地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1041-1056.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.05.001
魏传义1)( ), 尹功明1), 王旭龙2), 王度2,3), 姬昊1), 刘春茹1), 李新秀1)
), 尹功明1), 王旭龙2), 王度2,3), 姬昊1), 刘春茹1), 李新秀1)
收稿日期:2022-11-07
修回日期:2023-04-01
出版日期:2023-11-23
发布日期:2023-11-23
作者简介:魏传义, 男, 1990年生, 2019年于中国地质大学(武汉)获第四纪地质学博士学位, 副研究员, 主要从事第四纪年代学与地表过程研究, E-mail: chuanyiwei@ies.ac.cn。
基金资助:
WEI Chuan-yi1)( ), YIN Gong-ming1), WANG Xu-long2), WANG Duo2,3), JI Hao1), LIU Chun-ru1), LI Xin-xiu1)
), YIN Gong-ming1), WANG Xu-long2), WANG Duo2,3), JI Hao1), LIU Chun-ru1), LI Xin-xiu1)
Received:2022-11-07
Revised:2023-04-01
Online:2023-11-23
Published:2023-11-23
摘要:
第四纪碎屑沉积物是新构造运动和第四纪地质环境变化的重要信息载体。对第四纪碎屑沉积物, 尤其是对距今200ka以上不含火山灰的粗颗粒样品(如砾石堆积)进行测年, 一直是第四纪年代学研究中的重点和难点问题, 石英ESR测年法是能够直接测定这类样品的测年方法之一。但是, 将石英ESR法测年应用于早更新世沉积物(特别是粗颗粒沉积)结果的可靠性国内外至今鲜有报道, 是目前亟待解决的年代学问题之一。文中基于石英ESR法测年原理和前人的研究成果, 以已知年龄的下更新统靖远砾石层为研究对象, 探讨了早更新世砾石堆积石英ESR法测年的可靠性。结果显示: 1)靖远砾石层石英Ti-Li心在11 000Gy附加剂量范围内ESR信号未饱和, Al心在13 000Gy附加剂量范围内ESR信号未饱和; 2)单饱和指数函数和“指数+线性”函数可分别为Ti-Li心和Al心提供更优的等效剂量拟合结果, 且拟合效果均优于0.98; 3)靖远砾石层石英Ti-Li心和Al心的平均ESR测年结果分别为(1.67±0.15)Ma和(1.65±0.69)Ma, 与已知的宇生核素测年结果(约为(1.73±0.13)Ma)和岩石地层结果在误差范围内是一致的。综上所述, 石英Ti-Li心和Al心ESR法测年均可为早更新世含砂质透镜体的砾石层堆积提供可靠的年代学数据。
魏传义, 尹功明, 王旭龙, 王度, 姬昊, 刘春茹, 李新秀. 早更新世地层ESR法测年可靠性研究——以靖远剖面为例[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(5): 1041-1056.
WEI Chuan-yi, YIN Gong-ming, WANG Xu-long, WANG Duo, JI Hao, LIU Chun-ru, LI Xin-xiu. RELIABILITY EVALUATION OF QUARTZ ESR DATING METHOD ON EARLY PLEISTOCENE SEDIMENT: A CASE STUDY OF JINGYUAN SECTION[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(5): 1041-1056.
