地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 859-875.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.04.003
杨文健1,2)( ), 赵波1,2),*(
), 赵波1,2),*( ), 于红梅1,2), 许建东1,2), 潘波1,2), 王锡娇3)
), 于红梅1,2), 许建东1,2), 潘波1,2), 王锡娇3)
收稿日期:2021-05-08
修回日期:2021-06-16
出版日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-09-23
通讯作者:
赵波
作者简介:杨文健, 男, 1994年生, 2020年于中国地震局地质研究所获矿物学、 岩石学、 矿床学专业硕士学位, 现为中国地震局地质研究所矿物学、 岩石学、 矿床学专业在读博士研究生, 研究方向为岩石地球化学, E-mail: yangwenjian@ies.ac.cn。
基金资助:
YANG Wen-jian1,2)( ), ZHAO Bo1,2),*(
), ZHAO Bo1,2),*( ), YU Hong-mei1,2), XU Jian-dong1,2), PAN Bo1,2), WANG Xi-jiao3)
), YU Hong-mei1,2), XU Jian-dong1,2), PAN Bo1,2), WANG Xi-jiao3)
Received:2021-05-08
Revised:2021-06-16
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-09-23
Contact:
ZHAO Bo
摘要:
琼北作为中国最大的第四纪火山区之一, 其火山活动表现出多期、 多旋回的特征, 但位于其西北角的峨蔓火山岩的喷发时代依然存在争议。文中对峨蔓火山区展开了详细的火山地质及地貌调查, 并结合全岩主量元素分析及火山岩K-Ar年代学和贝壳14C年代学研究, 揭示了其火山活动时代和喷发特征等。峨蔓火山区包括笔架岭、 春历岭、 兵马角、 龙门激浪、 龙门灯塔及张屋等火山, 其火山喷发方式主要为溢流式喷发、 射汽-岩浆爆破式喷发和弱岩浆爆破式喷发。熔岩流几乎遍及整个火山区, 分布面积约为26.3km2; 基浪堆积物、 溅落堆积物以及火山渣分布范围较小, 仅限于龙门激浪-五彩湾和张屋村附近。峨蔓火山岩成分变化较大, 整体偏中性, 主要由玄武安山岩、 玄武粗安岩和粗安岩组成, 岩浆演化过程经历了橄榄石和单斜辉石的结晶分异。综合火山岩风化程度(球形风化、 红土层)、 火山地质与地貌特征(锥体形貌、 坡度)、 岩石学和地球化学特征(橄榄石斑晶蚀变、 全岩成分差异)以及K-Ar年龄(0.12~0.44Ma)和贝壳14C年代学结果((43.27±0.67)ka BP), 分析认为峨蔓火山区的火山活动时代应属于中、 晚更新世。
