地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1129-1146.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.05.006
刘金钊1,2)( ), 梁星辉2),*(
), 梁星辉2),*( ), 叶周润3), 陈兆辉1), 胡敏章4), 韩宇飞5), 王青华6), 刘东6), 郝洪涛4), 张双喜1), 陈铭1)
), 叶周润3), 陈兆辉1), 胡敏章4), 韩宇飞5), 王青华6), 刘东6), 郝洪涛4), 张双喜1), 陈铭1)
收稿日期:2022-12-26
修回日期:2023-05-31
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2023-11-23
通讯作者:
梁星辉, 男, 1983年生, 博士, 副研究员, 主要从事动态重力测量的理论、 方法与应用研究, E-mail: 作者简介:刘金钊, 男, 1986年生, 2015年于中国科学院测量与物理研究所获大地测量学与测量工程专业博士学位, 副研究员, 主要从事重力测量、 建模及应用方面的研究, E-mail: whiggliujinzhao@126.com。
基金资助:
LIU Jin-zhao1,2)( ), LIANG Xing-hui2),*(
), LIANG Xing-hui2),*( ), YE Zhou-run3), CHEN Zhao-hui1), HU Min-zhang4), HAN Yu-fei5), WANG Qing-hua6), LIU Dong6), HAO Hong-tao4), ZHANG Shuang-xi1), CHEN Ming1)
), YE Zhou-run3), CHEN Zhao-hui1), HU Min-zhang4), HAN Yu-fei5), WANG Qing-hua6), LIU Dong6), HAO Hong-tao4), ZHANG Shuang-xi1), CHEN Ming1)
Received:2022-12-26
Revised:2023-05-31
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2023-11-23
摘要:
文中推导并给出了基于非格网分布的起伏面扰动重力或重力异常解算区域扰动重力梯度场模型的数值计算公式。基于澳大利亚West Arnhem Land地区的格网重力数据, 以频谱域(二维快速傅里叶变换)解算的扰动重力梯度全张量作为“基准值”, 然后利用基于推导公式的最小二乘配置方法(LSC)对相同区域非规则范围的重力数据进行扰动重力梯度模型解算, 将结果作为“评估值”。对比“基准值”与“评估值”之差, 研究发现: 1)基于推导公式的最小二乘配置方法解算得到的扰动重力梯度值与频谱域方法得到扰动梯度“基准值”各分量在空间形变变化上是一致的; 2)统计扰动重力梯度各分量的差值 “基准值”与“评估值”差值的标准差分别为5.54E、 5.30E、 1.85E、 6.55E、 2.09E和9.67E(1E=1×10-9s-2), 远低于国际上实测重力梯度与解算模型差值的研究结果。最后, 基于云南地区实测地表差分重力值, 文中首次给出了该区域半波长约20km的重力梯度场年际变化模型。文中的思路和方法提高了广泛分布的重力数据(主要为重力异常和扰动重力)的使用效率, 可为地球物理学、 地质学研究更好地理解和解释重力数据、 重力梯度数据及其与场源的关系提供数据基础。
刘金钊, 梁星辉, 叶周润, 陈兆辉, 胡敏章, 韩宇飞, 王青华, 刘东, 郝洪涛, 张双喜, 陈铭. 考虑地表起伏的不规则区域重力梯度场模型构建方法——以云南地区为例[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(5): 1129-1146.
LIU Jin-zhao, LIANG Xing-hui, YE Zhou-run, CHEN Zhao-hui, HU Min-zhang, HAN Yu-fei, WANG Qing-hua, LIU Dong, HAO Hong-tao, ZHANG Shuang-xi, CHEN Ming. STUDY ON THE REGIONAL GRAVITY GRADIENT FIELD MODELING IN IRREGULAR AREA WITH CONSIDERATION OF SURFACE FLUCTUATION: A CASE STUDY OF YUNNAN PROVINCE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(5): 1129-1146.
| 起始经度 | 起始纬度 | 终止经度 | 终止纬度 | 经向 点数 | 纬向 点数 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 分辨率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 132.96443484° | -12.7732721555° | 133.78443484° | -12.2532721555° | 42 | 27 | 27.59mGal | 75.85mGal | 0.02° |
表1 自由空气重力异常统计
Table 1 Statistics of free air gravity anomaly
| 起始经度 | 起始纬度 | 终止经度 | 终止纬度 | 经向 点数 | 纬向 点数 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 分辨率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 132.96443484° | -12.7732721555° | 133.78443484° | -12.2532721555° | 42 | 27 | 27.59mGal | 75.85mGal | 0.02° |

图1 西澳地区自由空气重力异常及相应频谱方法解算的重力梯度全张量 a 扰动重力梯度δΓxx; b 扰动重力梯度δΓxy; c 扰动重力梯度δΓxz; d 扰动重力梯度δΓyy; e 扰动重力梯度δΓyz; f 扰动重力梯度δΓzz; g 重力异常Δg
Fig. 1 Free air gravity anomalies and the FFT-derived full tensor of gravity gradient of western Australia.
