地震地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 1269-1291.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.05.014
潘纪顺1)( ), 李朋辉1,3), 段永红2),*(
), 李朋辉1,3), 段永红2),*( ), 赵延娜2), 彭诣淙1), 孙凯旋1)
), 赵延娜2), 彭诣淙1), 孙凯旋1)
收稿日期:2020-06-02
修回日期:2020-11-12
出版日期:2021-10-20
发布日期:2021-12-06
通讯作者:
段永红
作者简介:潘纪顺, 男, 1968年生, 2007年于中国地震局地球物理研究所获固体地球物理学博士学位, 教授, 主要研究方向为地球物理反演、 地震数据处理、 浅地表地球物理勘探等, 电话: 13838111626, E-mail: jspan123@126.com。
基金资助:
PAN Ji-shun1)( ), LI Peng-hui1,3), DUAN Yong-hong2),*(
), LI Peng-hui1,3), DUAN Yong-hong2),*( ), ZHAO Yan-na2), PENG Yi-cong1), SUN Kai-xuan1)
), ZHAO Yan-na2), PENG Yi-cong1), SUN Kai-xuan1)
Received:2020-06-02
Revised:2020-11-12
Online:2021-10-20
Published:2021-12-06
Contact:
DUAN Yong-hong
摘要:
华北克拉通是中国最古老的克拉通, 是中国大陆的主要构造单元, 从太古代到中生代以来的地质记录较完整, 受到了国际上的广泛关注, 是研究大陆形成和演化的天然实验场地。中生代以后, 华北克拉通发生了一系列复杂的构造运动与演化进程, 东部因岩石圈减薄而形成一系列的裂陷盆地, 地壳结构复杂。而西部岩石圈厚度大, 鄂尔多斯地块的地壳结构相对简单。山西断陷带位于华北克拉通东部地块与西部鄂尔多斯地块之间, 其地壳与岩石圈结构从西部稳定的克拉通结构变化为东部破坏严重的克拉通结构, 过渡特征明显。因此, 揭示山西断陷带及其两侧区域的构造特征对研究华北克拉通的破坏动力学过程有着重要意义。文中利用华北克拉通中西部地区(34°~41°N, 107°~117°E)的150个流动地震台站近3a记录的远震波形资料, 采用P波接收函数的H-κ扫描叠加法和共转换点(CCP)叠加法处理计算, 获得了研究区的地壳速度结构图像。结果表明, 鄂尔多斯地块内的地壳厚度为37~47km, 莫霍面较为平坦。山西断陷带的地壳厚度为34~46km, 在临汾盆地凹陷的正下方, 莫霍面呈现出明显的上隆, 上隆量为4~10km, 推断山西断陷带的形成与地幔物质的运动有着密切关系。通过与该区域已有的布格重力异常资料进行对比, 研究区地壳厚度的分布特征与太行隆起东、 西部地区分别呈现出正、 负的布格重力异常分布特征一致。该区域不同构造单元内的地壳厚度和波速比计算结果表明, 3个构造单元内的波速比均随地壳厚度的增加而不同程度地减小。整体看来, 研究区以111.5°E为界分为东、 西2个区, 111.5°E以西的鄂尔多斯地区的泊松比较111.5°E以东的山西断陷带低, 反映出鄂尔多斯地块东部地区具有稳定的古老地块特征, 地壳结构相对简单; 而山西断陷带下方上地幔物质上涌导致其泊松比比两侧山区的泊松比高。就山西断陷带而言, 以38°N为界可分为南、 北2个区域, 38°N以北的区域内地壳因存在部分熔融而呈现低速特征, 而38°N以南的区域仍然保持着相对稳定的地壳特性而呈现高速特征。山西断陷带分南、 北2个区域的原因可能与山西断陷带不均匀沉降有关, 其有关的地球动力学过程需要更多的资料来进一步综合研究。
中图分类号:
潘纪顺, 李朋辉, 段永红, 赵延娜, 彭诣淙, 孙凯旋. 华北克拉通中西部地区的地壳结构研究[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1269-1291.
PAN Ji-shun, LI Peng-hui, DUAN Yong-hong, ZHAO Yan-na, PENG Yi-cong, SUN Kai-xuan. STUDY ON THE CRUSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE CENTRAL AND WESTERN PART OF THE NORTH CHINA CRATON[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(5): 1269-1291.
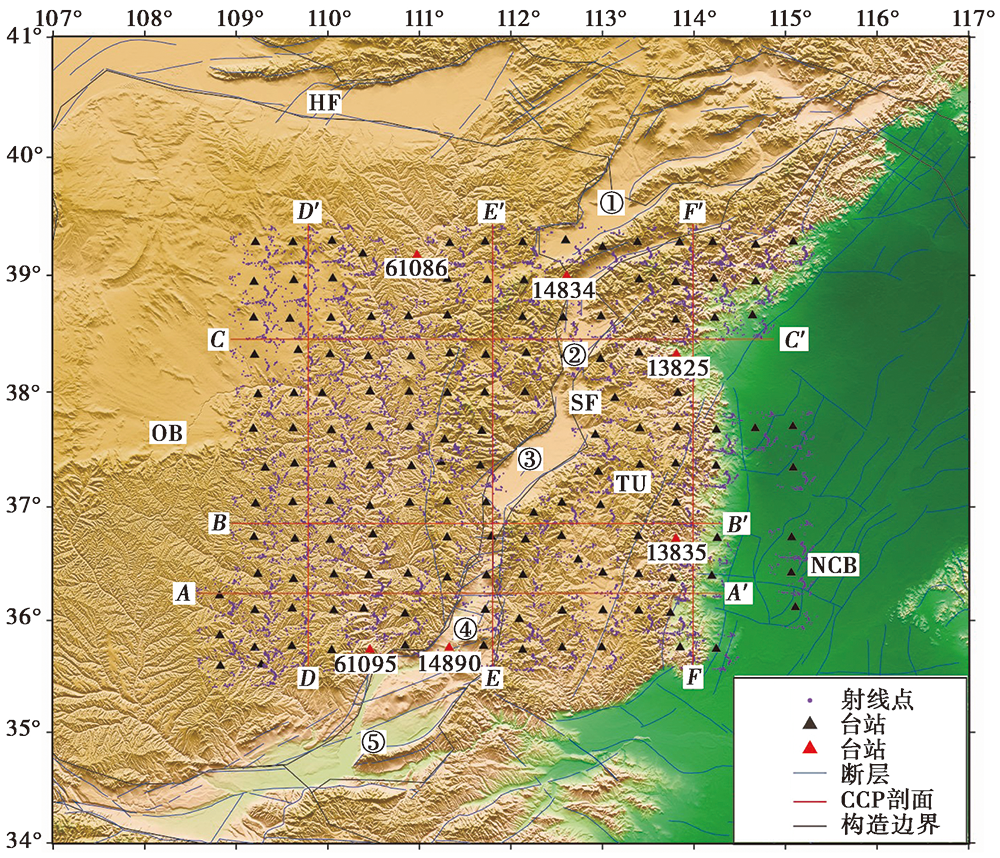
图 1 台站分布图 HF 河套断陷带; OB 鄂尔多斯地块; SF 山西断陷带; TU 太行隆起; NCB 华北盆地。 ①大同盆地; ②忻定盆地; ③太原盆地; ④临汾盆地; ⑤运城盆地。蓝色实线表示断裂(邓起东等, 2003), 黑色实线为活动地块边界 (张培震等, 2003; 张国民等, 2005)
Fig. 1 Distribution of stations in the study area.