中图分类号:
杨文健, 赵波, 于红梅, 许建东, 潘波, 王锡娇. 琼北峨蔓地区火山地质与喷发历史[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 859-875.
YANG Wen-jian, ZHAO Bo, YU Hong-mei, XU Jian-dong, PAN Bo, WANG Xi-jiao. STUDY ON VOLCANIC GEOLOGY AND HISTORY OF ERUPTION IN EMAN AREA, NORTHERN HAINAN ISLAND[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(4): 859-875.
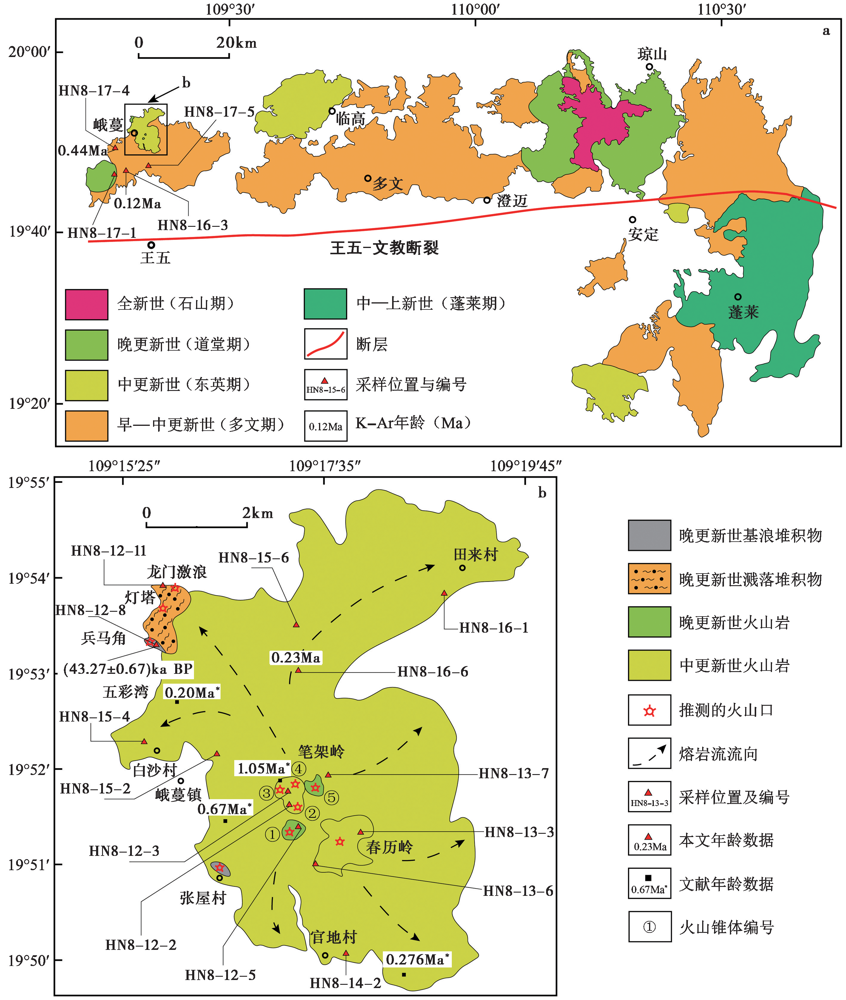
图1 a 琼北晚新生代火山岩分布图(据刘建强等, 2013修改); b 峨蔓火山区火山地质简图 年龄数据来自文献(葛同明等, 1989; 张仲英等, 1989; 朱炳泉等, 1989; 樊祺诚等, 2004)
Fig. 1 The distribution map of the Late Cenozoic volcanic rocks in Qiongbei (modified after LIU Jian-qiang et al., 2013)(a) and the brief geological map of Eman volcanic field(b).
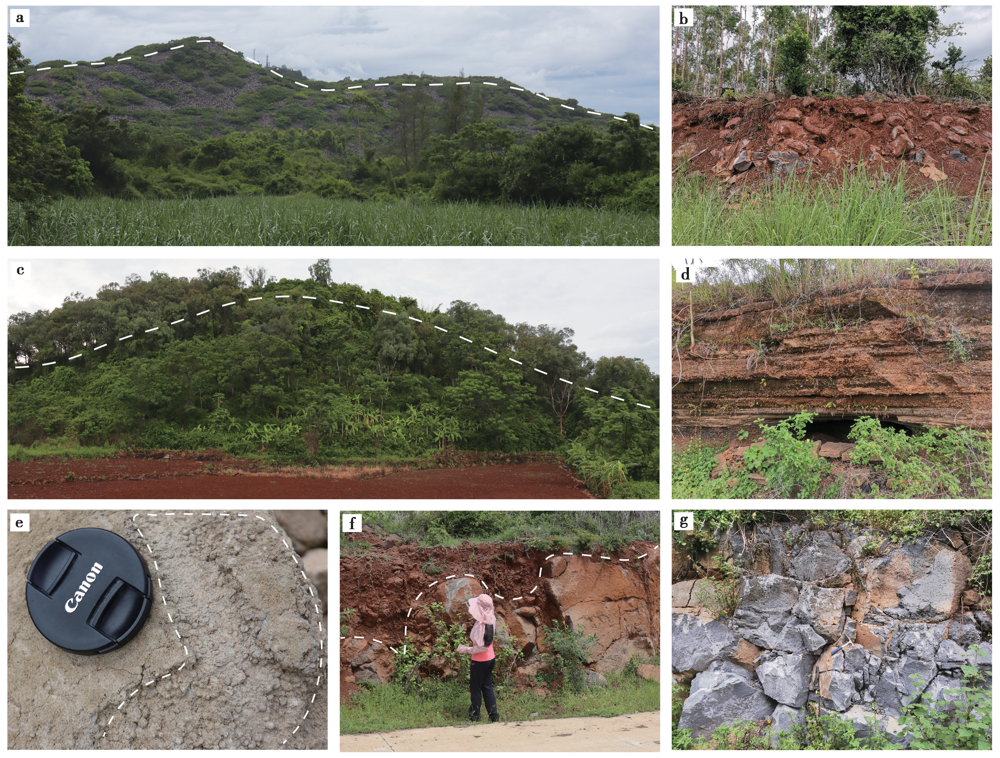

图2 峨蔓地区的野外地质照片 a 笔架岭5号火山, 块状熔岩较裸露, 且发育3级熔岩流阶梯; b 5号火山下部的露头剖面, 为致密的灰黑色块状熔岩, 其顶部被厚层红土所覆盖; c 春历岭火山, 坡度较缓, 森林和植被覆盖程度高; d、 e 分别为张屋村火山基浪堆积物中发育的平行层理和增生火山砾构造; f 峨蔓火山区外围和盛中更新世火山岩, 发育球形风化; g 海口石山镇全新世马鞍岭火山岩剖面照片, 该剖面节理和裂隙发育, 基本无风化
Fig. 2 Field geological photo in Eman region.
