地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1400-1418.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.06.009
徐志萍1)( ), 刘巧霞1),*(
), 刘巧霞1),*( ), 刘志1), 田晓峰1), 王夫运1), 段永红1), 林吉焱1), 邱勇1), 唐淋2)
), 刘志1), 田晓峰1), 王夫运1), 段永红1), 林吉焱1), 邱勇1), 唐淋2)
收稿日期:2023-01-30
修回日期:2023-07-06
出版日期:2023-12-20
发布日期:2024-01-16
通讯作者:
刘巧霞, 女, 1983年生, 副研究员, 主要从事台阵地震学方法及应用研究, E-mail: 作者简介:徐志萍, 女, 1987年生, 2012年于中国地质大学(武汉)获地球探测与信息技术专业硕士学位, 高级工程师, 主要研究方向为地壳深浅结构与构造, E-mail: xuzp@gec.ac.cn。
基金资助:
XU Zhi-ping1)( ), LIU Qiao-xia1),*(
), LIU Qiao-xia1),*( ), LIU Zhi1), TIAN Xiao-feng1), WANG Fu-yun1), DUAN Yong-hong1), LIN Ji-yan1), QIU Yong1), TANG Lin2)
), LIU Zhi1), TIAN Xiao-feng1), WANG Fu-yun1), DUAN Yong-hong1), LIN Ji-yan1), QIU Yong1), TANG Lin2)
Received:2023-01-30
Revised:2023-07-06
Online:2023-12-20
Published:2024-01-16
摘要:
龙门山断裂带南段芦山地区先后发生了2013年芦山 MS7.0 和2022年芦山 MS6.1 地震, 2次强震的孕育发生与所在区域深、 浅地震构造环境、 地壳物性结构参数密切相关。研究该区地壳浅部物性结构特征及其与深部动力学过程的映射关系对认识该区的孕震环境具有重要意义。因此, 文中利用金川—芦山—乐山深地震测深剖面资料的P波、 S波初至波走时数据, 采用二维射线追踪走时反演方法获取了沿剖面上地壳的精细P波、 S波速度和泊松比值。结果显示: 剖面西北段松潘-甘孜块体的上地壳具有高P波、 S波速度和低泊松比的特征, 而东南段的四川盆地上地壳具有低P波、 S波速度和高泊松比的特征。在松潘-甘孜块体和四川盆地之间的龙门山构造带, 上地壳P波、 S波速度和泊松比等值线形态受区域构造活动控制, 与地层产状基本一致, 呈近直立趋势展布。龙门山构造带下方沉积基底表现出明显的结构差异, 且速度和泊松比等值线形成“V”形特征。龙门山断裂带的上地壳速度、 泊松比横向变化梯度大, 可能是印度板块和欧亚板块碰撞的远程效应使得青藏高原东缘低泊松比地壳向坚硬的扬子地台(高泊松比)挤压, 进而产生地壳垂向变形的直接证据。芦山强震区 MS7.0 地震的余震主要发生在壳内高、 低速和泊松比变化梯级带偏高速和低泊松比的一侧, 该区的地震活动既受区域断裂构造的控制, 也与上地壳的物性结构特征密切相关。
徐志萍, 刘巧霞, 刘志, 田晓峰, 王夫运, 段永红, 林吉焱, 邱勇, 唐淋. 芦山强震区上地壳速度和泊松比分布特征及其动力学意义[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(6): 1400-1418.
XU Zhi-ping, LIU Qiao-xia, LIU Zhi, TIAN Xiao-feng, WANG Fu-yun, DUAN Yong-hong, LIN Ji-yan, QIU Yong, TANG Lin. DISTRIBUTION CHARACTERISTICS AND DYNAMIC SIGNIFICANCE OF UPPER CRUST VELOCITY AND POISSON’S RATIO IN LUSHAN STRONG EARTHQUAKE AREA[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(6): 1400-1418.