| 序号 | 台站代码 | 北纬/(°) | 东经/(°) | 接收函数数量 | H/km | к | σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | 61101 | 35.6 | 108.8 | 90 | 39.0±2.5 | 1.82±0.06 | 0.28 |
| 002 | 61135 | 35.6 | 109.3 | 188 | 39.5±2.2 | 1.72±0.06 | 0.25 |
| 003 | 61102 | 35.7 | 110.0 | 51 | 39.4±1.8 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 004 | 14892 | 35.7 | 112.1 | 131 | 42.0±2.0 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 005 | 61095 | 35.7 | 110.5 | 271 | 36.9±1.7 | 1.79±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 006 | 41226 | 35.7 | 114.2 | 139 | 30.4±2.1 | 1.92±0.08 | 0.31 |
| 007 | 61090 | 35.8 | 109.2 | 119 | 38.0±1.8 | 1.84±0.05 | 0.29 |
| 008 | 14890 | 35.8 | 111.3 | 67 | 33.5±3.4 | 1.84±0.10 | 0.29 |
| 009 | 14893 | 35.8 | 112.6 | 135 | 40.0±1.9 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 010 | 41225 | 35.8 | 113.8 | 198 | 34.6±3.0 | 1.71±0.07 | 0.24 |
| 011 | 14894 | 35.8 | 113.0 | 105 | 38.6±1.9 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 012 | 61106 | 35.8 | 109.6 | 122 | 39.4±1.9 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 013 | 14891 | 35.8 | 111.7 | 55 | 39.1±2.3 | 1.76±0.07 | 0.26 |
| 014 | 14889 | 35.8 | 110.8 | 28 | 39.6±2.4 | 1.75±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 015 | 61088 | 35.9 | 108.8 | 74 | 45.4±2.6 | 1.70±0.06 | 0.24 |
| 016 | 14885 | 36.0 | 112.1 | 123 | 41.0±1.8 | 1.80±0.05 | 0.28 |
| 017 | 14883 | 36.1 | 110.8 | 139 | 41.1±2.1 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 018 | 41227 | 36.1 | 113.7 | 175 | 30.5±3.0 | 1.89±0.16 | 0.31 |
| 019 | 14886 | 36.1 | 112.6 | 53 | 39.4±2.7 | 1.81±0.07 | 0.28 |
| 020 | 14888 | 36.1 | 113.4 | 133 | 37.1±2.4 | 1.77±0.06 | 0.27 |
| 021 | 61123 | 36.1 | 110.1 | 18 | 39.0±1.3 | 1.80±0.03 | 0.28 |
| 022 | 14887 | 36.1 | 113.0 | 80 | 38.9±1.7 | 1.78±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 023 | 61091 | 36.1 | 109.2 | 160 | 44.5±2.1 | 1.69±0.04 | 0.23 |
| 024 | 14884 | 36.1 | 111.7 | 124 | 38.9±3.6 | 1.83±0.09 | 0.29 |
| 025 | 61124 | 36.1 | 110.4 | 214 | 40.6±1.4 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 026 | 61092 | 36.1 | 109.6 | 125 | 43.0±1.7 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 027 | 41229 | 36.1 | 115.1 | 44 | 29.5±1.7 | 2.09±0.08 | 0.35 |
| 028 | 61089 | 36.2 | 108.8 | 168 | 44.9±1.8 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 029 | 61117 | 36.4 | 109.6 | 94 | 44.0±2.0 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 030 | 41230 | 36.4 | 113.8 | 142 | 34.4±1.5 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 031 | 14877 | 36.4 | 111.3 | 52 | 40.5±1.6 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 032 | 13839 | 36.4 | 114.2 | 79 | 30.6±2.6 | 1.78±0.07 | 0.27 |
| 033 | 61125 | 36.4 | 110.4 | 160 | 42.1±1.1 | 1.76±0.03 | 0.26 |
| 034 | 14878 | 36.4 | 111.7 | 73 | 33.0±2.8 | 1.76±0.11 | 0.26 |
| 035 | 14879 | 36.4 | 112.1 | 80 | 39.9±3.7 | 1.79±0.11 | 0.27 |
| 036 | 61119 | 36.4 | 110.1 | 64 | 44.1±2.0 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 037 | 14882 | 36.4 | 113.4 | 20 | 36.1±2.9 | 1.79±0.08 | 0.27 |
| 038 | 61093 | 36.4 | 109.2 | 118 | 44.9±2.0 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 039 | 14876 | 36.4 | 110.9 | 110 | 42.0±1.3 | 1.76±0.03 | 0.26 |
| 040 | 14881 | 36.4 | 113.0 | 54 | 40.1±2.0 | 1.83±0.07 | 0.29 |
| 041 | 13840 | 36.4 | 115.1 | 184 | 29.9±1.8 | 2.03±0.09 | 0.34 |
| 042 | 14880 | 36.5 | 112.7 | 45 | 40.9±5.5 | 1.78±0.11 | 0.27 |
| 043 | 61120 | 36.7 | 110.0 | 117 | 43.5±1.5 | 1.73±0.03 | 0.25 |
| 044 | 14873 | 36.7 | 112.2 | 69 | 41.0±4.5 | 1.70±0.10 | 0.24 |
| 045 | 61118 | 36.7 | 109.6 | 148 | 44.0±1.8 | 1.76±0.04 | 0.26 |
| 046 | 13835 | 36.7 | 113.8 | 74 | 33.1±2.0 | 1.71±0.06 | 0.24 |
| 047 | 13836 | 36.7 | 114.3 | 60 | 30.5±3.0 | 1.78±0.09 | 0.27 |
| 048 | 14871 | 36.7 | 111.3 | 47 | 40.5±1.9 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 049 | 13838 | 36.7 | 115.1 | 221 | 35.0±1.4 | 1.89±0.06 | 0.31 |
| 050 | 61081 | 36.7 | 109.2 | 94 | 44.0±2.6 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 051 | 14872 | 36.7 | 111.8 | 25 | 34.5±3.1 | 1.78±0.08 | 0.27 |
| 052 | 14875 | 36.7 | 113.4 | 38 | 35.5±2.3 | 1.79±0.07 | 0.27 |
| 053 | 14874 | 36.7 | 112.6 | 38 | 42.6±2.2 | 1.72±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 054 | 14870 | 36.8 | 110.5 | 95 | 42.1±1.7 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 055 | 14867 | 36.9 | 112.3 | 64 | 43.1±1.9 | 1.70±0.04 | 0.24 |
| 056 | 14863 | 37.0 | 110.5 | 70 | 41.5±2.0 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 057 | 14869 | 37.0 | 113.0 | 59 | 42.6±2.1 | 1.72±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 058 | 61082 | 37.0 | 109.2 | 87 | 41.9±1.6 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 059 | 13833 | 37.0 | 113.8 | 79 | 35.4±2.6 | 1.76±0.07 | 0.26 |