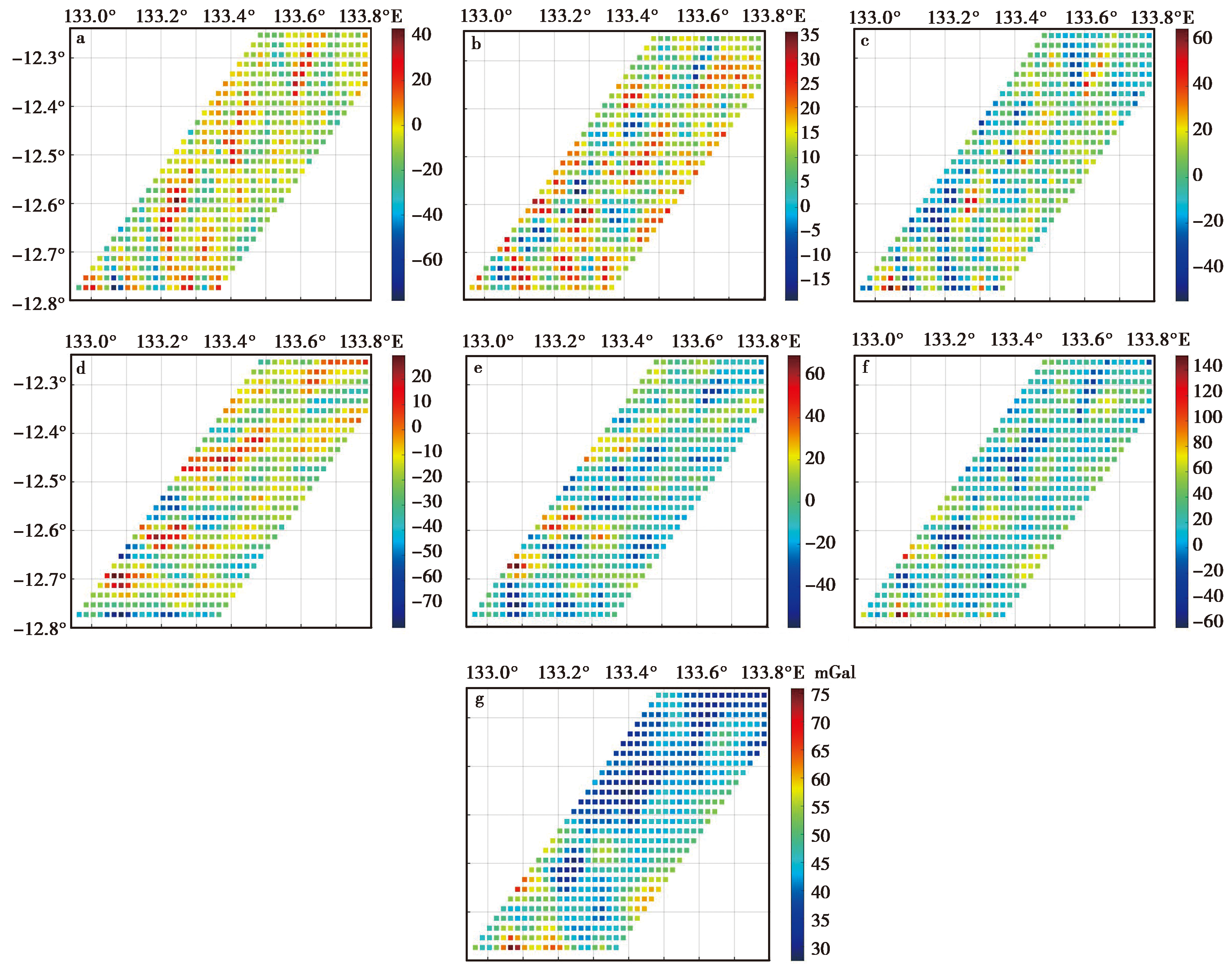
图2 西澳地区裁剪得到的自由空气重力异常及重力梯度全张量 a 扰动重力梯度δΓxx; b 扰动重力梯度δΓxy; c 扰动重力梯度δΓxz; d 扰动重力梯度δΓyy; e 扰动重力梯度δΓyz; f 扰动重力梯度δΓzz; g 重力异常Δg
Fig. 2 Tailored free air gravity anomalies and the full tensor of gravity gradients tailored of western Australia.