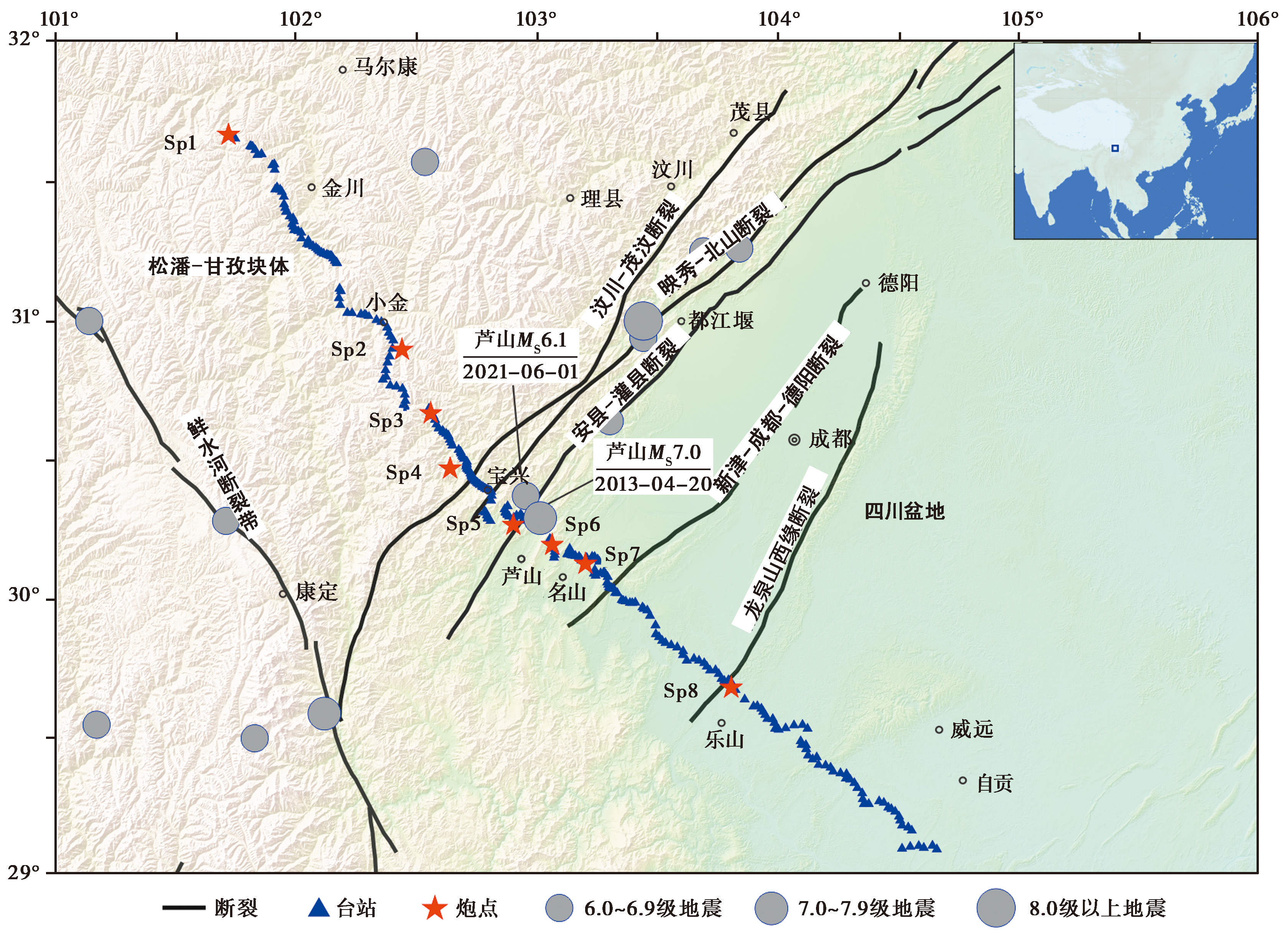
图1 深地震测深探测剖面的位置(断裂引自邓起东等, 2003)
Fig. 1 The location of wide angle reflection/refraction profile (The faults are quoted from DENG Qi-dong et al., 2003).