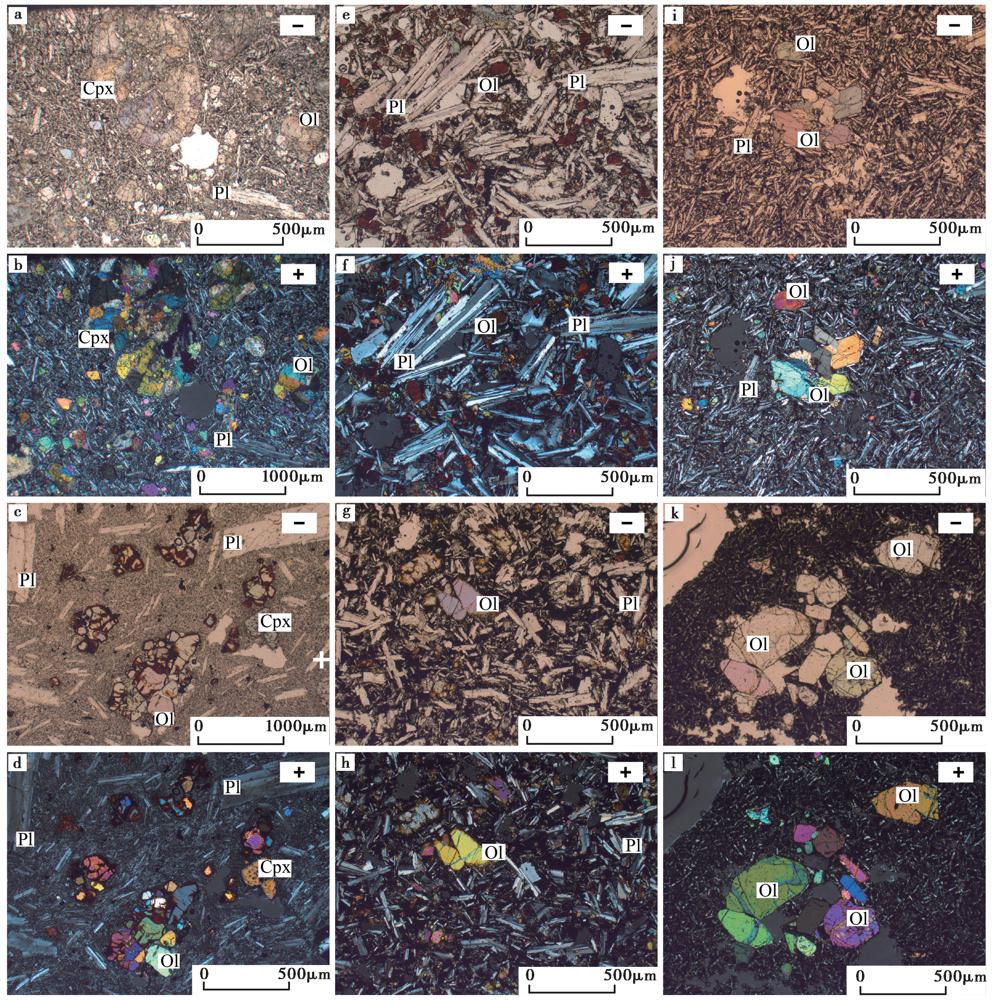
图5 峨蔓及外围的火山岩与海口地区(马鞍岭、 昌道岭)的火山岩显微照片 a、 b 峨蔓笔架岭玄武粗安岩, 辉石斑晶具有砂钟、 熔蚀结构, 基质为间隐结构, 可见斜长石微晶; c、 d 峨蔓春历岭粗安岩, 橄榄石斑晶伊丁石化现象明显, 辉石斑晶见内部溶蚀, 基质为间隐-玻璃结构, 含有斜长石和磁铁矿微晶; e、 f 峨蔓外围中更新世和盛粗面玄武岩, 橄榄石斑晶伊丁石化现象明显, 基质为间隐-玻璃结构, 含有斜长石和磁铁矿微晶; g、 h 马鞍岭北钻孔揭露的晚更新世玄武岩, 玻基斑状结构, 橄榄石斑晶发育伊丁石化现象; i、 j 马鞍岭全新世玄武岩, 基质为间隐结构, 含有大量斜长石和辉石微晶; k、 l 昌道岭全新世玄武岩, 基质为间隐结构, 含有大量斜长石微晶。Ol 橄榄石; Cpx 单斜辉石; Pl 斜长石。“-”和“+”分别表示单偏光和正交偏光照片
Fig. 5 Microphotographs of volcanic rocks in Eman, its periphery and Haikou area(Maanling and Changdaoling).