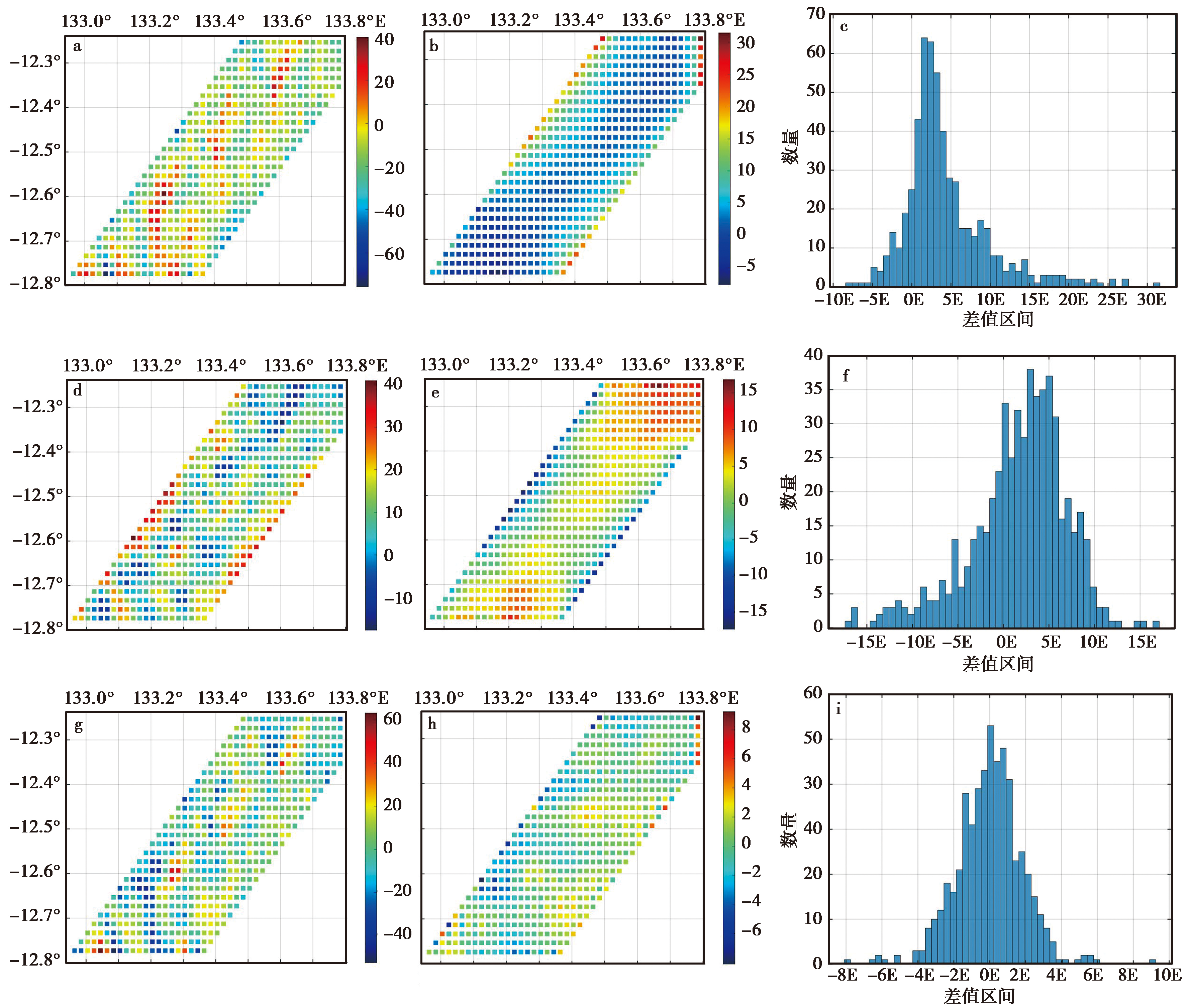
图3 基于推导公式的最小二乘配置方法与频谱方法解算的重力梯度扰动结果的比较(δΓxx, δΓxy, δΓxz分量) a 解算的扰动重力梯度δ Γ x x l s c; b 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ x x f f t-δ Γ x x l s c; c 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ x x f f t-δ Γ x x l s c的直方图; d 解算的扰动重力梯度δ Γ x y l s c; e 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ x y f f t-δ Γ x y l s c; f 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ x y f f t-δ Γ x y l s c的直方图; g 解算的扰动重力梯度δ Γ x z l s c; h 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ x z f f t-δ Γ x z l s c; i 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ x z f f t-δ Γ x z l s c的直方图
Fig. 3 Comparison of LSC-derived gravity gradient and FFT-derived gravity gradient(component δΓxx, δΓxy, δΓxz).