| 060 | 14864 | 37.0 | 110.9 | 38 | 40.6±1.6 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 061 | 14868 | 37.0 | 112.6 | 102 | 41.6±3.5 | 1.73±0.07 | 0.25 |
| 062 | 14866 | 37.0 | 111.7 | 48 | 34.5±3.3 | 1.83±0.11 | 0.29 |
| 063 | 61130 | 37.0 | 109.6 | 84 | 41.0±2.3 | 1.77±0.06 | 0.27 |
| 064 | 14865 | 37.0 | 111.3 | 46 | 41.1±3.1 | 1.70±0.07 | 0.24 |
| 065 | 61109 | 37.0 | 110.0 | 153 | 41.5±2.4 | 1.75±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 066 | 14860 | 37.3 | 113.0 | 129 | 41.5±2.1 | 1.78±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 067 | 13832 | 37.3 | 115.1 | 119 | 36.5±1.6 | 1.81±0.05 | 0.28 |
| 068 | 61105 | 37.3 | 109.3 | 107 | 41.5±1.7 | 1.76±0.04 | 0.26 |
| 069 | 14856 | 37.4 | 110.9 | 83 | 41.1±2.5 | 1.76±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 070 | 13831 | 37.4 | 114.2 | 256 | 32.9±2.5 | 1.85±0.08 | 0.29 |
| 071 | 61115 | 37.4 | 110.5 | 128 | 42.6±1.8 | 1.72±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 072 | 14858 | 37.4 | 111.7 | 117 | 39.0±4.9 | 1.96±0.14 | 0.32 |
| 073 | 14861 | 37.4 | 113.4 | 38 | 39.0±2.1 | 1.78±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 074 | 61132 | 37.4 | 110.0 | 110 | 41.5±1.8 | 1.77±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 075 | 14862 | 37.4 | 113.8 | 86 | 38.9±2.7 | 1.77±0.07 | 0.27 |
| 076 | 61131 | 37.4 | 109.6 | 119 | 40.4±1.4 | 1.80±0.04 | 0.28 |
| 077 | 14857 | 37.4 | 111.2 | 91 | 42.9±2.4 | 1.72±0.06 | 0.25 |
| 078 | 14851 | 37.6 | 111.3 | 122 | 44.4±1.6 | 1.71±0.04 | 0.24 |
| 079 | 14853 | 37.6 | 112.9 | 149 | 40.4±1.8 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 080 | 14852 | 37.7 | 111.7 | 47 | 41.5±4.3 | 1.79±0.10 | 0.27 |
| 081 | 61133 | 37.7 | 110.0 | 184 | 41.6±1.5 | 1.76±0.03 | 0.26 |
| 082 | 13828 | 37.7 | 114.2 | 142 | 34.0±2.2 | 1.75±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 083 | 61097 | 37.7 | 109.2 | 74 | 41.0±2.2 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 084 | 13829 | 37.7 | 114.7 | 159 | 32.1±3.1 | 1.89±0.10 | 0.31 |
| 085 | 61099 | 37.7 | 109.6 | 5 | 38.4±3.3 | 1.85±0.12 | 0.29 |
| 086 | 14854 | 37.7 | 113.4 | 43 | 40.6±2.6 | 1.78±0.06 | 0.27 |
| 087 | 14855 | 37.7 | 113.8 | 45 | 37.5±2.6 | 1.85±0.09 | 0.29 |
| 088 | 14850 | 37.7 | 110.9 | 91 | 41.9±2.3 | 1.74±0.06 | 0.25 |
| 089 | 61116 | 37.7 | 110.5 | 126 | 42.1±2.2 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 090 | 13830 | 37.7 | 115.1 | 77 | 32.0±2.3 | 1.91±0.11 | 0.31 |
| 091 | 14847 | 37.9 | 113.1 | 49 | 37.1±5.3 | 1.94±0.15 | 0.32 |
| 092 | 61098 | 38.0 | 109.2 | 117 | 41.5±2.0 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 093 | 61100 | 38.0 | 109.6 | 120 | 40.9±1.5 | 1.78±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 094 | 61128 | 38.0 | 109.9 | 123 | 40.6±3.0 | 1.80±0.07 | 0.28 |
| 095 | 14844 | 38.0 | 111.3 | 83 | 45.0±1.8 | 1.73±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 096 | 14849 | 38.0 | 113.8 | 50 | 38.0±1.8 | 1.76±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 097 | 14845 | 38.0 | 111.7 | 33 | 42.4±2.3 | 1.71±0.05 | 0.24 |
| 098 | 14846 | 38.0 | 112.2 | 130 | 42.1±2.9 | 1.73±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 099 | 14843 | 38.0 | 110.9 | 89 | 43.5±2.2 | 1.65±0.07 | 0.21 |
| 100 | 61103 | 38.0 | 110.5 | 90 | 41.5±1.4 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 101 | 14823 | 38.3 | 113.0 | 122 | 39.6±1.8 | 1.92±0.05 | 0.31 |
| 102 | 14840 | 38.3 | 110.9 | 62 | 43.4±3.0 | 1.71±0.06 | 0.24 |
| 103 | 61104 | 38.3 | 110.4 | 159 | 41.9±1.7 | 1.75±0.04 | 0.26 |
| 104 | 14842 | 38.3 | 111.7 | 180 | 34.5±2.2 | 1.97±0.08 | 0.33 |
| 105 | 14822 | 38.3 | 112.6 | 96 | 36.5±4.0 | 1.84±0.16 | 0.29 |
| 106 | 61126 | 38.3 | 109.2 | 82 | 41.9±1.6 | 1.71±0.04 | 0.24 |
| 107 | 61129 | 38.3 | 110.0 | 153 | 42.0±1.5 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 108 | 13825 | 38.3 | 113.8 | 168 | 44.3±2.3 | 1.68±0.04 | 0.23 |
| 109 | 14841 | 38.3 | 111.3 | 100 | 41.6±2.1 | 1.79±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 110 | 14821 | 38.3 | 112.2 | 117 | 40.5±2.7 | 1.73±0.06 | 0.25 |
| 111 | 14824 | 38.3 | 113.4 | 71 | 42.0±1.7 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 112 | 61134 | 38.4 | 109.7 | 92 | 41.9±1.3 | 1.73±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 113 | 13821 | 38.6 | 113.8 | 167 | 39.5±2.2 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 114 | 61127 | 38.6 | 109.6 | 142 | 41.9±1.5 | 1.72±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 115 | 13822 | 38.6 | 114.2 | 80 | 34.4±2.6 | 1.79±0.08 | 0.27 |
| 116 | 61111 | 38.6 | 110.0 | 199 | 42.0±1.3 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 117 | 15799 | 38.6 | 109.2 | 123 | 42.6±1.2 | 1.71±0.03 | 0.24 |
| 118 | 14828 | 38.6 | 112.6 | 69 | 34.5±2.4 | 1.84±0.07 | 0.29 |
| 119 | 14827 | 38.6 | 112.1 | 94 | 41.6±2.7 | 1.77±0.06 | 0.27 |
| 120 | 61113 | 38.6 | 110.5 | 143 | 42.1±1.7 | 1.79±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 121 | 14829 | 38.6 | 113.0 | 114 | 35.0±2.2 | 1.82±0.07 | 0.28 |
