地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 952-969.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.04.009
王嘉沛1,2)( ), 谈洪波1,2), 李忠亚1,2), 刘少明1,2), 张毅3), 郝洪涛1,2), 胡敏章1,2), 申重阳1,2)
), 谈洪波1,2), 李忠亚1,2), 刘少明1,2), 张毅3), 郝洪涛1,2), 胡敏章1,2), 申重阳1,2)
收稿日期:2022-08-10
修回日期:2022-10-09
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-09-20
作者简介:王嘉沛, 男, 1989年生, 2022年于中国科学院大学获固体地球物理学专业博士学位, 助理研究员, 主要从事地壳形变与重力变化的分析研究, E-mail: wang_jia_pei@163.com。
基金资助:
WANG Jia-pei1,2)( ), TAN Hong-bo1,2), LI Zhong-ya1,2), LIU Shao-ming1,2), ZHANG Yi3), HAO Hong-tao1,2), HU Min-zhang1,2), SHEN Chong-yang1,2)
), TAN Hong-bo1,2), LI Zhong-ya1,2), LIU Shao-ming1,2), ZHANG Yi3), HAO Hong-tao1,2), HU Min-zhang1,2), SHEN Chong-yang1,2)
Received:2022-08-10
Revised:2022-10-09
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-09-20
摘要:
为研究2019年四川长宁地震前后地壳内部物质的运移过程, 文中利用流动重力和GNSS资料对地震前后的重力变化特征、 地壳垂直形变及其关系进行了深入分析。地震震中处于重力变化正、 负异常的梯度带上, 并在地震前后呈现明显反向。小波多尺度分解表明, 浅部的离散性局部变化特征明显, 深部的趋势变化特征显著。震中周边4个站点的重力变化与地壳垂直形变的关系与近似规律不一致。长宁震区长期的动力是青藏高原的物质在深部向四川盆地南边界运移的结果。在震中及周边区域的地表浅层可能存在一些空洞或气囊等空间, 在地震前后出现气体、 液体或高密度物质流失和填充的现象。结合前人对长宁地震发震机制的研究成果分析认为, 该区域的采盐、 采气及废水回注等因素可能是触发四川长宁地震的原因之一。
王嘉沛, 谈洪波, 李忠亚, 刘少明, 张毅, 郝洪涛, 胡敏章, 申重阳. 长宁地震前后重力变化和地壳垂直形变特征及其关系[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(4): 952-969.
WANG Jia-pei, TAN Hong-bo, LI Zhong-ya, LIU Shao-ming, ZHANG Yi, HAO Hong-tao, HU Min-zhang, SHEN Chong-yang. CHARACTERISTICS AND RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN GRAVITY VARIATION AND CRUSTAL VERTICAL DEFORMATION BEFORE AND AFTER CHANGNING EARTHQUAKE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(4): 952-969.