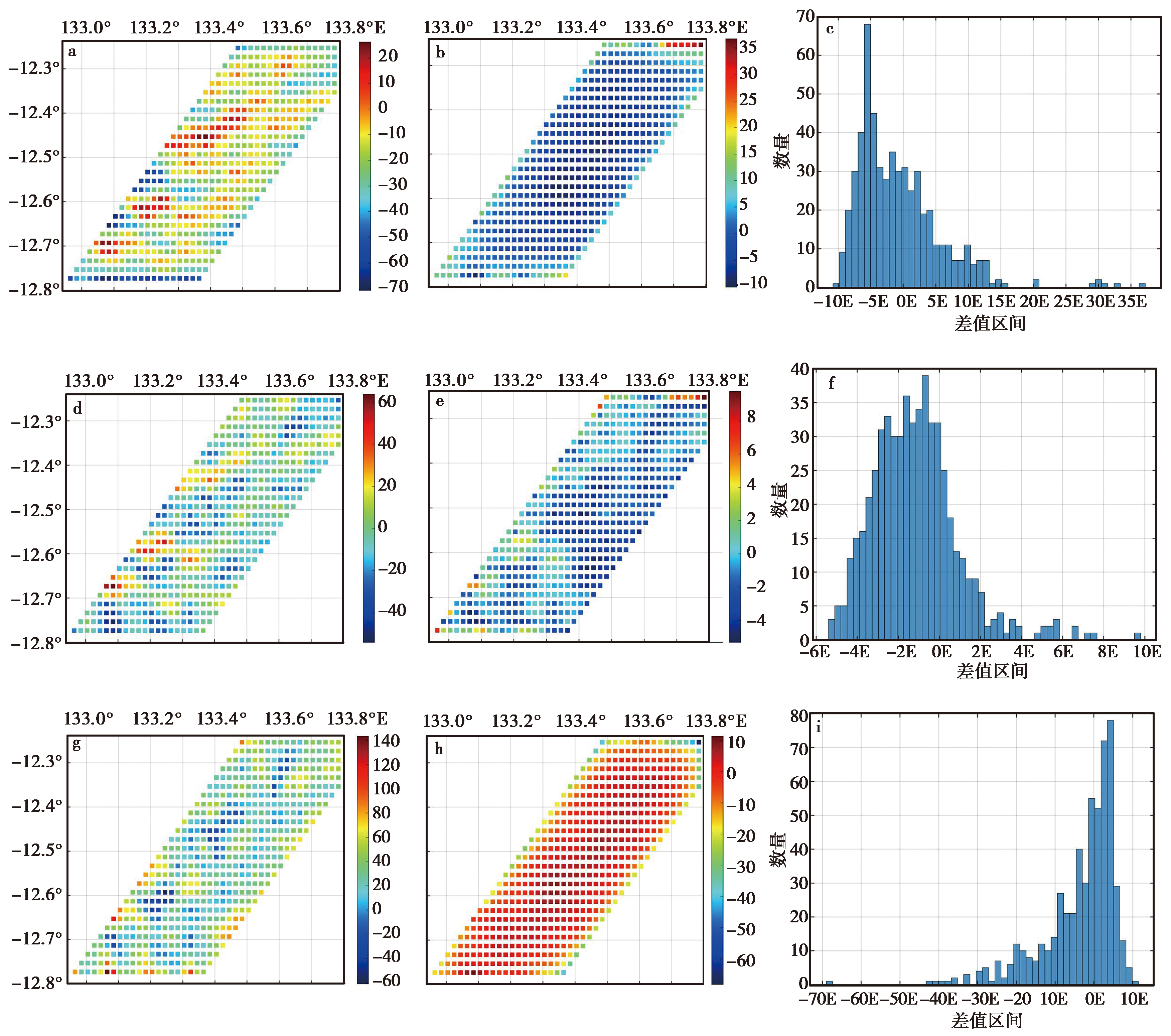
图4 协方差函数-最小二乘配置与频谱方法解算的重力梯度结果的比较(δΓyy、 δΓyz、 δΓzz分量) a 解算的扰动重力梯度δ Γ y y l s c; b 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ y y f f t-δ Γ y y l s c; c 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ y y f f t-δ Γ y y l s c的直方图; d 解算的扰动重力梯度δ Γ y z l s c; e 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ y z f f t-δ Γ y z l s c; f 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ y z f f t-δ Γ y z l s c的直方图; g 解算的扰动重力梯度δ Γ z z l s c; h 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ z z f f t-δ Γ z z l s c; i 扰动重力梯度差值δ Γ z z f f t-δ Γ z z l s c的直方图
Fig. 4 Comparison of lsc-derived gravity gradient and FFT-derived gravity gradient(component δΓyy, δΓyz, δΓzz).