| 122 | 61114 | 38.7 | 110.9 | 156 | 42.4±2.0 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 123 | 14825 | 38.7 | 111.3 | 92 | 45.1±2.0 | 1.70±0.04 | 0.24 |
| 124 | 13823 | 38.7 | 114.6 | 141 | 31.1±2.8 | 1.80±0.08 | 0.28 |
| 125 | 13818 | 38.9 | 113.8 | 130 | 40.4±1.8 | 1.77±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 126 | 15797 | 38.9 | 109.2 | 192 | 43.1±1.3 | 1.72±0.03 | 0.25 |
| 127 | 13820 | 38.9 | 114.7 | 157 | 33.5±1.9 | 1.82±0.07 | 0.28 |
| 128 | 14833 | 39.0 | 112.1 | 98 | 42.4±3.0 | 1.77±0.07 | 0.27 |
| 129 | 15798 | 39.0 | 109.6 | 173 | 42.9±1.9 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 130 | 14832 | 39.0 | 111.7 | 114 | 42.0±3.2 | 1.77±0.07 | 0.27 |
| 131 | 14835 | 39.0 | 113.4 | 127 | 34.5±2.5 | 1.93±0.07 | 0.32 |
| 132 | 14831 | 39.0 | 111.3 | 95 | 40.5±2.6 | 1.76±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 133 | 13819 | 39.0 | 114.2 | 260 | 36.4±2.6 | 1.90±0.09 | 0.31 |
| 134 | 61112 | 39.0 | 110.1 | 207 | 42.6±1.6 | 1.78±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 135 | 14834 | 39.0 | 112.6 | 126 | 46.1±2.8 | 1.72±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 136 | 61086 | 39.2 | 111.0 | 99 | 47.0±5.3 | 1.63±0.09 | 0.20 |
| 137 | 61085 | 39.2 | 110.4 | 211 | 41.9±2.3 | 1.80±0.06 | 0.28 |
| 138 | 14836 | 39.2 | 113.0 | 84 | 43.5±1.6 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 139 | 13816 | 39.3 | 114.7 | 217 | 31.4±2.3 | 1.96±0.08 | 0.32 |
| 140 | 14817 | 39.3 | 111.3 | 141 | 40.0±2.9 | 1.87±0.07 | 0.30 |
| 141 | 14838 | 39.3 | 113.8 | 102 | 39.5±2.3 | 1.82±0.06 | 0.28 |
| 142 | 15795 | 39.3 | 109.6 | 190 | 42.5±1.7 | 1.82±0.05 | 0.28 |
| 143 | 14819 | 39.3 | 112.1 | 140 | 44.0±2.3 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 144 | 15794 | 39.3 | 109.2 | 142 | 43.5±1.8 | 1.79±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 145 | 14837 | 39.3 | 113.4 | 113 | 43.1±2.7 | 1.73±0.06 | 0.25 |
| 146 | 14839 | 39.3 | 114.2 | 151 | 38.4±2.6 | 1.80±0.06 | 0.28 |
| 147 | 14818 | 39.3 | 111.7 | 98 | 44.9±2.1 | 1.72±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 148 | 13817 | 39.3 | 115.1 | 219 | 34.9±2.5 | 1.78±0.06 | 0.27 |
| 149 | 15796 | 39.3 | 110.0 | 167 | 43.0±1.6 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 150 | 14820 | 39.3 | 112.6 | 79 | 44.6±2.0 | 1.78±0.04 | 0.27 |
表1 台站下方区域的地壳厚度H、地壳平均波速比к以及泊松比σ
Table 1 Crustal thickness H,wave velocity ratio к and Poisson’s ratio σ under some stations
| 序号 | 台站代码 | 北纬/(°) | 东经/(°) | 接收函数数量 | H/km | к | σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | 61101 | 35.6 | 108.8 | 90 | 39.0±2.5 | 1.82±0.06 | 0.28 |
| 002 | 61135 | 35.6 | 109.3 | 188 | 39.5±2.2 | 1.72±0.06 | 0.25 |
| 003 | 61102 | 35.7 | 110.0 | 51 | 39.4±1.8 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 004 | 14892 | 35.7 | 112.1 | 131 | 42.0±2.0 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 005 | 61095 | 35.7 | 110.5 | 271 | 36.9±1.7 | 1.79±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 006 | 41226 | 35.7 | 114.2 | 139 | 30.4±2.1 | 1.92±0.08 | 0.31 |
| 007 | 61090 | 35.8 | 109.2 | 119 | 38.0±1.8 | 1.84±0.05 | 0.29 |
| 008 | 14890 | 35.8 | 111.3 | 67 | 33.5±3.4 | 1.84±0.10 | 0.29 |
| 009 | 14893 | 35.8 | 112.6 | 135 | 40.0±1.9 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 010 | 41225 | 35.8 | 113.8 | 198 | 34.6±3.0 | 1.71±0.07 | 0.24 |
| 011 | 14894 | 35.8 | 113.0 | 105 | 38.6±1.9 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 012 | 61106 | 35.8 | 109.6 | 122 | 39.4±1.9 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 013 | 14891 | 35.8 | 111.7 | 55 | 39.1±2.3 | 1.76±0.07 | 0.26 |
| 014 | 14889 | 35.8 | 110.8 | 28 | 39.6±2.4 | 1.75±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 015 | 61088 | 35.9 | 108.8 | 74 | 45.4±2.6 | 1.70±0.06 | 0.24 |
| 016 | 14885 | 36.0 | 112.1 | 123 | 41.0±1.8 | 1.80±0.05 | 0.28 |
| 017 | 14883 | 36.1 | 110.8 | 139 | 41.1±2.1 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 018 | 41227 | 36.1 | 113.7 | 175 | 30.5±3.0 | 1.89±0.16 | 0.31 |
| 019 | 14886 | 36.1 | 112.6 | 53 | 39.4±2.7 | 1.81±0.07 | 0.28 |
| 020 | 14888 | 36.1 | 113.4 | 133 | 37.1±2.4 | 1.77±0.06 | 0.27 |
| 021 | 61123 | 36.1 | 110.1 | 18 | 39.0±1.3 | 1.80±0.03 | 0.28 |
| 022 | 14887 | 36.1 | 113.0 | 80 | 38.9±1.7 | 1.78±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 023 | 61091 | 36.1 | 109.2 | 160 | 44.5±2.1 | 1.69±0.04 | 0.23 |
| 024 | 14884 | 36.1 | 111.7 | 124 | 38.9±3.6 | 1.83±0.09 | 0.29 |
| 025 | 61124 | 36.1 | 110.4 | 214 | 40.6±1.4 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 026 | 61092 | 36.1 | 109.6 | 125 | 43.0±1.7 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 027 | 41229 | 36.1 | 115.1 | 44 | 29.5±1.7 | 2.09±0.08 | 0.35 |
