度[J]. 岩石学报, 33(1): 291-303.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
周志华, 赵烽帆, 李营, 等. 2014. 首都圈土壤气中氡环境地球化学特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(7): 1729-1733.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
朱宏任, 汪成民. 1990. 地球的脱气过程及对人类生活环境的影响[J]. 灾害学, 5(4): 84-88.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
DOI URL |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
DOI URL |
| [40] |
DOI URL |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
DOI URL |
| [43] |
DOI URL |
| [44] |
DOI URL |
| [45] |
DOI URL |
| [46] |
DOI URL |
| [47] |
DOI URL |
| [48] |
DOI URL |
| [49] |
DOI URL |
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
DOI URL |
| [52] |
DOI URL |
| [53] |
|
| [1] | 朱成英, 闫玮, 麻荣, 李志海, 汪成国, 黄建明, 周晓成. 2017年8月9日精河MS6.6地震宏观烈度及其余震分布的断层气体地球化学表征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1225-1239. |
| [2] | 泽仁志玛, 张学民, 刘静, 欧阳新艳, 熊攀, 申旭辉. 利用DEMETER卫星LANGMIUR探针观测数据研究强震前的电离层扰动[J]. 地震地质, 2010, 32(3): 424-433. |
| [3] | 李陈侠, 徐锡伟, F Perrier, P Richon, 陈桂华, Y Klinger, J-M Nocquet, C Romieu, 张晓清, 常振广. 东昆仑活动断裂带西大滩段断层气(Rn,CO2)的释放特征[J]. 地震地质, 2007, 29(4): 905-909. |
| [4] | 上官志冠, 高清武, 赵慈平. 腾冲热海地区NW向断裂活动性的地球化学证据[J]. 地震地质, 2004, 26(1): 46-51. |
| [5] | 高清武, 上官志冠, 胡金文. 琼北火山及断裂的活动性——氡、钍气体放射性示踪[J]. 地震地质, 2003, 25(2): 280-288. |
| [6] | 张玉松, 胡玉台, 李建华. 218Po和210Po对比测量寻找隐伏活断层[J]. 地震地质, 1992, 14(1): 12-22. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||