| 样品 编号 | 228U /Bg·kg-1 | 226Ra /Bg·kg-1 | 232Th /Bg·kg-1 | 40K /Bg·kg-1 | 含水量 /% | 剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | 等效剂量/Gy | 年龄/ka | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-Li心 | Al心 | Ti-Li心 | Al心 | |||||||||||
| SSE | DSE | SSE | EXP+LIN | SSE | DSE | SSE | EXP+LIN | |||||||
| JY01 | 12.45±5.60 | 17.88±0.51 | 20.83±0.51 | 367.30±12.47 | 10±3 | 1.7±0.22 | 2787±186 | 2787±197 | 6769±705 | 2781±1298 | 1639±109 | 1639±116 | 3982±415 | 1636±764 |
| JY02 | 27.02±6.59 | 24.05±0.62 | 27.19±0.62 | 419.44±14.17 | 10±3 | 2.13±0.24 | 3540±367 | 3540±389 | 6588±677 | 3631±1291 | 1662±172 | 1662±183 | 3093±318 | 1705±606 |
| JY04 | 25.78±7.31 | 27.91±0.71 | 29.57±0.67 | 412.57±14.11 | 10±3 | 2.07±0.24 | 3546±314 | 3546±331 | 6864±1212 | 3318±2270 | 1713±152 | 1713±160 | 3316±586 | 1603±1010 |
表 1 靖远砾石层石英Al心和Ti-Li心ESR测年结果
Table1 The quartz Al center and Ti-Li center ESR dating results of Jingyuan gravel layer
| 样品 编号 | 228U /Bg·kg-1 | 226Ra /Bg·kg-1 | 232Th /Bg·kg-1 | 40K /Bg·kg-1 | 含水量 /% | 剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | 等效剂量/Gy | 年龄/ka | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-Li心 | Al心 | Ti-Li心 | Al心 | |||||||||||
| SSE | DSE | SSE | EXP+LIN | SSE | DSE | SSE | EXP+LIN | |||||||
| JY01 | 12.45±5.60 | 17.88±0.51 | 20.83±0.51 | 367.30±12.47 | 10±3 | 1.7±0.22 | 2787±186 | 2787±197 | 6769±705 | 2781±1298 | 1639±109 | 1639±116 | 3982±415 | 1636±764 |