| 028 | 61089 | 36.2 | 108.8 | 168 | 44.9±1.8 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 029 | 61117 | 36.4 | 109.6 | 94 | 44.0±2.0 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 030 | 41230 | 36.4 | 113.8 | 142 | 34.4±1.5 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 031 | 14877 | 36.4 | 111.3 | 52 | 40.5±1.6 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 032 | 13839 | 36.4 | 114.2 | 79 | 30.6±2.6 | 1.78±0.07 | 0.27 |
| 033 | 61125 | 36.4 | 110.4 | 160 | 42.1±1.1 | 1.76±0.03 | 0.26 |
| 034 | 14878 | 36.4 | 111.7 | 73 | 33.0±2.8 | 1.76±0.11 | 0.26 |
| 035 | 14879 | 36.4 | 112.1 | 80 | 39.9±3.7 | 1.79±0.11 | 0.27 |
| 036 | 61119 | 36.4 | 110.1 | 64 | 44.1±2.0 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 037 | 14882 | 36.4 | 113.4 | 20 | 36.1±2.9 | 1.79±0.08 | 0.27 |
| 038 | 61093 | 36.4 | 109.2 | 118 | 44.9±2.0 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 039 | 14876 | 36.4 | 110.9 | 110 | 42.0±1.3 | 1.76±0.03 | 0.26 |
| 040 | 14881 | 36.4 | 113.0 | 54 | 40.1±2.0 | 1.83±0.07 | 0.29 |
| 041 | 13840 | 36.4 | 115.1 | 184 | 29.9±1.8 | 2.03±0.09 | 0.34 |
| 042 | 14880 | 36.5 | 112.7 | 45 | 40.9±5.5 | 1.78±0.11 | 0.27 |
| 043 | 61120 | 36.7 | 110.0 | 117 | 43.5±1.5 | 1.73±0.03 | 0.25 |
| 044 | 14873 | 36.7 | 112.2 | 69 | 41.0±4.5 | 1.70±0.10 | 0.24 |
| 045 | 61118 | 36.7 | 109.6 | 148 | 44.0±1.8 | 1.76±0.04 | 0.26 |
| 046 | 13835 | 36.7 | 113.8 | 74 | 33.1±2.0 | 1.71±0.06 | 0.24 |
| 047 | 13836 | 36.7 | 114.3 | 60 | 30.5±3.0 | 1.78±0.09 | 0.27 |
| 048 | 14871 | 36.7 | 111.3 | 47 | 40.5±1.9 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 049 | 13838 | 36.7 | 115.1 | 221 | 35.0±1.4 | 1.89±0.06 | 0.31 |
| 050 | 61081 | 36.7 | 109.2 | 94 | 44.0±2.6 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 051 | 14872 | 36.7 | 111.8 | 25 | 34.5±3.1 | 1.78±0.08 | 0.27 |
| 052 | 14875 | 36.7 | 113.4 | 38 | 35.5±2.3 | 1.79±0.07 | 0.27 |
| 053 | 14874 | 36.7 | 112.6 | 38 | 42.6±2.2 | 1.72±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 054 | 14870 | 36.8 | 110.5 | 95 | 42.1±1.7 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 055 | 14867 | 36.9 | 112.3 | 64 | 43.1±1.9 | 1.70±0.04 | 0.24 |
| 056 | 14863 | 37.0 | 110.5 | 70 | 41.5±2.0 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 057 | 14869 | 37.0 | 113.0 | 59 | 42.6±2.1 | 1.72±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 058 | 61082 | 37.0 | 109.2 | 87 | 41.9±1.6 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 059 | 13833 | 37.0 | 113.8 | 79 | 35.4±2.6 | 1.76±0.07 | 0.26 |
| 060 | 14864 | 37.0 | 110.9 | 38 | 40.6±1.6 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 061 | 14868 | 37.0 | 112.6 | 102 | 41.6±3.5 | 1.73±0.07 | 0.25 |
| 062 | 14866 | 37.0 | 111.7 | 48 | 34.5±3.3 | 1.83±0.11 | 0.29 |
| 063 | 61130 | 37.0 | 109.6 | 84 | 41.0±2.3 | 1.77±0.06 | 0.27 |
| 064 | 14865 | 37.0 | 111.3 | 46 | 41.1±3.1 | 1.70±0.07 | 0.24 |
| 065 | 61109 | 37.0 | 110.0 | 153 | 41.5±2.4 | 1.75±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 066 | 14860 | 37.3 | 113.0 | 129 | 41.5±2.1 | 1.78±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 067 | 13832 | 37.3 | 115.1 | 119 | 36.5±1.6 | 1.81±0.05 | 0.28 |
| 068 | 61105 | 37.3 | 109.3 | 107 | 41.5±1.7 | 1.76±0.04 | 0.26 |
| 069 | 14856 | 37.4 | 110.9 | 83 | 41.1±2.5 | 1.76±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 070 | 13831 | 37.4 | 114.2 | 256 | 32.9±2.5 | 1.85±0.08 | 0.29 |
| 071 | 61115 | 37.4 | 110.5 | 128 | 42.6±1.8 | 1.72±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 072 | 14858 | 37.4 | 111.7 | 117 | 39.0±4.9 | 1.96±0.14 | 0.32 |
| 073 | 14861 | 37.4 | 113.4 | 38 | 39.0±2.1 | 1.78±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 074 | 61132 | 37.4 | 110.0 | 110 | 41.5±1.8 | 1.77±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 075 | 14862 | 37.4 | 113.8 | 86 | 38.9±2.7 | 1.77±0.07 | 0.27 |
| 076 | 61131 | 37.4 | 109.6 | 119 | 40.4±1.4 | 1.80±0.04 | 0.28 |
| 077 | 14857 | 37.4 | 111.2 | 91 | 42.9±2.4 | 1.72±0.06 | 0.25 |
| 078 | 14851 | 37.6 | 111.3 | 122 | 44.4±1.6 | 1.71±0.04 | 0.24 |
| 079 | 14853 | 37.6 | 112.9 | 149 | 40.4±1.8 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 080 | 14852 | 37.7 | 111.7 | 47 | 41.5±4.3 | 1.79±0.10 | 0.27 |
| 081 | 61133 | 37.7 | 110.0 | 184 | 41.6±1.5 | 1.76±0.03 | 0.26 |
| 082 | 13828 | 37.7 | 114.2 | 142 | 34.0±2.2 | 1.75±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 083 | 61097 | 37.7 | 109.2 | 74 | 41.0±2.2 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 084 | 13829 | 37.7 | 114.7 | 159 | 32.1±3.1 | 1.89±0.10 | 0.31 |
| 085 | 61099 | 37.7 | 109.6 | 5 | 38.4±3.3 | 1.85±0.12 | 0.29 |
| 086 | 14854 | 37.7 | 113.4 | 43 | 40.6±2.6 | 1.78±0.06 | 0.27 |
| 087 | 14855 | 37.7 | 113.8 | 45 | 37.5±2.6 | 1.85±0.09 | 0.29 |
| 088 | 14850 | 37.7 | 110.9 | 91 | 41.9±2.3 | 1.74±0.06 | 0.25 |
| 089 | 61116 | 37.7 | 110.5 | 126 | 42.1±2.2 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 090 | 13830 | 37.7 | 115.1 | 77 | 32.0±2.3 | 1.91±0.11 | 0.31 |