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | P2O5 | H2O+ | H2O- | LOI | 总和 | Mg# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HN8-12-2 | 54.05 | 1.59 | 14.35 | 11.50 | 7.99 | 8.09 | 6.11 | 0.70 | 3.07 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.73 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 99.87 | 51.3 |
| HN8-12-3 | 55.00 | 1.55 | 15.64 | 9.01 | 2.28 | 4.80 | 3.94 | 3.50 | 4.98 | 0.10 | 0.52 | 0.65 | 0.44 | 0.67 | 99.71 | 46.4 |
| HN8-12-5 | 51.54 | 2.02 | 14.48 | 10.82 | 7.79 | 6.99 | 6.79 | 2.59 | 4.36 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.26 | 0.42 | -0.47 | 99.76 | 55.4 |
| HN8-12-8 | 53.36 | 1.64 | 14.45 | 11.78 | 8.54 | 8.26 | 6.17 | 0.62 | 3.42 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.65 | 0.44 | -0.18 | 99.87 | 50.9 |
| HN8-12-11 | 53.42 | 1.62 | 14.60 | 11.58 | 1.23 | 8.02 | 6.25 | 0.70 | 3.05 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 99.86 | 51.7 |
| HN8-13-3 | 53.90 | 1.60 | 14.16 | 11.67 | 8.66 | 8.20 | 6.31 | 0.73 | 2.95 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.54 | 0.35 | -0.1 | 99.81 | 51.7 |
| HN8-13-6 | 54.99 | 1.59 | 15.23 | 9.12 | 5.95 | 5.09 | 5.10 | 3.42 | 4.75 | 0.10 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.36 | -0.19 | 99.72 | 52.6 |
| HN8-13-7 | 51.78 | 2.01 | 14.41 | 10.78 | 7.36 | 6.99 | 6.75 | 2.56 | 4.13 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.18 | -0.3 | 99.76 | 55.4 |
| HN8-14-2 | 52.79 | 1.68 | 14.89 | 12.08 | 8.90 | 8.39 | 6.41 | 0.49 | 3.02 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.58 | 0.33 | -0.23 | 99.87 | 51.2 |
| HN8-15-2 | 54.13 | 1.76 | 16.22 | 10.06 | 4.39 | 4.91 | 4.09 | 2.97 | 4.49 | 0.12 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 99.71 | 44.6 |
| HN8-15-4 | 54.28 | 1.67 | 15.04 | 9.45 | 5.47 | 6.18 | 5.47 | 2.60 | 4.52 | 0.10 | 0.46 | 0.35 | 0.32 | -0.03 | 99.74 | 53.4 |
| HN8-15-6 | 51.49 | 2.06 | 14.88 | 11.20 | 7.00 | 6.92 | 6.12 | 2.52 | 3.87 | 0.12 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 99.73 | 52.0 |
| HN8-16-1 | 51.39 | 2.10 | 14.96 | 11.23 | 4.75 | 6.84 | 5.80 | 2.52 | 3.83 | 0.13 | 0.52 | 0.63 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 99.73 | 50.6 |
| HN8-16-6 | 51.55 | 2.05 | 14.55 | 11.11 | 7.14 | 6.94 | 6.83 | 2.43 | 3.71 | 0.14 | 0.49 | 0.61 | 0.34 | -0.08 | 99.72 | 54.9 |
| HN8-16-3 | 52.32 | 1.97 | 14.66 | 10.24 | 6.24 | 6.84 | 6.42 | 2.57 | 4.10 | 0.12 | 0.51 | 0.35 | 0.36 | -0.02 | 99.73 | 55.4 |
| HN8-17-1 | 51.70 | 1.90 | 14.26 | 11.42 | 7.70 | 7.87 | 7.13 | 1.66 | 3.86 | 0.14 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.11 | -0.57 | 99.79 | 55.3 |
| HN8-17-4 | 51.39 | 1.83 | 14.32 | 11.45 | 6.08 | 8.05 | 7.10 | 1.58 | 3.78 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.23 | 0.17 | -0.24 | 99.77 | 55.1 |
| HN8-17-5 | 52.39 | 1.66 | 14.83 | 12.07 | 8.20 | 8.37 | 6.61 | 0.38 | 2.97 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.62 | 0.48 | 0.24 | 99.86 | 52.1 |
表1 峨蔓及外围火山岩主量元素的分析结果(wt%)
Table 1 Major element(wt%)analyses of volcanic rocks in Eman and its periphery
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO | P2O5 | H2O+ | H2O- | LOI | 总和 | Mg# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HN8-12-2 | 54.05 | 1.59 | 14.35 | 11.50 | 7.99 | 8.09 | 6.11 | 0.70 | 3.07 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.73 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 99.87 | 51.3 |