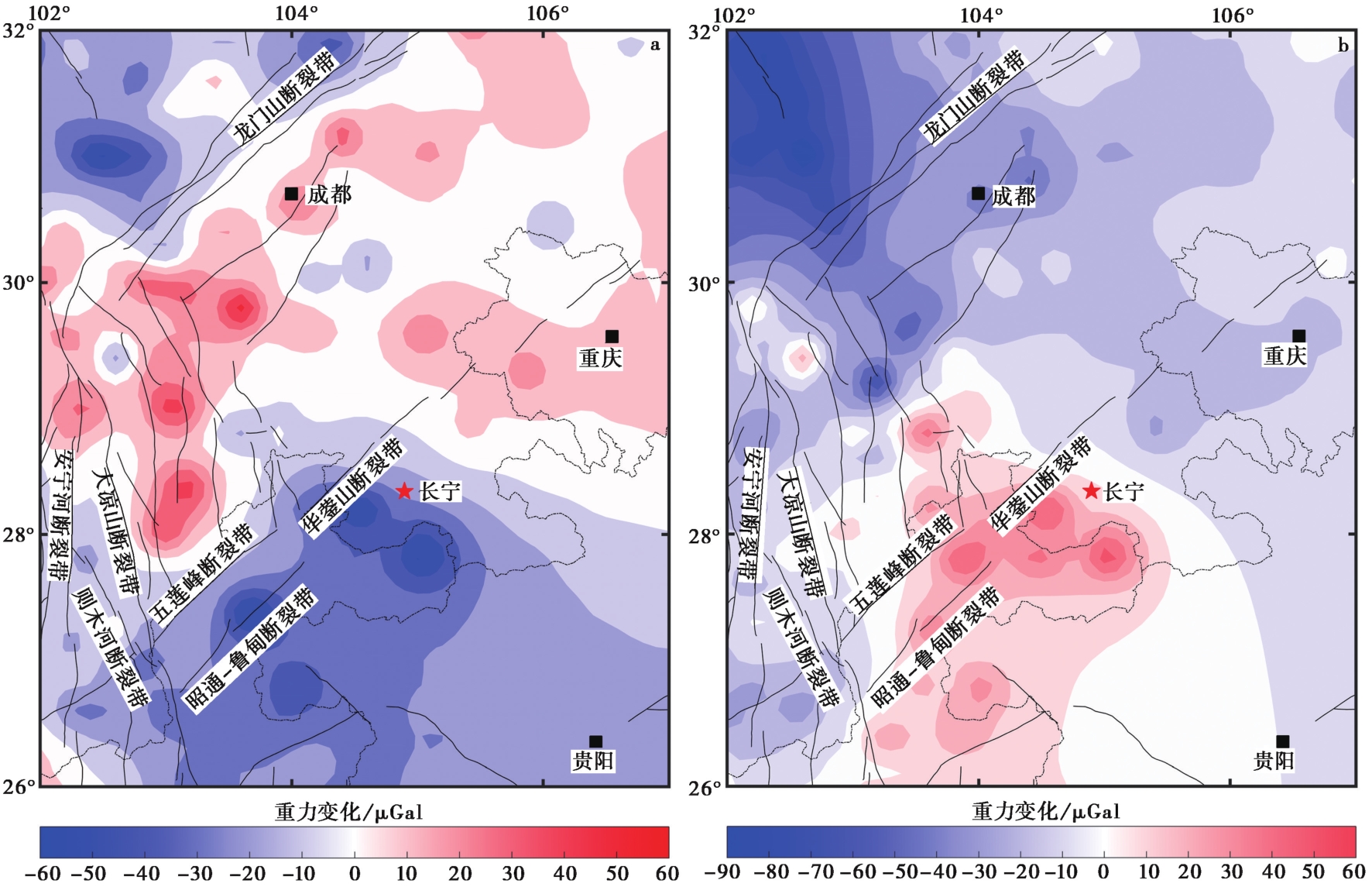
图 4 长宁6.0级地震前后2期重力场动态变化图
Fig. 4 Dynamic change diagram of the gravity field in two phases before and after the Changning earthquake. a 2018-09-2019-04 b 2019-04-2019-08
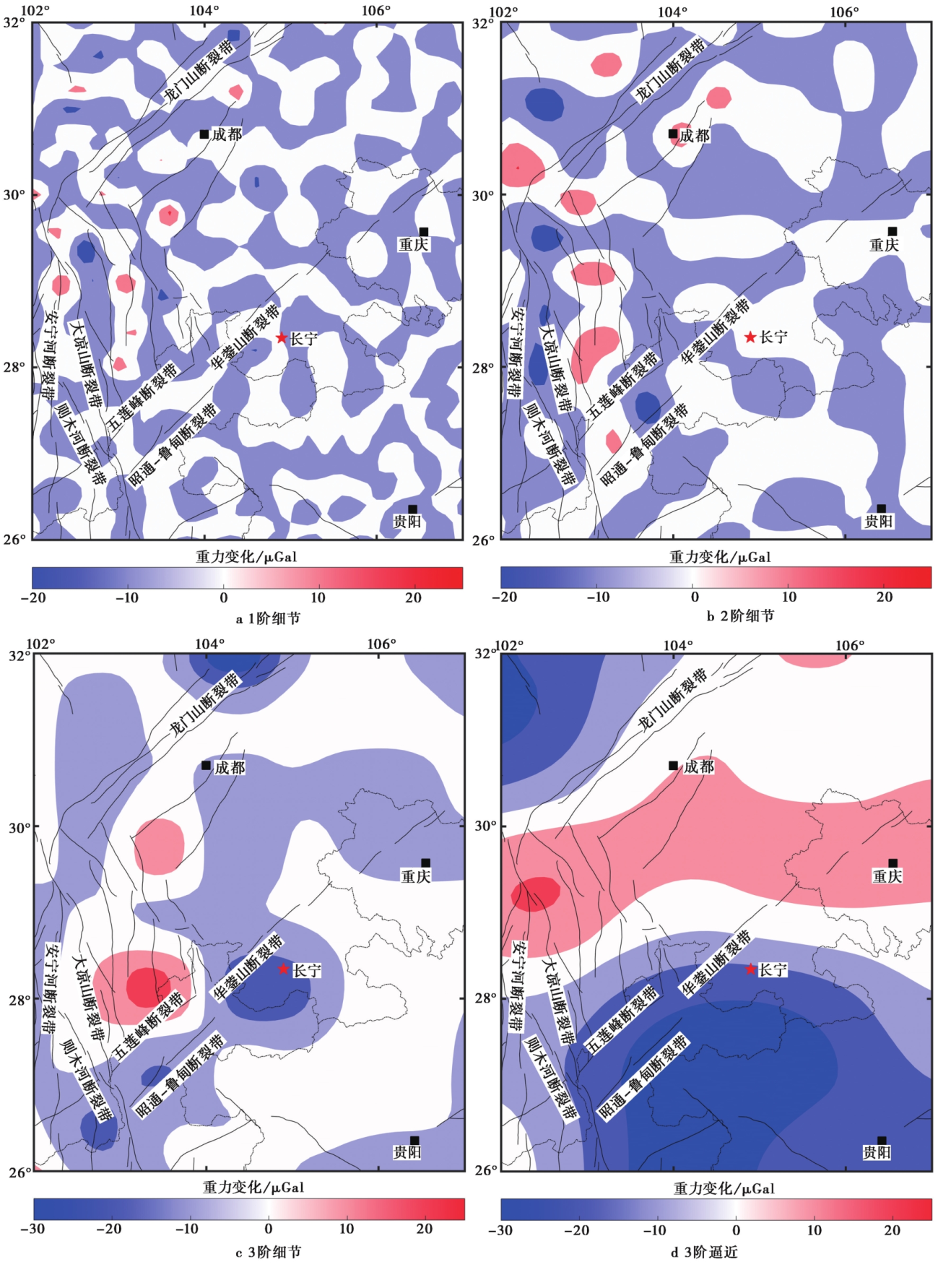
图 5 2018-09-2019-04四川长宁地区重力变化的小波多尺度分解图像 a 1阶细节; b 2阶细节; c 3阶细节; d 3阶逼近
Fig. 5 Wavelet multiscale decomposition image of gravity change in Changning area, Sichuan Province from September 2018 to April 2019.
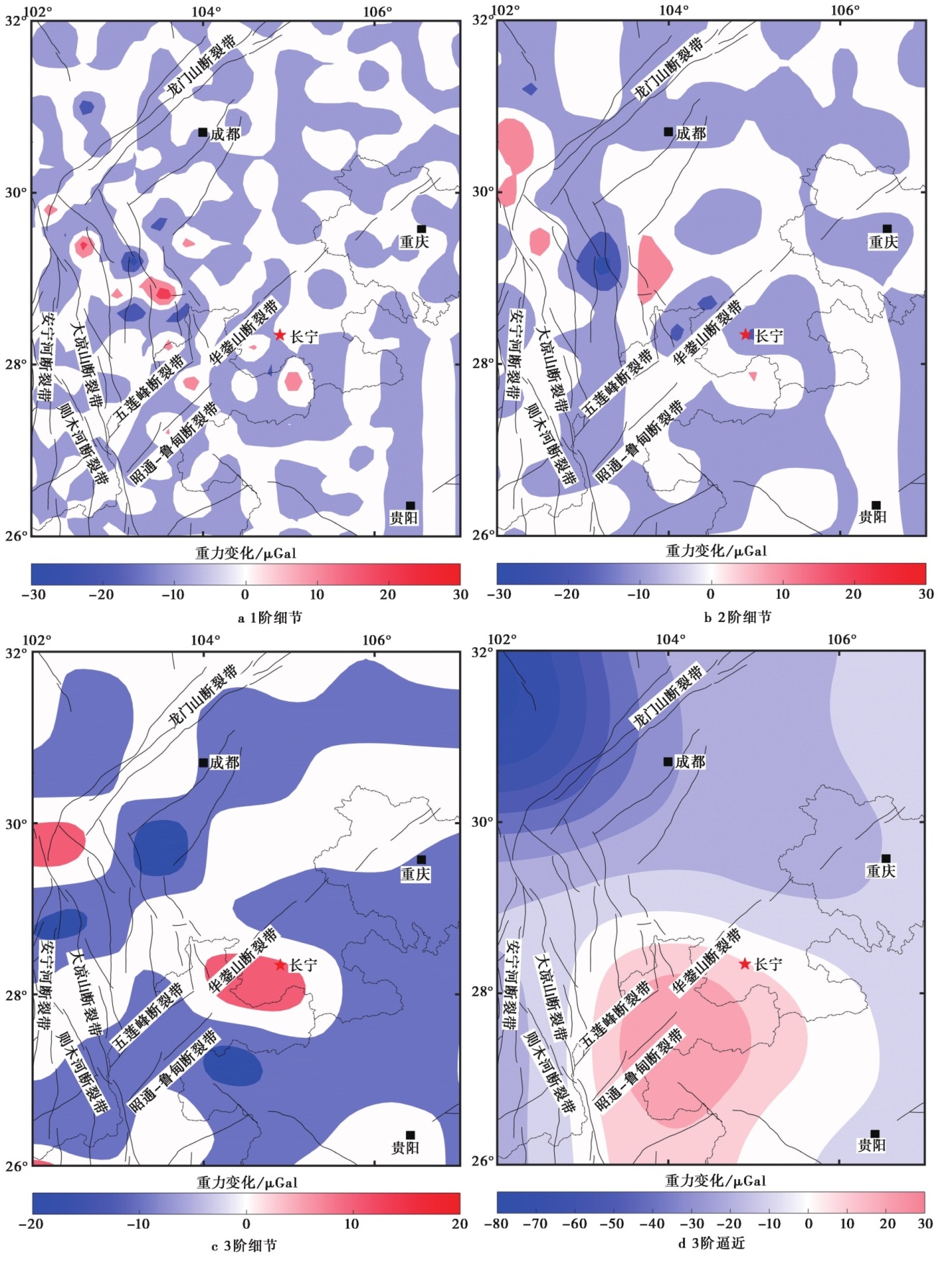
Fig. 6 2019-04-2019-08四川长宁地区重力变化的小波多尺度分解图像 Wavelet multiscale decomposition image of gravity change in Changning area, Sichuan Province from April 2019 to August 2019.a 1阶细节; b 2阶细节; c 3阶细节; d 3阶逼近
| 站点 | 2018-09——2019-04 | 重力变化 /μGal | 比值 /μGal·mm-1 | 2019-04——2019-08 | 重力变化 /μGal | 比值 /μGal·mm-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 形变速率 /mm·a-1 | 形变量 /mm | 形变速率 /mm·a-1 | 形变量 /mm | |||||
| SCMB | 59.77 | 39.85 | -5 | -0.1255 | -69.58 | -28.99 | 5 | -0.1724 |
| GZSC | 49.31 | 32.87 | -12 | -0.3651 | -36.77 | -15.32 | 5 | -0.3263 |
| SCJU | 49.71 | 33.14 | -25 | -0.7543 | -28.73 | -11.97 | 20 | -1.671 |
| LUZH | 39.94 | 26.63 | 8 | 0.3755 | -33.4 | -13.92 | -8 | 0.7184 |
表 1 4个站点的对比
Table 1 Comparison of four sites
| 站点 | 2018-09——2019-04 | 重力变化 /μGal | 比值 /μGal·mm-1 | 2019-04——2019-08 | 重力变化 /μGal | 比值 /μGal·mm-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 形变速率 /mm·a-1 | 形变量 /mm | 形变速率 /mm·a-1 | 形变量 /mm | |||||
| SCMB | 59.77 | 39.85 | -5 | -0.1255 | -69.58 | -28.99 | 5 | -0.1724 |