| 091 | 14847 | 37.9 | 113.1 | 49 | 37.1±5.3 | 1.94±0.15 | 0.32 |
| 092 | 61098 | 38.0 | 109.2 | 117 | 41.5±2.0 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 093 | 61100 | 38.0 | 109.6 | 120 | 40.9±1.5 | 1.78±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 094 | 61128 | 38.0 | 109.9 | 123 | 40.6±3.0 | 1.80±0.07 | 0.28 |
| 095 | 14844 | 38.0 | 111.3 | 83 | 45.0±1.8 | 1.73±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 096 | 14849 | 38.0 | 113.8 | 50 | 38.0±1.8 | 1.76±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 097 | 14845 | 38.0 | 111.7 | 33 | 42.4±2.3 | 1.71±0.05 | 0.24 |
| 098 | 14846 | 38.0 | 112.2 | 130 | 42.1±2.9 | 1.73±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 099 | 14843 | 38.0 | 110.9 | 89 | 43.5±2.2 | 1.65±0.07 | 0.21 |
| 100 | 61103 | 38.0 | 110.5 | 90 | 41.5±1.4 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 101 | 14823 | 38.3 | 113.0 | 122 | 39.6±1.8 | 1.92±0.05 | 0.31 |
| 102 | 14840 | 38.3 | 110.9 | 62 | 43.4±3.0 | 1.71±0.06 | 0.24 |
| 103 | 61104 | 38.3 | 110.4 | 159 | 41.9±1.7 | 1.75±0.04 | 0.26 |
| 104 | 14842 | 38.3 | 111.7 | 180 | 34.5±2.2 | 1.97±0.08 | 0.33 |
| 105 | 14822 | 38.3 | 112.6 | 96 | 36.5±4.0 | 1.84±0.16 | 0.29 |
| 106 | 61126 | 38.3 | 109.2 | 82 | 41.9±1.6 | 1.71±0.04 | 0.24 |
| 107 | 61129 | 38.3 | 110.0 | 153 | 42.0±1.5 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 108 | 13825 | 38.3 | 113.8 | 168 | 44.3±2.3 | 1.68±0.04 | 0.23 |
| 109 | 14841 | 38.3 | 111.3 | 100 | 41.6±2.1 | 1.79±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 110 | 14821 | 38.3 | 112.2 | 117 | 40.5±2.7 | 1.73±0.06 | 0.25 |
| 111 | 14824 | 38.3 | 113.4 | 71 | 42.0±1.7 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 112 | 61134 | 38.4 | 109.7 | 92 | 41.9±1.3 | 1.73±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 113 | 13821 | 38.6 | 113.8 | 167 | 39.5±2.2 | 1.75±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 114 | 61127 | 38.6 | 109.6 | 142 | 41.9±1.5 | 1.72±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 115 | 13822 | 38.6 | 114.2 | 80 | 34.4±2.6 | 1.79±0.08 | 0.27 |
| 116 | 61111 | 38.6 | 110.0 | 199 | 42.0±1.3 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 117 | 15799 | 38.6 | 109.2 | 123 | 42.6±1.2 | 1.71±0.03 | 0.24 |
| 118 | 14828 | 38.6 | 112.6 | 69 | 34.5±2.4 | 1.84±0.07 | 0.29 |
| 119 | 14827 | 38.6 | 112.1 | 94 | 41.6±2.7 | 1.77±0.06 | 0.27 |
| 120 | 61113 | 38.6 | 110.5 | 143 | 42.1±1.7 | 1.79±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 121 | 14829 | 38.6 | 113.0 | 114 | 35.0±2.2 | 1.82±0.07 | 0.28 |
| 122 | 61114 | 38.7 | 110.9 | 156 | 42.4±2.0 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 123 | 14825 | 38.7 | 111.3 | 92 | 45.1±2.0 | 1.70±0.04 | 0.24 |
| 124 | 13823 | 38.7 | 114.6 | 141 | 31.1±2.8 | 1.80±0.08 | 0.28 |
| 125 | 13818 | 38.9 | 113.8 | 130 | 40.4±1.8 | 1.77±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 126 | 15797 | 38.9 | 109.2 | 192 | 43.1±1.3 | 1.72±0.03 | 0.25 |
| 127 | 13820 | 38.9 | 114.7 | 157 | 33.5±1.9 | 1.82±0.07 | 0.28 |
| 128 | 14833 | 39.0 | 112.1 | 98 | 42.4±3.0 | 1.77±0.07 | 0.27 |
| 129 | 15798 | 39.0 | 109.6 | 173 | 42.9±1.9 | 1.74±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 130 | 14832 | 39.0 | 111.7 | 114 | 42.0±3.2 | 1.77±0.07 | 0.27 |
| 131 | 14835 | 39.0 | 113.4 | 127 | 34.5±2.5 | 1.93±0.07 | 0.32 |
| 132 | 14831 | 39.0 | 111.3 | 95 | 40.5±2.6 | 1.76±0.06 | 0.26 |
| 133 | 13819 | 39.0 | 114.2 | 260 | 36.4±2.6 | 1.90±0.09 | 0.31 |
| 134 | 61112 | 39.0 | 110.1 | 207 | 42.6±1.6 | 1.78±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 135 | 14834 | 39.0 | 112.6 | 126 | 46.1±2.8 | 1.72±0.05 | 0.25 |
| 136 | 61086 | 39.2 | 111.0 | 99 | 47.0±5.3 | 1.63±0.09 | 0.20 |
| 137 | 61085 | 39.2 | 110.4 | 211 | 41.9±2.3 | 1.80±0.06 | 0.28 |
| 138 | 14836 | 39.2 | 113.0 | 84 | 43.5±1.6 | 1.74±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 139 | 13816 | 39.3 | 114.7 | 217 | 31.4±2.3 | 1.96±0.08 | 0.32 |
| 140 | 14817 | 39.3 | 111.3 | 141 | 40.0±2.9 | 1.87±0.07 | 0.30 |
| 141 | 14838 | 39.3 | 113.8 | 102 | 39.5±2.3 | 1.82±0.06 | 0.28 |
| 142 | 15795 | 39.3 | 109.6 | 190 | 42.5±1.7 | 1.82±0.05 | 0.28 |
| 143 | 14819 | 39.3 | 112.1 | 140 | 44.0±2.3 | 1.76±0.05 | 0.26 |
| 144 | 15794 | 39.3 | 109.2 | 142 | 43.5±1.8 | 1.79±0.05 | 0.27 |
| 145 | 14837 | 39.3 | 113.4 | 113 | 43.1±2.7 | 1.73±0.06 | 0.25 |
| 146 | 14839 | 39.3 | 114.2 | 151 | 38.4±2.6 | 1.80±0.06 | 0.28 |
| 147 | 14818 | 39.3 | 111.7 | 98 | 44.9±2.1 | 1.72±0.04 | 0.25 |
| 148 | 13817 | 39.3 | 115.1 | 219 | 34.9±2.5 | 1.78±0.06 | 0.27 |
| 149 | 15796 | 39.3 | 110.0 | 167 | 43.0±1.6 | 1.77±0.04 | 0.27 |
| 150 | 14820 | 39.3 | 112.6 | 79 | 44.6±2.0 | 1.78±0.04 | 0.27 |
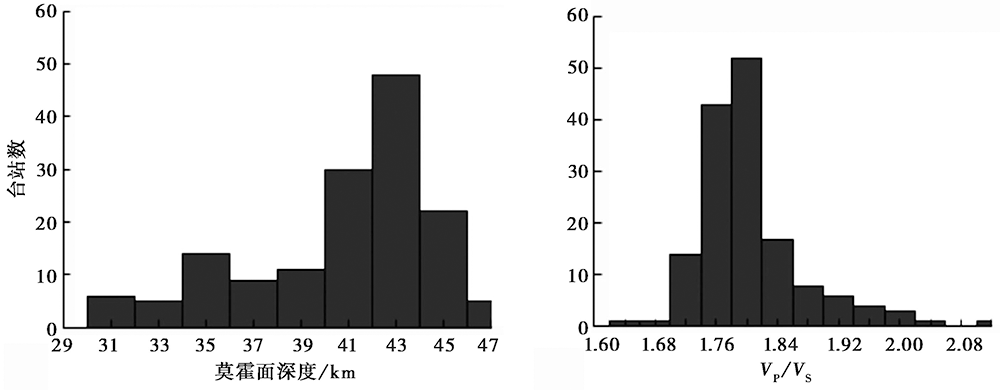
图 5 华北克拉通中、 西部地区的地壳厚度与波速比分布范围统计
Fig. 5 Distribution of crustal thickness and Poisson's ratio in the central and western parts of the North China Craton.