| HN8-12-3 | 55.00 | 1.55 | 15.64 | 9.01 | 2.28 | 4.80 | 3.94 | 3.50 | 4.98 | 0.10 | 0.52 | 0.65 | 0.44 | 0.67 | 99.71 | 46.4 |
| HN8-12-5 | 51.54 | 2.02 | 14.48 | 10.82 | 7.79 | 6.99 | 6.79 | 2.59 | 4.36 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.26 | 0.42 | -0.47 | 99.76 | 55.4 |
| HN8-12-8 | 53.36 | 1.64 | 14.45 | 11.78 | 8.54 | 8.26 | 6.17 | 0.62 | 3.42 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.65 | 0.44 | -0.18 | 99.87 | 50.9 |
| HN8-12-11 | 53.42 | 1.62 | 14.60 | 11.58 | 1.23 | 8.02 | 6.25 | 0.70 | 3.05 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 99.86 | 51.7 |
| HN8-13-3 | 53.90 | 1.60 | 14.16 | 11.67 | 8.66 | 8.20 | 6.31 | 0.73 | 2.95 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.54 | 0.35 | -0.1 | 99.81 | 51.7 |
| HN8-13-6 | 54.99 | 1.59 | 15.23 | 9.12 | 5.95 | 5.09 | 5.10 | 3.42 | 4.75 | 0.10 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.36 | -0.19 | 99.72 | 52.6 |
| HN8-13-7 | 51.78 | 2.01 | 14.41 | 10.78 | 7.36 | 6.99 | 6.75 | 2.56 | 4.13 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.18 | -0.3 | 99.76 | 55.4 |
| HN8-14-2 | 52.79 | 1.68 | 14.89 | 12.08 | 8.90 | 8.39 | 6.41 | 0.49 | 3.02 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.58 | 0.33 | -0.23 | 99.87 | 51.2 |
| HN8-15-2 | 54.13 | 1.76 | 16.22 | 10.06 | 4.39 | 4.91 | 4.09 | 2.97 | 4.49 | 0.12 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 99.71 | 44.6 |
| HN8-15-4 | 54.28 | 1.67 | 15.04 | 9.45 | 5.47 | 6.18 | 5.47 | 2.60 | 4.52 | 0.10 | 0.46 | 0.35 | 0.32 | -0.03 | 99.74 | 53.4 |
| HN8-15-6 | 51.49 | 2.06 | 14.88 | 11.20 | 7.00 | 6.92 | 6.12 | 2.52 | 3.87 | 0.12 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 99.73 | 52.0 |
| HN8-16-1 | 51.39 | 2.10 | 14.96 | 11.23 | 4.75 | 6.84 | 5.80 | 2.52 | 3.83 | 0.13 | 0.52 | 0.63 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 99.73 | 50.6 |
| HN8-16-6 | 51.55 | 2.05 | 14.55 | 11.11 | 7.14 | 6.94 | 6.83 | 2.43 | 3.71 | 0.14 | 0.49 | 0.61 | 0.34 | -0.08 | 99.72 | 54.9 |
| HN8-16-3 | 52.32 | 1.97 | 14.66 | 10.24 | 6.24 | 6.84 | 6.42 | 2.57 | 4.10 | 0.12 | 0.51 | 0.35 | 0.36 | -0.02 | 99.73 | 55.4 |
| HN8-17-1 | 51.70 | 1.90 | 14.26 | 11.42 | 7.70 | 7.87 | 7.13 | 1.66 | 3.86 | 0.14 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.11 | -0.57 | 99.79 | 55.3 |
| HN8-17-4 | 51.39 | 1.83 | 14.32 | 11.45 | 6.08 | 8.05 | 7.10 | 1.58 | 3.78 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.23 | 0.17 | -0.24 | 99.77 | 55.1 |
| HN8-17-5 | 52.39 | 1.66 | 14.83 | 12.07 | 8.20 | 8.37 | 6.61 | 0.38 | 2.97 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.62 | 0.48 | 0.24 | 99.86 | 52.1 |
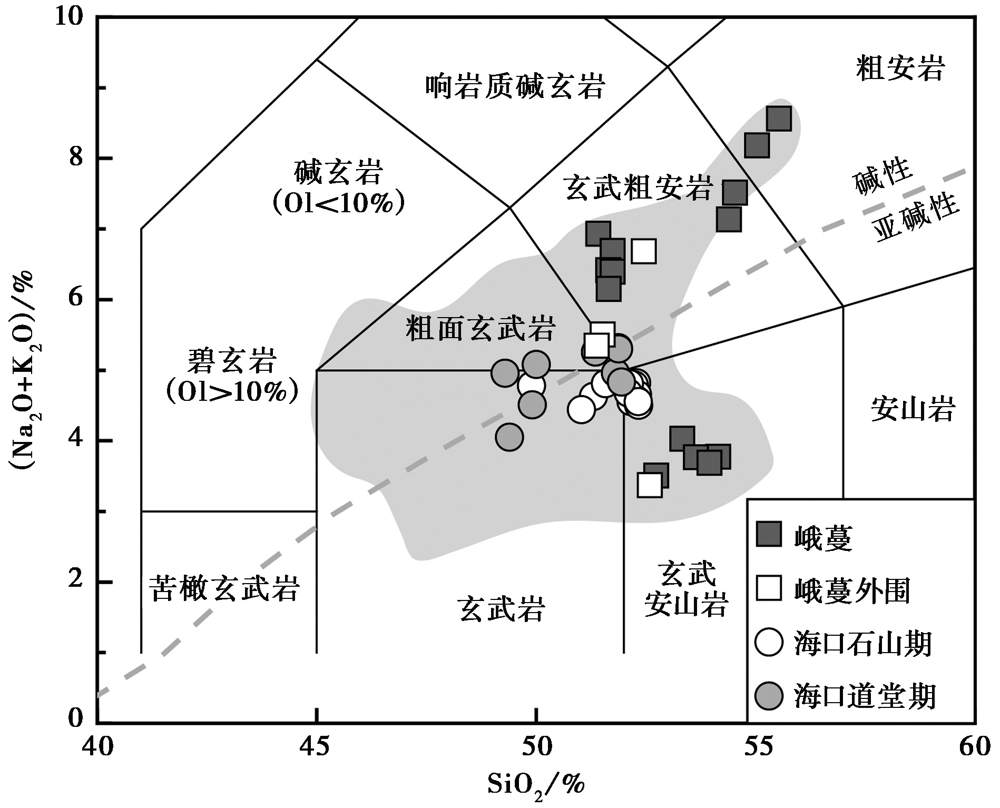
图6 峨蔓以及外围地区火山岩的TAS分类图解(底图据Le Bas et al., 1986) 海口全新世石山期(马鞍岭火山、 昌道岭火山)火山岩和晚更新世道堂期(马鞍岭北)火山岩的数据来自于红梅未发表的成果; 阴影区域代表琼北火山岩的成分变化范围, 数据来自文献(韩江伟等, 2009; Ho et al., 2000; Zou et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2012; Liu et al., 2015; 丁望, 2017)
Fig. 6 TAS diagram of volcanic rocks in Eman and its periphery(after Le Bas et al., 1986).
| 位置 | 锥底直径1/m | 锥底直径2/m | 高度/m | 平均坡度/(°) | 最大坡度/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 笔架岭1号火山 | 355 | 338 | 40 | 11.79 | 23.12 |