| JY02 | 27.02±6.59 | 24.05±0.62 | 27.19±0.62 | 419.44±14.17 | 10±3 | 2.13±0.24 | 3540±367 | 3540±389 | 6588±677 | 3631±1291 | 1662±172 | 1662±183 | 3093±318 | 1705±606 |
| JY04 | 25.78±7.31 | 27.91±0.71 | 29.57±0.67 | 412.57±14.11 | 10±3 | 2.07±0.24 | 3546±314 | 3546±331 | 6864±1212 | 3318±2270 | 1713±152 | 1713±160 | 3316±586 | 1603±1010 |
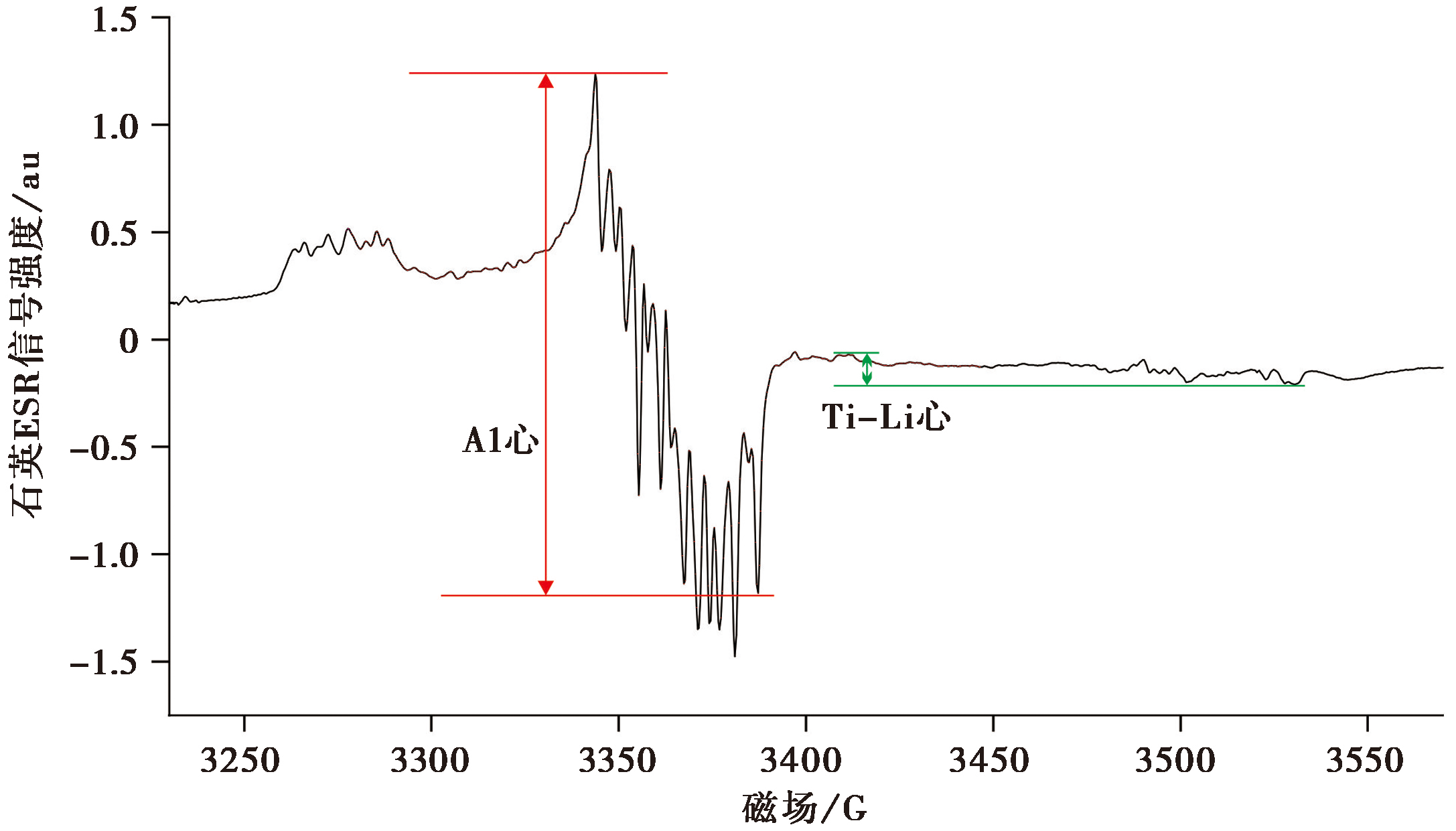
图2 靖远砾石层样品JY02(辐照剂量为4 116.5Gy)的石英低温Al心和Ti-Li心ESR信号谱图
Fig. 2 The Al center and Ti-Li center ESR spectrum at low temperature of sample JY02 collected from Jingyuan gravel layer.
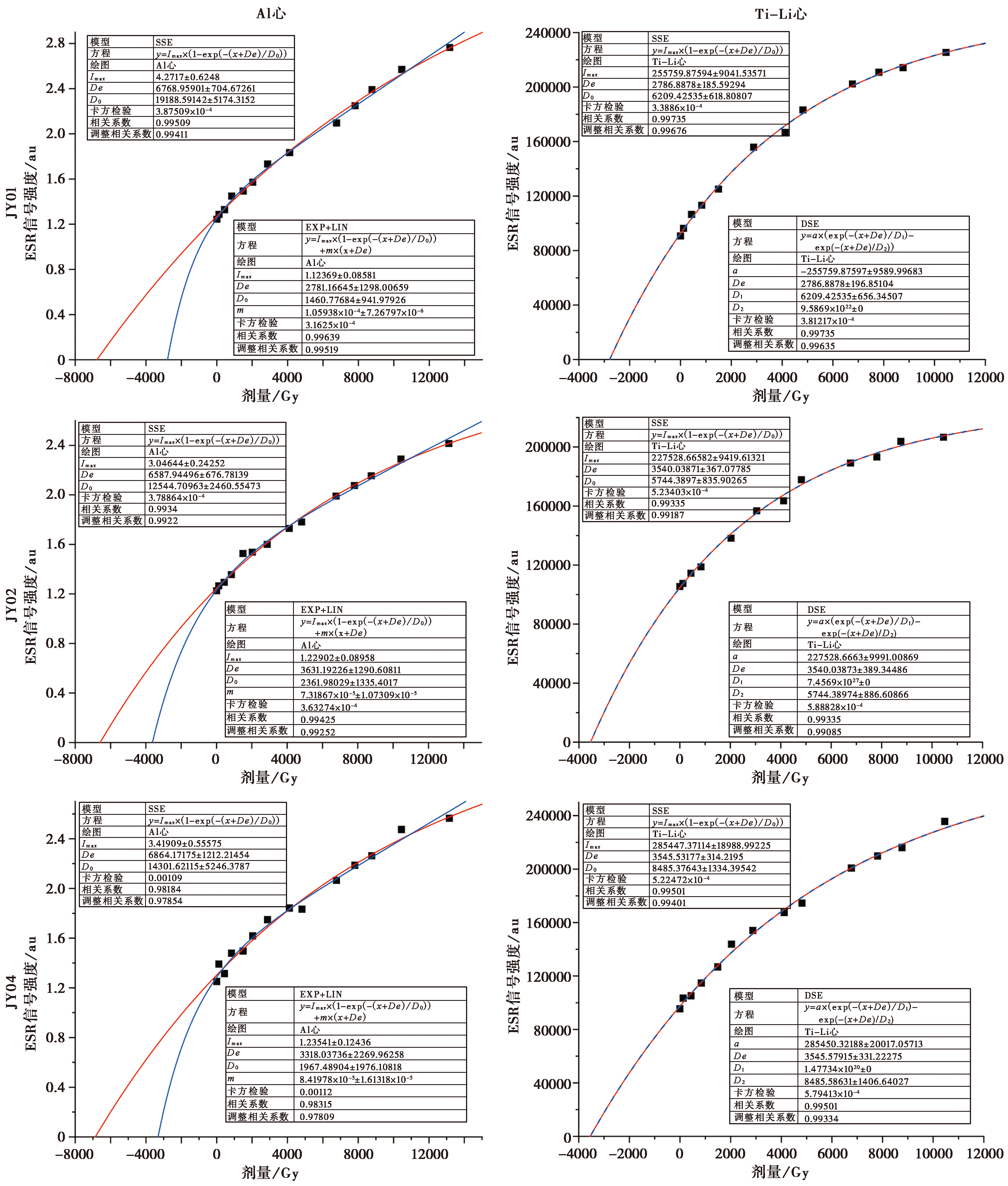
图3 靖远砾石层砂质透镜体石英Al心和Ti-Li心的附加剂量响应曲线
Fig. 3 Al center and Ti-Li center additional dose response curves of quartz collected from sand lens of Jingyuan gravel layer.
| [1] |
顾兆炎, 刘东生,
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
韩非. 2012. 电子自旋共振(ESR)测年方法在我国早更新世考古遗址年代学研究中的应用探索[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
韩非, 陈杰, 尹功明. 2015. 西域砾岩宇宙成因核素 26Al/10Be埋藏定年探索[J]. 第四纪研究, 35(1): 109—117.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
韩非, 顾兆炎, 尹功明, 等. 2016. 宇宙成因核素 26Al/10Be埋藏测年法在宁夏沙坡头黄河砾石阶地年代研究中的应用[J]. 第四纪研究, 36(5): 1216—1223.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
刘春茹, 尹功明, 高璐, 等. 2011. 第四纪沉积物ESR年代学研究进展[J]. 地震地质, 33(2): 490—498. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.02.022.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
魏传义. 2019. 石英ESR法在长江流域沉积物源示踪中的探讨及应用[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
魏传义. 2021. 晚新生代沉积物石英ESR法年代学研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