| [1] | 陈九辉, 刘启元, 李顺成, 等. 2005. 青藏高原东北缘-鄂尔多斯地块地壳上地幔S波速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 48(2): 333-342. |
| CHEN Jiu-hui, LIU Qi-yuan, LI Shun-cheng, et al. 2005. Crust and upper mantle S-wave velocity structure across northeastern Tibetan plateau and Ordos block[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 48(2): 333-342. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 陈凌, 危自根, 程骋. 2010. 从华北克拉通中、 西部结构的区域差异性探讨克拉通破坏[J]. 地学前缘, 17(1): 212-228. |
| CHEN Ling, WEI Zi-gen, CHENG Cheng. 2010. Significant structural variations in the central and western North China craton and its implications for the craton destruction[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(1): 212-228. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 陈石, 王谦身, 徐伟民, 等. 2011. 华北地区热均衡、 重力均衡与深部构造[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(11): 2864-2875. |
| CHEN Shi, WANG Qian-shen, XU Wei-min, et al. 2011. Thermal isostasy of North China and its gravity isostasy and deep structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(11): 2864-2875. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2003. 中国活动构造与地震活动[J]. 地学前缘, 10(S1): 66-73. |
| DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Pei-zhen, RAN Yong-kang, et al. 2003. Active tectonics and earthquake activities in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(S1): 66-73. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 段永红, 张先康, 刘志, 等. 2005. 长白山-镜泊湖火山区上地幔间断面接收函数研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 48(4): 834-842. |
| DUAN Yong-hong, ZHANG Xian-kang, LIU Zhi, et al. 2005. A study on crustal structures of Changbaishan-Jingpohu volcanic area using receiver function[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 48(4): 834-842. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 段永红, 刘保金, 赵金仁, 等. 2015. 华北构造区岩石圈二维P波速度结构特征: 来自盐城-包头深地震测深剖面的约束[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 45(8): 1183-1197. |
| DUAN Yong-hong, LIU Bao-jin, ZHAO Jin-ren, et al. 2015. 2-D P-wave velocity structure of lithosphere in the North China tectonic zone: Constraints from the Yancheng-Baotou deep seismic profile[J]. Science in China (Ser D), 45(8): 1183-1197. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 段永红, 王夫运, 张先康, 等. 2016. 华北克拉通中东部地壳三维速度结构模型(HBCrust1.0)[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 46(6): 845-856. |
| DUAN Yong-hong, WANG Fu-yun, ZHANG Xian-kang, et al. 2016. Three-dimensional crustal velocity structure model of the middle-eastern North China Craton(HBCrust1.0)[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 46(6): 845-856. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 葛粲, 郑勇, 熊熊. 2011. 华北地区地壳厚度与泊松比研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(10): 2538-2548. |
| GE Can, ZHENG Yong, XIONG Xiong. 2011. Study of crustal thickness and Poisson ratio of the North China Craton[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(10): 2538-2548. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 郭震, 陈永顺, 殷伟伟. 2015. 背景噪声面波与布格重力异常联合反演: 山西断陷带三维地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(3): 821-831. |
| GUO Zhen, CHEN Yong-shun, YIN Wei-wei. 2015. Three-dimensional crustal model of Shanxi graben from 3D joint inversion of ambient noise surface wave and Bouguer gravity anomalies[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(3): 821-831. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 何凯, 杜瑞林, 董彦君, 等. 2018. 利用远震接收函数研究湖北地区地壳结构[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 38(6): 646-649. |
| HE Kai, DU Rui-lin, DONG Yan-jun, et al. 2018. Crustal structure and Poisson ratio beneath Hubei Province derived from teleseismic receiver functions[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 38(6): 646-649. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 嵇少丞, 王茜, 杨文采. 2009. 华北克拉通泊松比与地壳厚度的关系及其大地构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 83(3): 324-330. |
| JI Shao-cheng, WANG Qian, YANG Wen-cai. 2009. Correlation between crustal thickness and Poisson's ratio in the North China craton and its implication for lithospheric thinning[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(3): 324-330. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 贾萌, 王显光, 李世林, 等. 2015. 鄂尔多斯块体及周边区域地壳结构的接收函数研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 30(6): 2474-2481. |
| JIA Meng, WANG Xian-guang, LI Shi-lin, et al. 2015. Crustal structures of Ordos block and surrounding regions from receiver functions[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 30(6): 2474-2481. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 嘉世旭, 张先康. 2005. 华北不同构造块体地壳结构及其对比研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 48(3): 611-620. |
|
JIA Shi-xu, ZHANG Xian-kang. 2005. Crustal structure and comparison of different tectonic blocks in North China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 48(3): 611-620. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [14] | 李自红, 刘保金, 袁洪克, 等. 2014. 临汾盆地地壳精细结构和构造: 地震反射剖面结果[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(5): 1487-1497. |
| LI Zi-hong, LIU Bao-jin, YUAN Hong-ke, et al. 2014. Fine crustal structure and tectonics of Linfen Basin: From the results of seismic reflection profile[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(5): 1487-1497. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 卢海峰, 李玉森, 马保起, 等. 2009. 山西断陷北部NEE向断裂带晚第四纪活动性探讨[J]. 现代地质, 23(3): 440-446. |
| LU Hai-feng, LI Yu-sen, MA Bao-qi, et al. 2009. Late Quaternary activity of the NEE-striking fault belt in northern Shanxi fault-depression zone[J]. Geoscience, 23(3): 440-446. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 马宗晋, 高祥林, 宋正范. 2006. 中国布格重力异常水平梯度图的判读和构造解释[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(1): 106-114. |
| MA Zong-jin, GAO Xiang-lin, SONG Zheng-fan. 2006. Analysis and tectonic interpretation to the horizontal-gradient map calculated from Bouguer gravity data in the China mainland[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(1): 106-114. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 任枭, 徐志国, 杨辉, 等. 2012. 鄂尔多斯地块东南缘地带Moho深度变化特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(12): 4089-4096. |
| REN Xiao, XU Zhi-guo, YANG Hui, et al. 2012. Moho depth distribution character beneath the Ordos block's southeastern margin areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(12): 4089-4096. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 石岚, 高国明. 2017. 华北克拉通及其邻区的重力异常特征[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 39(S2): 259-263. |
| SHI Lan, GAO Guo-ming. 2017. Gravitational anomaly characteristics of North China Craton and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Yunnan University(Natural Sciences Edition), 39(S2): 259-263. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 宋美琴, 何正勤, 郑勇, 等. 2013. 山西地区面波相速度分布图像[J]. 地球物理学进展, 28(4): 1836-1848. |
| SONG Mei-qin, HE Zheng-qin, ZHENG Yong, et al. 2013. Rayleigh-wave phase velocity distribution in Shanxi region[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 28(4): 1836-1848. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 唐新功, 陈永顺, 严良俊, 等. 2008. 应用布格重力异常研究太行山地区地壳密度结构[J]. 西北地震学报, 30(4): 305-309. |
| TANG Xin-gong, CHEN Yong-shun, YAN Liang-jun, et al. 2008. Research on crustal density structure in the piedmont fault zone of Taihang Mountains area using the Bouguer gravity data[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 30(4): 305-309. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 唐有彩, 冯永革, 陈永顺, 等. 2010. 山西断陷带地壳结构的接收函数研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(9): 2102-2109. |
| TANG You-cai, FENG Yong-ge, CHEN Yong-shun, et al. 2010. Receiver function analysis at Shanxi Rift[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(9): 2102-2109. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] |
王霞, 宋美琴, 郑勇, 等. 2019. 山西及邻区壳幔速度图像特征及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 41(1): 119-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.01.008.