| GZSC | 49.31 | 32.87 | -12 | -0.3651 | -36.77 | -15.32 | 5 | -0.3263 |
| SCJU | 49.71 | 33.14 | -25 | -0.7543 | -28.73 | -11.97 | 20 | -1.671 |
| LUZH | 39.94 | 26.63 | 8 | 0.3755 | -33.4 | -13.92 | -8 | 0.7184 |
| [1] |
胡敏章, 郝洪涛, 李辉, 等. 2019. 地震分析预报的重力变化异常指标分析[J]. 中国地震, 35(3): 417-430.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
胡亚轩, 王雄. 2009. 应用形变和重力资料分析腾冲火山区岩浆的活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 31(4): 655-663. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2009.04.009.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [3] |
李大虎, 詹艳, 丁志峰, 等. 2021. 四川长宁 MS6.0 地震震区上地壳速度结构特征与孕震环境[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(1): 18-35.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
申重阳, 李辉, 孙少安, 等. 2009. 重力场动态变化与汶川 MS8.0 地震孕育过程[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(10): 2547-2557.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
申重阳, 祝意青, 胡敏章, 等. 2020. 中国大陆重力场时变监测与强震预测[J]. 中国地震, 36(4): 729-743.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
孙权, 裴顺平, 苏金蓉, 等. 2021. 2019年6月17日四川长宁 MS6.0 地震震源区三维速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(1): 36-53.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
王嘉沛, 张新林, 张毅, 等. 2022. 武汉九峰地震台重力变化与地壳垂直形变分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 47(6): 964-971.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
杨光亮, 申重阳, 吴桂桔, 等. 2015. 金川-芦山-犍为剖面重力异常和地壳密度结构特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(7): 2424-2435.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
杨文采, 施志群, 侯遵泽, 等. 2001. 离散小波变换与重力异常多重分解[J]. 地球物理学报, 44(4): 534-541.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