| 笔架岭5号火山 | 301 | 420 | 60 | 12.39 | 28.74 |
| 春历岭火山西南侧 | 300 | 198 | 35 | 18.65 | 21.31 |
| 春历岭火山北侧 | 561 | 563 | 30 | 5.01 | 11.83 |
| 马鞍岭火山 | 500 | 408 | 40 | 15.64 | 30.50 |
表2 笔架岭、 春历岭和马鞍岭火山的主要参数
Table 2 Major parameters of Bijialing, Chunliling and Maanling volcanoes
| 位置 | 锥底直径1/m | 锥底直径2/m | 高度/m | 平均坡度/(°) | 最大坡度/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 笔架岭1号火山 | 355 | 338 | 40 | 11.79 | 23.12 |
| 笔架岭5号火山 | 301 | 420 | 60 | 12.39 | 28.74 |
| 春历岭火山西南侧 | 300 | 198 | 35 | 18.65 | 21.31 |
| 春历岭火山北侧 | 561 | 563 | 30 | 5.01 | 11.83 |
| 马鞍岭火山 | 500 | 408 | 40 | 15.64 | 30.50 |
| 样品编号 | 采样点 | 岩性 | K/% | | | 表面年龄±1σ/Ma | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81-K-15 | 笔架山 | 火山岩 | 1.52 | 2.402×10-12 | 4.95 | 1.05±0.30 | 朱炳泉等, |
| K-3 | 峨蔓 | 火山岩 | 2.24 | 7.86×10-13 | 16.58 | 0.20±0.01 | 葛同明等, |
| EMB-6 | 峨蔓岭西 | 火山岩 | 1.03 | 1.196×10-12 | 7.517 | 0.67±0.07 | 樊祺诚等, |
| HN8-16-3 | 三都村东 | 火山岩 | 1.73 | 2.96×10-13 | 7.23 | 0.12±0.01 | 本工作 |
| HN8-16-6 | 鱼骨村南 | 火山岩 | 2.24 | 6.98×10-13 | 25.06 | 0.23±0.01 | 本工作 |
| HN8-17-4 | 和盛北 | 火山岩 | 2.55 | 1.54×10-12 | 5.16 | 0.44±0.06 | 本工作 |
表3 峨蔓火山岩的K-Ar年龄结果
Table 3 The K-Ar chronology of volcanic rocks in Eman
| 样品编号 | 采样点 | 岩性 | K/% | | | 表面年龄±1σ/Ma | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81-K-15 | 笔架山 | 火山岩 | 1.52 | 2.402×10-12 | 4.95 | 1.05±0.30 | 朱炳泉等, |
| K-3 | 峨蔓 | 火山岩 | 2.24 | 7.86×10-13 | 16.58 | 0.20±0.01 | 葛同明等, |
| EMB-6 | 峨蔓岭西 | 火山岩 | 1.03 | 1.196×10-12 | 7.517 | 0.67±0.07 | 樊祺诚等, |
| HN8-16-3 | 三都村东 | 火山岩 | 1.73 | 2.96×10-13 | 7.23 | 0.12±0.01 | 本工作 |
| HN8-16-6 | 鱼骨村南 | 火山岩 | 2.24 | 6.98×10-13 | 25.06 | 0.23±0.01 | 本工作 |
| HN8-17-4 | 和盛北 | 火山岩 | 2.55 | 1.54×10-12 | 5.16 | 0.44±0.06 | 本工作 |
| 样品编号 | 采样点 | 岩性 | 测年方法 | 距今年龄/ka | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 峨蔓南部 | 凝灰岩烘烤层 | TL | 276±13.8 | 张仲英等, |
| HN8-12-8 | 兵马角 | 贝壳 | 14C | 43.27±0.67 | 本工作 |
表4 峨蔓浪堆积层中贝壳14C年龄和火山岩热释光(TL)年龄结果
| 样品编号 | 采样点 | 岩性 | 测年方法 | 距今年龄/ka | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 峨蔓南部 | 凝灰岩烘烤层 | TL | 276±13.8 | 张仲英等, |
| HN8-12-8 | 兵马角 | 贝壳 | 14C | 43.27±0.67 | 本工作 |
| [1] | 白志达, 谭庆伟, 许桂玲, 等. 2012. 内蒙东部晚第四纪火山活动与新构造[J]. 岩石学报, 28(4): 1099-1107. |
| BAI Zhi-da, TAN Qing-wei, XU Gui-ling, et al. 2012. Late Quaternary volcanic activity and neotectonics in the eastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(4): 1099-1107. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 白志达, 徐德斌, 魏海泉, 等. 2003. 琼北马鞍岭地区第四纪火山活动期次划分[J]. 地震地质, 25(S1): 12-20. |
| BAI Zhi-da, XU De-bin, WEI Hai-quan, et al. 2003. Division of the active period of Quaternary volcanism in Maanling, northern Hainan Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 25(S1): 12-20. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 白志达, 徐德斌, 张秉良, 等. 2006. 龙岗火山群第四纪爆破式火山作用类型与期次研究[J]. 岩石学报, 22(6): 1473-1480. |
| BAI Zhi-da, XU De-bin, ZHANG Bing-liang, et al. 2006. Study on type and phase of Quaternary explosive volcanism in Longgang volcanic cluster[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(6): 1473-1480. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 白志达, 张进奎, 史志伟, 等. 2020. 内蒙中部辉腾锡勒第四纪火山群初步研究[J]. 岩石学报, 36(11): 3257-3264. |
|