DOI |
| WANG Xia, SONG Mei-qin, ZHENG Yong, et al. 2019. Velocity characteristics of Shanxi and adjacent area and its tectonic significance[J]. Seismology and Geology, 41(1): 119-136. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 危自根, 储日升, 陈凌. 2015. 华北克拉通地壳结构区域差异的接收函数研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 45(10): 1504-1514. |
| WEI Zi-gen, CHU Ri-sheng, CHEN Ling. 2015. Regional differences in crustal structure of the North China Craton from receiver functions[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 45(10): 1504-1514. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 吴乾蕃, 谢毅真, 祖金华, 等. 1988. 华北地热场研究[J]. 中国地震, 4(1): 43-50. |
| WU Qian-fan, XIE Yi-zhen, ZU Jin-hua, et al. 1988. A study on the geothermal field in North China[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 4(1): 43-50. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 吴庆举, 曾融生. 1998. 用宽频带远震接收函数研究青藏高原的地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 41(5): 669-679. |
| WU Qing-ju, ZENG Rong-sheng. 1998. The crustal structure of Qinghai-Xizang plateau inferred from broadband teleseismic waveform[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 41(5): 669-679. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 武岩, 丁志峰, 朱露培. 2011. 利用共转换点叠加方法研究华北地区地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(10): 2528-2537. |
| WU Yan, DING Zhi-feng, ZHU Lu-pei. 2011. Crustal structure of the North China Craton from teleseismic receiver function by the common conversion point stacking method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(10): 2528-2537. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 邢集善, 叶志光, 孙振国, 等. 1991. 山西板内构造及其演化特征初探[J]. 山西地质, 6(1): 3-15. |
| XING Ji-shan, YE Zhi-guang, SUN Zhen-guo, et al. 1991. Preliminary discussions on intraplate structural features and their evolution in Shanxi Province[J]. Shanxi Geology, 6(1): 3-15. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 于利民, 刁桂苓, 李钦祖, 等. 1995. 由深源远震体波记录反演华北北部地壳上地幔速度结构[J]. 华北地震科学, 13(3): 11-20. |
| YU Li-min, DIAO Gui-ling, LI Qin-zu, et al. 1995. Inverse of velocity structure of upper mantle of crust in northern part of North China by body wave recordings of deep focus distant earthquakes[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 13(3): 11-20. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 原世豪, 陈永顺. 2015. 利用P波接收函数方法研究华北克拉通西部地壳和上地幔间断面[J]. 地球物理学进展, 30(6): 2589-2595. |
| YUAN Shi-hao, CHEN Yong-shun. 2015. Investigation on crustal and upper mantle discontinuities in western part of North China Craton using P wave receiver functions[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 30(6): 2589-2595. (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 张国民, 马宏生, 王辉, 等. 2005. 中国大陆活动地块边界带与强震活动[J]. 地球物理学报, 48(3): 602-610. |
|
ZHANG Guo-min, MA Hong-sheng, WANG Hui, et al. 2005. Boundaries between active-tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the China mainland[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 48(3): 602-610. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [31] | 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等. 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12-20. |
| ZHANG Pei-zhen, DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Guo-min, et al. 2003. Active tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the continent of China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 33(S1): 12-20. (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 张先康, 李松林, 王夫运, 等. 2003. 青藏高原东北缘、 鄂尔多斯和华北唐山震区的地壳结构差异: 深地震测深的结果[J]. 地震地质, 25(1): 52-60. |
| ZHANG Xian-kang, LI Song-lin, WANG Fu-yun, et al. 2003. Differences of crustal structures in northeastern edge of Tibet plateau, Ordos and Tangshan earthquake region in North China: Results of deep seismic sounding[J]. Seismology and Geology, 25(1): 52-60. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | 赵延娜, 段永红, 魏运浩, 等. 2017. 华南大陆东部赣闽地区地壳厚度与泊松比研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 37(3): 261-266. |
| ZHAO Yan-na, DUAN Yong-hong, WEI Yun-hao, et al. 2017. Crustal thickness and Poisson's ratio in Jiangxi and Fujian Province in eastern areas of South China[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamic, 37(3): 261-266. (in Chinese) | |
| [34] | 赵延娜, 段永红, 邹长桥, 等. 2015. 江西九江-福建宁化接收函数剖面研究[J]. 地震学报, 37(5): 722-732. |
| ZHAO Yan-na, DUAN Yong-hong, ZOU Chang-qiao, et al. 2015. Study of the receiver function profile from Jiujiang, Jiangxi Province to Ninghua, Fujian Province[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 37(5): 722-732. (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | 祝治平, 张建狮, 周雪松, 等. 1994. 山西临汾震区地壳上地幔构造的研究[J]. 华北地震科学, 12(1): 77-84. |
| ZHU Zhi-ping, ZHANG Jian-shi, ZHOU Xue-song, et al. 1994. Study on the structure of the crust and upper mantle in Linfen earthquake region in Shanxi[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 12(1): 77-84. (in Chinese) | |
| [36] | 祝治平, 张建狮, 张成科, 等. 1999. 山西中南部壳幔结构的研究[J]. 地震学报, 21(1): 42-49. |
| ZHU Zhi-ping, ZHANG Jian-shi, ZHANG Cheng-ke, et al. 1999. Study on the crust-mantle structure in the central and southern parts of Shanxi[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 21(1): 42-49. (in Chinese) | |
| [37] |
Chen L, Cheng C, Wei Z. 2009. Seismic evidence for significant lateral variations in lithospheric thickness beneath the central and western North China Craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 286(1): 171-183.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Christensen N I. 1996. Poisson's ratio and crustal seismology[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 101(B2): 3139-3156. |
| [39] |
Gao S, Rudnick R L, Yuan H L, et al. 2004. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton[J]. Nature, 432(7019): 892-897.
DOI URL |
| [40] | He J, Liu M, Li Y. 2003. Is the Shanxi rift of northern China extending?[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(23): 2213-2216. |
| [41] |
Xu X, Ma X. 1992. Geodynamics of the Shanxi rift system, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 208(1-3): 325-340.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Zandt G, Ammon C J. 1995. Continental crust composition constrained by measurements of crustal Poisson's ratio[J]. Nature, 374(6518): 152-154.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Zhu L. 2000. Crustal structure across the San Andreas Fault, southern California from teleseismic converted waves[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 179(1): 183-190.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Zhu L, Kanamori H. 2000. Moho depth variation in southern California from teleseismic receiver functions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105(B2): 2969-2980.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 杨建文, 金明培, 茶文剑, 张天继, 叶泵. 利用接收函数两步反演法研究小江断裂带及邻区地壳S波速度结构[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 190-207. |
| [2] | 宋婷, 沈旭章, 梅秀苹, 焦煜媛, 李敏娟, 苏小芸, 季婉婧. 利用接收函数频率特征研究青藏高原东北缘地区的莫霍面性质[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1290-1312. |
| [3] | 顾勤平, 许汉刚, 晏云翔, 赵启光, 李丽梅, 孟科, 杨浩, 王金艳, 蒋新, 马董伟. 郯庐断裂带新沂段地壳浅部结构和断裂活动性探测[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(4): 825-843. |
| [4] | 高见, 杨宜海, 黄世源, 杨聪, 张元生, 柳存喜, 李少睿, 花茜. 重庆地区地壳各向异性及其构造启示[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(1): 147-162. |
| [5] | 唐明帅, 王海涛, 魏芸芸, 李艳永, 葛粲, 王琼, 苏金波, 魏斌. 2012年新源-和静MS6.6地震前后地壳介质泊松比变化[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(5): 1123-1135. |
| [6] | 王霞, 宋美琴, 郑勇, 艾三喜. 山西及邻区壳幔速度图像特征及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(1): 119-136. |
| [7] | 谈洪波, 申重阳, 玄松柏, 吴桂桔, 杨光亮, 汪健. 鲁甸MS6.5地震孕育环境的重力学分析[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(2): 356-373. |
| [8] | 王林, 周青云, 王峻, 李文巧, 周连庆, 陈翰林, 苏鹏, 梁朋. 基于深部地震资料与地表变形资料的芦山地震发震构造研究[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(2): 458-476. |
| [9] | 王鑫, 张景发, 付萍杰, 高敏. 沂沭断裂带重力场及地壳结构特征[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(3): 731-747. |
| [10] | 杨光亮, 申重阳, 谈洪波, 王嘉沛, 吴桂桔. 云南鲁甸MS6.5地震震区地壳密度结构特征[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(4): 1145-1156. |
| [11] | 李永华, 徐小明, 张恩会, 高家乙. 青藏高原东南缘地壳结构及云南鲁甸、景谷地震深部孕震环境[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(4): 1204-1216. |
| [12] | 洪德全, 王行舟, 李军辉, 倪四道. 利用远震接收函数研究安徽地区地壳厚度[J]. 地震地质, 2013, 35(4): 853-863. |
| [13] | 王小龙, 马胜利, 雷兴林, 郭欣, 王强, 于国政, 勾宪斌, 桑原保人, 今西和俊, 蒋霞东. 重庆荣昌诱发地震区精细速度结构及2010年ML5.1地震序列精确定位[J]. 地震地质, 2012, (2): 348-358. |
| [14] | 王小龙, 倪四道, 刘渊源, 余国政, 李克昌. 利用远震接收函数分析三峡库区重庆段地壳厚度变化[J]. 地震地质, 2010, 32(4): 543-551. |
| [15] | 赵国泽, 詹艳, 王立凤, 王继军, 汤吉, 陈小斌, 肖骑彬. 鄂尔多斯断块地壳电性结构[J]. 地震地质, 2010, 32(3): 345-359. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||