易桂喜, 龙锋, 梁明剑, 等. 2019. 2019 年 6 月 17 日四川长宁 MS6.0 地震序列震源机制解与发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 62(9): 3432-3447.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
张岳桥. 2020. 四川盆地南部地震区发震构造及其新构造背景[J]. 地质学报, 94(11): 3161-3177.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
张致伟, 程万正, 梁明剑, 等. 2012. 四川自贡-隆昌地区注水诱发地震研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(5): 1635-1645.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
祝意青, 李铁明, 郝明, 等. 2016. 2016年青海门源 MS6.4 地震前重力变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 59(10): 3744-3752.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
祝意青, 张勇, 张国庆, 等. 2020. 21世纪以来青藏高原大震前重力变化[J]. 科学通报, 65(7): 622-632.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
DOI URL |
| [16] |
DOI URL |
| [17] |
DOI URL |
| [18] |
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DOI URL |
| [20] |
DOI URL |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
DOI URL |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
PMID |
| [27] |
DOI URL |
| [28] |
DOI URL |
| [29] |
DOI |
| [30] |
PMID |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
DOI URL |
| [1] | 汪健, 张新林, 谈洪波, 胡敏章, 吴桂桔, 李忠亚, 张明辉. 木兰山重力基线场的初值测定及重力变化分析[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 553-569. |
| [2] | 郭树松, 祝意青, 徐云马, 刘芳, 赵云峰, 张国庆, 朱辉. 汶川地震前失稳过程的重力场观测证据[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1368-1380. |
| [3] | 汪健, 申重阳, 孙文科, 谈洪波, 胡敏章, 梁伟锋, 韩宇飞, 张新林, 吴桂桔, 王青华. 红河断裂带北、 中段近期重力变化及深部变形[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1537-1562. |