| 炮点编号 | 桩号 /km | 炮点坐标 | 药量 /kg | 岩性 | 炮点地名 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东经 | 北纬 | |||||||||
| Sp1 | 450.71 | 101°43.09' | 31°39.85' | 3504 | 花岗岩 | 四川阿坝金川太阳河乡且斯都村 | ||||
| Sp2 | 342.54 | 102°26.27' | 30°53.84' | 1512 | 砾石 | 四川阿坝州小金县美沃乡双河村 | ||||
| Sp3 | 317.31 | 102°33.45' | 30°40.20' | 1992 | 基岩 | 四川雅安市宝兴县永富乡中岗村 | ||||
| Sp4 | 297.44 | 102°38.28' | 30°28.27' | 1200 | 基岩 | 四川省雅安市宝兴县隆东乡电厂 | ||||
| Sp5 | 263.73 | 102°54.04' | 30°16.12' | 1512 | 基岩 | 四川雅安市芦山县双石镇 | ||||
| Sp6 | 246.55 | 103°03.70' | 30°11.76' | 1008 | 基岩 | 四川雅安市雨城区上里镇治安村 | ||||
| Sp7 | 231.56 | 103°12.01' | 30°07.69' | 2496 | 风化基岩 | 四川雅安市名山县车岭镇古城村 | ||||
| Sp8 | 154.85 | 103°48.35' | 29°40.80' | 2808 | 风化基岩 | 四川乐山市市中区关庙乡板桥村 | ||||
表1 炮点参数一览表
Table1 List of shot point parameters
| 炮点编号 | 桩号 /km | 炮点坐标 | 药量 /kg | 岩性 | 炮点地名 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东经 | 北纬 | |||||||||
| Sp1 | 450.71 | 101°43.09' | 31°39.85' | 3504 | 花岗岩 | 四川阿坝金川太阳河乡且斯都村 | ||||
| Sp2 | 342.54 | 102°26.27' | 30°53.84' | 1512 | 砾石 | 四川阿坝州小金县美沃乡双河村 | ||||
| Sp3 | 317.31 | 102°33.45' | 30°40.20' | 1992 | 基岩 | 四川雅安市宝兴县永富乡中岗村 | ||||
| Sp4 | 297.44 | 102°38.28' | 30°28.27' | 1200 | 基岩 | 四川省雅安市宝兴县隆东乡电厂 | ||||
| Sp5 | 263.73 | 102°54.04' | 30°16.12' | 1512 | 基岩 | 四川雅安市芦山县双石镇 | ||||
| Sp6 | 246.55 | 103°03.70' | 30°11.76' | 1008 | 基岩 | 四川雅安市雨城区上里镇治安村 | ||||
| Sp7 | 231.56 | 103°12.01' | 30°07.69' | 2496 | 风化基岩 | 四川雅安市名山县车岭镇古城村 | ||||
| Sp8 | 154.85 | 103°48.35' | 29°40.80' | 2808 | 风化基岩 | 四川乐山市市中区关庙乡板桥村 | ||||
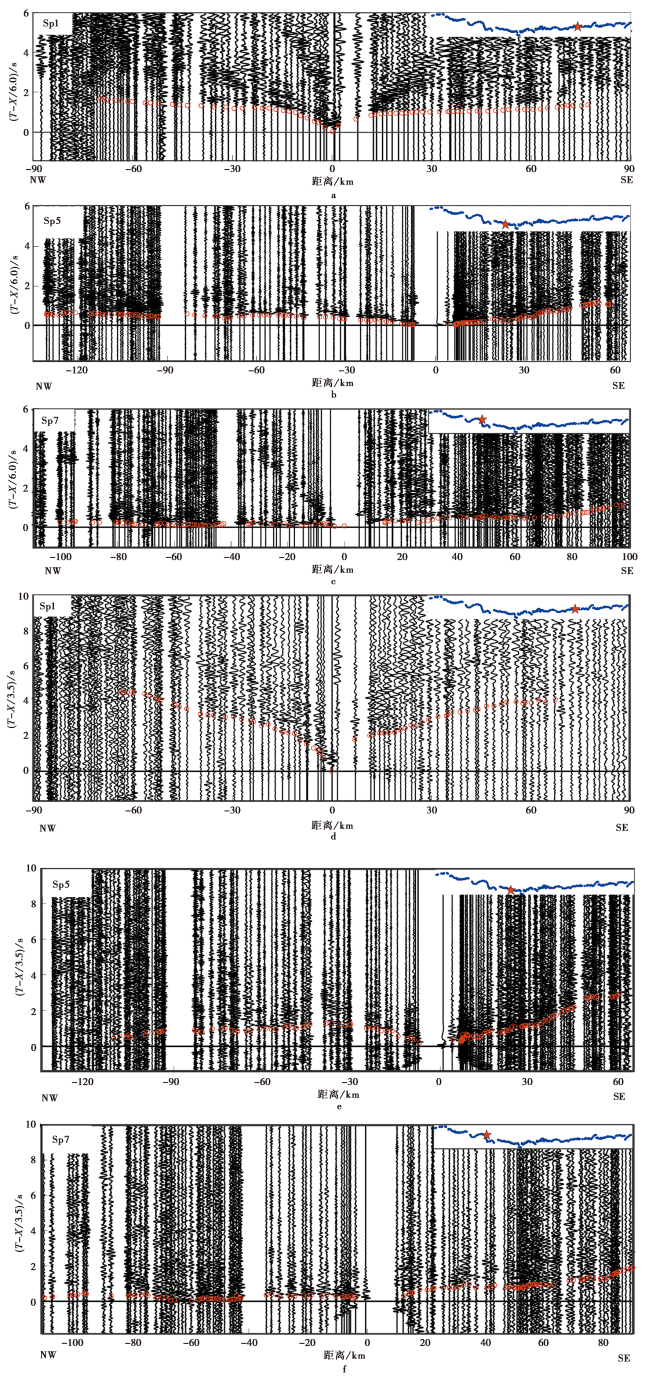
图3 部分炮点记录的截面图 a Sp1炮点的P波记录截面; b Sp5炮点的P波记录截面; c Sp7炮点的P波记录截面; d Sp1炮点的S波记录截面图; e Sp5炮点的S波记录截面图; f Sp7炮点的S波记录截面图。图中红圈为拾取的Pg、 Sg震相
Fig. 3 Section of observed seismogram from shot.
| [1] | |
|
|
|
| [2] |
邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2003. 中国活动构造与地震活动[J]. 地学前缘, 10(S1): 66—73.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
冯杨洋, 于常青, 范柱国, 等. 2016. 从反射地震剖面中认识芦山地区的地壳精细结构和构造[J]. 地球物理学报, 59(9): 3248—3259.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [4] |
戈革, 董敏煜. 1983. 地震波动力学基础[M]. 北京: 工业出版社:65—67.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
胡健民, 孟庆任, 石玉若, 等. 2005. 松潘-甘孜地体内花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 21(3): 867—880.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
嵇少丞, 王茜, 王勤, 等. 2007. 苏鲁-大别超高压变质岩的弹性力学性质与密度的关系[J]. 岩石学报, 23(12): 3054—3064.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
嵇少丞, 王茜, 杨文采. 2009. 华北克拉通泊松比与地壳厚度的关系及其大地构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 83(3): 324—330.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