BAI Zhi-da, ZHANG Jin-kui, SHI Zhi-wei, et al. 2020. Preliminary study on Quaternary volcanic cluster in Huitengxile, central Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(11): 3257-3264. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [5] | 边兆祥. 1958. 海南岛第四纪火山[J]. 第四纪研究, 1(1): 250-251. |
| BIAN Zhao-xiang. 1958. Quaternary volcano of Hainan Island[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1(1): 250-251. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 丁望. 2017. 南海扩张期后西北缘岩浆-构造活动解析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学:22-23. |
| DING Wang. 2017. Approach to magmatic and tectonic activities in post-spreading stage of the South China Sea by analyzing relics from its northern and western margin[D]. China University of Geosciences, Beijing: 22-23. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 樊祺诚, 孙建中. 1987. 琼北第四纪玄武岩的岩石学和地球化学[J]. 科学通报, 32(4): 287-291. |
| FAN Qi-cheng, SUN Jian-zhong. 1987. Petrology and geochemistry of Quaternary basalt in north Hainan Island[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 32(4): 287-291. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 樊祺诚, 孙谦, 李霓, 等. 2004. 琼北火山活动分期与全新世岩浆演化[J]. 岩石学报, 20(3): 533-544. |
| FAN Qi-cheng, SUN Qian, LI Ni, et al. 2004. Periods of volcanic activity and magma evolution of Holocene in north Hainan Island[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3): 533-544. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 樊祺诚, 孙谦, 龙安明, 等. 2006. 北部湾涠洲岛及斜阳岛火山地质与喷发历史研究[J]. 岩石学报, 22(6): 1529-1537. |
| FAN Qi-cheng, SUN Qian, LONG An-ming, et al. 2006. Geology and eruption history of volcanoes in Weizhou Island and Xieyang Island, Northern Bay[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(6): 1529-1537. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 付建明. 1997. 琼北新生代火山作用与构造环境[J]. 桂林工学院学报, 17(1): 26-33. |
| FU Jian-ming. 1997. Cenozoic volcanism and tectonic settings in north Hainan Island[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 17(1): 26-33. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 符启基, 沈金羽, 林才. 2012. 海南省笔架岭火山口及峨蔓湾地质遗迹景观开发初探[J]. 资源环境与工程, 26(6): 641-644. |
| FU Qi-ji, SHEN Jin-yu, LIN Cai. 2012. Discussion on development of geological relic landscape of Bijialing crater and Mindanao Man Bay in Hainan Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 26(6): 641-644. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 葛同明, 陈文寄, 徐行, 等. 1989. 雷琼地区第四纪地磁极性年表: 火山岩钾-氩年龄及古地磁学证据[J]. 地球物理学报, 32(5): 550-558. |
| GE Tong-ming, CHEN Wen-ji, XU Xing, et al. 1989. The geomagnetic polarity timescale of Quaternary for Leiqiong region: The K-Ar dating and palaeomagnetic evidences from igneous rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 32(5): 550-558. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 海南省地质调查院. 2007. 东方县幅E49C001001 1︰25万区域地质调查报告[R]. 海口: 海南省地质调查院. |
| Hainan Institute of Geological Survey. 2007. Regional geological survey report of Dongfang County map(E49C001001)[R]. Hainan Institute of Geological Survey, Haikou. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 韩江伟, 熊小林, 朱照宇. 2009. 雷琼地区晚新生代玄武岩地球化学: EM2成分来源及大陆岩石圈地幔的贡献[J]. 岩石学报, 25(12): 3208-3220. |