魏传义, 刘春茹, 李长安, 等. 2018. 石英不同Ti-Li 心电子自旋共振信号光晒退特征及其测年意义[J]. 地球环境学报, 9(6): 607—613.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
魏传义, 刘春茹, 李长安, 等. 2020. 宜昌砾石层石英Ti-Li 心 ESR 年龄及其对三峡贯通时限的指示[J]. 地震地质, 42(1): 65—78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.01.005.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
尹功明, 林敏. 2005. 沉积物电子自旋共振测年现状[J]. 核技术, 28(5): 399—402.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
DOI URL |
| [12] |
DOI URL |
| [13] |
DOI URL |
| [14] |
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DOI URL |
| [16] |
DOI URL |
| [17] |
DOI URL |
| [18] |
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DOI |
| [20] |
DOI URL |
| [21] |
DOI URL |
| [22] |
DOI URL |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
DOI URL |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
DOI URL |
| [29] |
DOI URL |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
DOI URL |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
DOI URL |
| [34] |
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] |
DOI URL |
| [36] |
DOI URL |
| [37] |
DOI |
| [38] |
DOI |
| [39] |
DOI URL |
| [40] |
PMID |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
DOI URL |
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
DOI URL |
| [46] |
DOI URL |
| [47] |
DOI URL |
| [48] |
DOI URL |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
DOI URL |
| [51] |
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张明洋, 杨晓松. 蒙脱石的弹性性质实验[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(5): 1229-1239. |