| [4] | 刘东, 郝洪涛, 王青华, 郑秋月, 黄江培. 2021年云南漾濞MS6.4地震前重力变化[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1157-1170. |
| [5] | 韦进, 郝洪涛, 韩宇飞, 胡敏章, 江颖, 刘子维. 基于连续重力台观测的玛多MS7.4地震的同震重力变化特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 984-998. |
| [6] | 张新林, 汪健, 胡敏章, 王嘉沛, 李忠亚, 张毅. 2010-2020年云南及周缘绝对重力变化特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 972-983. |
| [7] | 谈洪波, 王嘉沛, 杨光亮, 陈正松, 吴桂桔, 申重阳, 黄金水. 2021年玛多MS7.4地震的震后效应模拟[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 936-957. |
| [8] | 邹正波, 张毅, 谈洪波, 崔立鲁, 尹鹏, 吴桂桔. 利用重力卫星研究青海玛多及云南漾濞地震周边2002-2021年重力变化[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 999-1012. |
| [9] | 赵博, 高原, 刘杰, 梁姗姗. 四川长宁MS6.0地震震源干涉成像定位[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(6): 1474-1491. |
| [10] | 隗寿春, 祝意青, 赵云峰, 张松, 刘芳, 李瑞, 高铎文. 呼图壁MS6.2地震前后重力变化特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(4): 923-935. |
| [11] | 梁姗姗, 徐志国, 盛书中, 张广伟, 赵博, 邹立晔. 2019年四川长宁6.0级地震主震及中强余震(MS≥4.0)的震源机制及其应力场[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(3): 547-561. |
| [12] | 文翔, 周斌, 史水平, 覃坚, 李家宁, 何衍, 阎春恒, 罗远鹏. 桂西北地区近期重力与地壳形变综合分析[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(4): 927-943. |
| [13] | 姜磊, 徐志萍, 方盛明, 杨利普, 李怡青, 徐顺强. 利用重震资料研究豫北及邻区地壳结构特征与地震分布[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(2): 323-336. |
| [14] | 祝意青, 梁伟锋, 郝明, 赵凌强, 郝庆花, 张国庆, 刘练. 青藏高原东北缘近期重力与地壳形变综合分析与研究[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(4): 768-780. |
| [15] | 祝意青, 付广裕, 梁伟锋, 徐云马. 鲁甸MS6.5、芦山MS7.0、汶川MS8.0地震前区域重力场时变[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(1): 319-330. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||