嘉世旭, 刘保金, 徐朝繁, 等. 2014. 龙门山中段及两侧地壳结构与汶川地震构造[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 44(3): 497—509.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
嘉世旭, 刘昌铨. 1995. 华北地区人工地震测深震相与地壳结构研究[J]. 地震地质, 17(2): 97—105.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
李国玉, 吕鸣岗, 张健, 等. 2002. 中国含油气盆地图集[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社:185—194.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
林吉焱, 唐国彬, 徐涛, 等. 2020. 钦杭—武夷山成矿带上地壳速度结构与基底特征: 万载—惠安宽角反射/折射地震剖面约束[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(12): 4396—4409.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
刘保金, 张先康, 酆少英, 等. 2009. 龙门山山前彭州隐伏断裂高分辨率地震反射剖面[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(2): 538—546.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
刘巧霞, 朱介寿, 曹俊兴, 等. 2010. 汶川 MS8.0 地震余震重新定位及其空间分布特征研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 30(4): 736—744.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
鲁人齐, 房立华, 郭志, 等. 2022. 2022年6月1日四川芦山 MS6.1 强震构造精细特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 65(11): 4299—4310.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
鲁人齐, 徐锡伟, 何登发, 等. 2017. 龙门山南段芦山震区浅层沉积与构造变形: 对深部发震构造的约束[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(8): 2924—2934.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [16] |
马丽芳. 2002. 中国地质图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
宋春彦, 刘顺, 何利. 2009. 龙门山南段构造变形及应力序列[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 33(3): 334—342.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
苏金蓉, 郑钰, 杨建思, 等. 2013. 2013年4月20日四川芦山M7.0地震与余震精确定位及发震构造初探[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(8): 2636—2644.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
孙茁, 吴建平, 房立华, 等. 2014. 利用sPn震相测定芦山 MS7.0 地震余震的震源深度[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(2): 430—440.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
唐新功, 尤双双, 胡文宝, 等. 2012. 龙门山断裂带地壳密度结构[J]. 地震地质, 34(1): 28—38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.01.004.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
田晓峰, 熊伟, 王夫运, 等. 2020. 京津地区顺义—塘沽高分辨地震折射剖面的走时成像结果及其揭示的上地壳断裂构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 42(2): 414—434. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.02.011.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
王椿镛, 楼海, 姚志祥, 等. 2010. 龙门山及其邻区的地壳厚度和泊松比[J]. 第四纪研究, 30(4): 652—661.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