| [2] | 魏传义, 刘春茹, 李长安, 尹功明, 韩非, 张岱, 李亚伟, 张玉芬. 宜昌砾石层石英Ti-Li心ESR年龄及其对三峡贯通时限的指示[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(1): 65-78. |
| [3] | 路珍, 何昌荣. 软弱成分层对断层泥强度的影响[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(1): 68-80. |
| [4] | 戴训也, 沈军, 吴传勇, 杨会丽. 新疆阜康断裂带中段大黄山探槽晚第四纪沉积物的光释光测年[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(4): 1053-1063. |
| [5] | 张进, 李岩峰, 肖文霞. 一种雁行石英脉体的形成及构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2012, (4): 684-695. |
| [6] | 杨会丽, 陈杰, 刘进峰, 余松. 2008年汶川地震相关堆积物的细颗粒石英光释光测年研究[J]. 地震地质, 2011, 33(2): 413-420. |
| [7] | 郑荣章, 陈桂华, 徐锡伟, 李建平. 原地宇宙成因核素测年中石英样品分离提纯的几组实验对比[J]. 地震地质, 2010, 32(2): 303-311. |
| [8] | 纪洪磊, 赵华, 王成敏, 毛洪亮, 卢演俦. 水成沉积物回授光释光测年可行性初探[J]. 地震地质, 2010, 32(2): 320-326. |
| [9] | 康树刚, 卢演俦, 王旭龙, 杜金花. 黄土细颗粒石英光释光测年中预热温度选取的简易方法[J]. 地震地质, 2009, 31(3): 544-550. |
| [10] | 张秉良, 刘瑞珣, 向宏发, 楚全芝, 黄雄南, 郑勇刚. 红河断裂带中南段糜棱岩分形特征及主要流变参数的估算[J]. 地震地质, 2008, 30(2): 473-483. |
| [11] | 杨传成, 陈杰, 张克旗, 刘进峰, 王昌盛, 雷生学. 水成相沉积物细颗粒石英光释光综合生长曲线的建立与应用[J]. 地震地质, 2007, 29(2): 402-411. |
| [12] | 张克旗, 陈杰, 刘进峰, 尹金辉, 王昌盛, 王同利. 海原断裂带刺儿沟剖面烘烤次生黄土的光释光测年及其地质意义[J]. 地震地质, 2007, 29(2): 390-401. |
| [13] | 王旭龙, 卢演俦, 李晓妮. 细颗粒石英光释光测年:简单多片再生法[J]. 地震地质, 2005, 27(4): 615-623. |
| [14] | 王昌盛, 陈杰, 张克旗. 西南天山明尧勒背斜河流阶地沉积物的光释光测年[J]. 地震地质, 2005, 27(4): 586-598. |
| [15] | 周永胜, 何昌荣, 马胜利, 马瑾. 差应力在超高压变质岩形成过程中的作用——来自石英-柯石英转化的高温高压实验证据[J]. 地震地质, 2003, 25(4): 566-573. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||