| 差值 | 最大值/E | 最小值/E | 平均值/E | 标准差/E |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ -δ | 31.53 | -7.73 | 4.42 | 5.54 |
| δ -δ | 16.76 | -17.12 | 1.66 | 5.30 |
| δ -δ | 9.23 | -8.09 | -0.004 | 1.85 |
| δ -δ | 36.76 | -10.09 | -0.73 | 6.55 |
| δ -δ | 9.77 | -5.33 | -1.16 | 2.09 |
| δ -δ | 11.32 | -68.22 | -3.54 | 9.67 |
表2 基于推导公式的最小二乘配置方法与频谱域方法解算重力梯度结果的差值统计(1E=1×10-9s-2)
Table 2 The statistical difference of calculated gravity gradient between LSC method and FFT method(1E=1×10-9s-2)
| 差值 | 最大值/E | 最小值/E | 平均值/E | 标准差/E |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ -δ | 31.53 | -7.73 | 4.42 | 5.54 |
| δ -δ | 16.76 | -17.12 | 1.66 | 5.30 |
| δ -δ | 9.23 | -8.09 | -0.004 | 1.85 |
| δ -δ | 36.76 | -10.09 | -0.73 | 6.55 |
| δ -δ | 9.77 | -5.33 | -1.16 | 2.09 |
| δ -δ | 11.32 | -68.22 | -3.54 | 9.67 |
| 绝对重力测点数 | 相对重力点数 | 相对重力测段数 | 相对重力仪编号及格值参数 | 点值精度平均值 | 观测年月 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 249 | 274 | CG5-C169, 1.000089 | 7.80 | 2020-03 |
| CG5-C170, 0.999928 | |||||
| 9 | 249 | 274 | CG5-C169, 1.000089 | 10.30 | 2021-03 |
| CG5-C170, 0.999928 |
表3 研究区域测网的重力数据、 仪器参数及平差后的结果统计(单位: μGal)
Table 3 Statistics of the survey points, instrument parameters and gravity data after adjustment of regional survey network(Unit:μGal)
| 绝对重力测点数 | 相对重力点数 | 相对重力测段数 | 相对重力仪编号及格值参数 | 点值精度平均值 | 观测年月 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 249 | 274 | CG5-C169, 1.000089 | 7.80 | 2020-03 |
| CG5-C170, 0.999928 | |||||
| 9 | 249 | 274 | CG5-C169, 1.000089 | 10.30 | 2021-03 |
| CG5-C170, 0.999928 |
| 数据类型 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 标准差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 测点高程/m | 3330.00 | 0.00 | 1574.00 | 584.08 |
| 重力变化/μGal | 30.69 | -48.70 | -10.27 | 14.78 |
表4 研究区域测点的高程分布及重力值变化统计
Table 4 The statistics of elevation distribution of survey points and gravity variation in the study area
| 数据类型 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 标准差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 测点高程/m | 3330.00 | 0.00 | 1574.00 | 584.08 |
| 重力变化/μGal | 30.69 | -48.70 | -10.27 | 14.78 |

图7 基于推导公式的最小二乘配置方法解算的云南地区地表重力梯度年度变化模型(2020年3月—2021年3月)
Fig. 7 Annual variation model of surface gravity gradient in Yunnan province by using the least squares configuration method based on the derived data from Mar. 2020 to Mar. 2021.