王夫运, 赵成彬, 酆少英, 等. 2015. 深反射剖面揭示的芦山7.0级地震发震构造[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(9): 3183—3192.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [24] |
王林, 周青云, 王峻, 等. 2016. 基于深部地震资料与地表变形资料的芦山地震发震构造研究[J]. 地震地质, 38(2): 458—476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.02.018.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
王帅军, 王夫运, 张建狮, 等. 2015. 利用宽角反射/折射地震剖面揭示芦山 MS7.0 地震震区深部孕震环境[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(9): 3193—3204.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [26] |
王小娜, 于湘伟, 章文波. 2015. 芦山震区地壳三维P波速度精细结构及地震重定位研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(4): 1179—1193.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [27] |
吴建平, 黄媛, 张天中, 等. 2009. 汶川 MS8.0 地震余震分布及周边区域P 波三维速度结构研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(2): 320—328.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
徐锡伟, 陈桂华, 于贵华, 等. 2013. 芦山地震发震构造及其与汶川地震关系讨论[J]. 地学前缘, 20(3): 11—20.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
徐志萍, 王夫运, 姜磊, 等. 2019. 龙门山中南段地壳上地幔三维密度结构[J]. 地震地质, 41(1): 84—98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2009.01.006.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
许志琴, 侯立玮, 王宗秀. 1992. 中国松潘-甘孜造山带的造山过程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社:189.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
杨光亮, 申重阳, 吴桂桔, 等. 2015. 金川—芦山—犍为剖面重力异常和地壳密度结构特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(7): 2424—2435.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [32] |
易桂喜, 龙锋,
DOI |
|
|
|
| [33] |
詹艳, 赵国泽,
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
张恩会, 石磊, 李永华, 等. 2015. 基于抛物线密度模型的频率域三维界面反演及其在川滇地区的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(2): 556—565.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [35] |
张广伟, 雷建设. 2013. 四川芦山7.0级强震及其余震序列重定位[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(5): 1764—1771.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
赵荣涛, 安美建, 冯梅, 等. 2015. 利用余震震中分析芦山 MS7.0 地震发震构造[J]. 地震学报, 37(2): 205—217.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
赵永久, 袁超, 周美夫, 等. 2007. 川西老君沟和孟通沟花岗岩的地球化学特征、 成因机制及对松潘-甘孜地体基底性质的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 23(5): 995—1006.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
DOI |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
DOI URL |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
DOI URL |
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
DOI URL |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||