| 重力梯度年度变化 | 最大值/E | 最小值/E | 平均值/E | 标准差/E |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔΓxx | 52.36 | -76.26 | 2.91 | 15.57 |
| ΔΓxy | 78.75 | -42.00 | 0.47 | 11.79 |
| ΔΓxz | 74.59 | -89.26 | -2.62 | 22.09 |
| ΔΓyy | 49.36 | -67.62 | 2.64 | 13.61 |
| ΔΓyz | 82.68 | -2.27 | -4.92 | 31.99 |
| ΔΓzz | 64.65 | -49.35 | -5.55 | 17.23 |
表5 研究区域地表重力梯度年度变化模型量值统计(1E=1×10-9s-2)
Table 5 Statistics of the annual variation of surface gravity gradient model in the study area(1E=1×10-9s-2)
| 重力梯度年度变化 | 最大值/E | 最小值/E | 平均值/E | 标准差/E |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔΓxx | 52.36 | -76.26 | 2.91 | 15.57 |
| ΔΓxy | 78.75 | -42.00 | 0.47 | 11.79 |
| ΔΓxz | 74.59 | -89.26 | -2.62 | 22.09 |
| ΔΓyy | 49.36 | -67.62 | 2.64 | 13.61 |
| ΔΓyz | 82.68 | -2.27 | -4.92 | 31.99 |
| ΔΓzz | 64.65 | -49.35 | -5.55 | 17.23 |
| [1] |
韩宇飞, 汪健, 徐如刚, 等. 2020. 陆态网络重力测网的分形特征与地震监测能力分析[J]. 中国地震, 36(4): 879—887.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
胡敏章, 郝洪涛, 韩宇飞, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多 MS7.4 地震的重力挠曲均衡背景与震前重力变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(9): 3135—3149.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
刘东, 郝洪涛, 王青华, 等. 2021. 2021年云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震前重力变化[J]. 地震地质, 43(5): 1157—1170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.05.008.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
刘繁明, 张迎发, 荆心, 等. 2013. 基于余弦变换的重力梯度Parker正演方法及其应用[J]. 测绘学报, 42(2): 177—183, 190.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
刘金钊, 梁星辉, 叶周润, 等. 2020. 融合多源数据构建区域航空重力梯度扰动全张量[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(8): 3131—3143.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
刘金钊, 柳林涛, 梁星辉, 等. 2013. 基于实测重力异常和地形数据确定重力梯度的研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(7): 2245—2256.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
刘金钊, 柳林涛, 梁星辉, 等. 2015. 利用重力异常数据构建重力梯度场的方法比较[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 40(12): 1677—1682.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
刘金钊, 王岩, 高春春, 等. 2018. 航空重力梯度数据的模拟退火参数反演[J]. 测绘科学, 43(8): 7—13.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
马国庆, 黄大年, 于平, 等. 2012. 改进的均衡滤波器在位场数据边界识别中的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(12): 4288—4295.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
宋宏伟. 2017. 基于冷原子干涉仪的重力梯度精密测量研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
王青华, 郝洪涛, 汪健, 等. 2019. 云南地震流动重力监测网建设与映震能力分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 39(3): 317—324.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
周文月, 陈昌昕, 侯振隆, 等. 2018. 不同高度数据联合欧拉反褶积法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(8): 3400—3409.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
周文月, 马国庆, 侯振隆, 等. 2017. 重力全张量数据联合欧拉反褶积法研究及应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(12): 4855—4865.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DOI URL |
| [16] |
DOI URL |
| [17] |
DOI URL |
| [18] |
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DOI URL |
| [20] |
DOI URL |
| [21] |
DOI |
| [22] |
DOI URL |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
DOI URL |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
DOI URL |
| [27] |
DOI URL |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
DOI |
| [31] |
DOI URL |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
DOI URL |
| [34] |
|
| [1] | 孙业君, 赵小艳, 黄耘, 杨浩, 李锋. 云南地区震源机制及应力场特征[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(2): 390-407. |
| [2] | 皇甫岗, 苏有锦, 张建国. 缅甸孟帕亚7.2级地震及其对云南强震活动趋势的意义[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(3): 598-608. |
| [3] | 钱晓东, 秦嘉政, 刘丽芳. 云南地区现代构造应力场研究[J]. 地震地质, 2011, 33(1): 91-106. |
| [4] | 皇甫岗, 秦嘉政. 云南地区大震活动规律研究[J]. 地震地质, 2006, 28(1): 37-47. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||