| HAN Jiang-wei, XIONG Xiao-lin, ZHU Zhao-yu. 2009. Geochemistry of Late-Cenozoic basalts from Leiqiong area: The origin of EM2 and the contribution from sub-continental lithosphere mantle[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(12): 3208-3220. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 黄镇国, 蔡福祥. 1994. 雷琼第四纪火山活动的新认识[J]. 热带地理, (1): 1-10. |
| HUANG Zhen-guo, CAI Fu-xiang. 1994. A new approach to the Quaternary volcanicity in the Leiqiong area[J]. Tropical Geography, (1): 1-10. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 黄镇国, 蔡福祥, 韩中元, 等. 1993. 雷琼第四纪火山[M]. 北京: 科学出版社:1-220. |
| HUANG Zhen-guo, CAI Fu-xiang, HAN Zhong-yuan, et al. 1993. Quaternary Volcanoes of Leiqiong Area[M]. Science Press, Beijing: 1-220. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 梁光河. 2018. 海南岛的成因机制研究[J]. 中国地质, 45(4): 693-705. |
| LIANG Guang-he. 2018. A study of the genesis of Hainan Island[J]. Geology in China, 45(4): 693-705. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 刘建强, 任钟元. 2013. 玄武岩源区母岩的多样性和识别特征: 以海南岛玄武岩为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 37(3): 471-488. |
| LIU Jian-qiang, REN Zhong-yuan. 2013. Diversity of source lithology and its identification for basalts: A case study of the Hainan basalts[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 37(3): 471-488. | |
| [19] | 刘祥. 1996. 当代火山喷发碎屑堆积物的研究进展及其主要类型[J]. 世界地质, 15(1): 1-6. |
| LIU Xiang. 1996. Advances in pyroclastic deposits at present and the main types of the pyroclastic deposits[J]. Global Geology, 15(1): 1-6. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 孙谦. 2003. 琼北第四纪火山活动与岩浆演化[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所:1-35. |
| SUN Qian. 2003. Quaternary volcanic activity and magma evolution in north Hainan Island [D]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing: 1-35. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 王薇华. 2007. 海口火山旅游资源开发研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学:18-20. |
| WANG Wei-hua. 2007. Research on the development of volcanic traveling resources in Haikou City[D]. China University of Geosciences, Beijing: 18-20. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 汪啸风, 马大铨, 蒋大海. 1992. 海南岛地质(二): 岩浆岩[M]. 北京: 地质出版社:167-169. |
| WANG Xiao-feng, MA Da-quan, JIANG Da-hai. 1992. Geology of Hainan Province(Volume Two): Magmatic Rocks[M]. Geological Publishing House, Beijing: 167-169. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 魏海泉, 白志达, 胡久常, 等. 2003. 琼北全新世火山区火山系统的划分与锥体结构参数研究[J]. 地震地质, 25(S1): 21-32. |
| WEI Hai-quan, BAI Zhi-da, HU Jiu-chang, et al. 2003. Nomenclature of the Holocene volcanic systems and research on the textural parameters of the scoria cones in northern Hainan Island[J]. Seismology and Geology, 25(S1): 21-32. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] |
许建东, 于红梅, 周本刚, 等. 2019. 核电厂选址的火山安全评价与灾害评估[J]. 地震地质, 41(5): 1289-1301.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.05.015.
DOI |
| XU Jian-dong, YU Hong-mei, ZHOU Ben-gang, et al. 2019. Site evaluation and volcanic hazard assessment for the nuclear power plants of China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 41(5): 1289-1301. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 杨文健, 于红梅, 赵波, 等. 2020. 广西涠洲岛晚新生代玄武岩地幔源区及岩浆成因[J]. 岩石学报, 36(7): 2092-2110. |
|
YANG Wen-jian, YU Hong-mei, ZHAO Bo, et al. 2020. Mantle sources and magma genesis of late Cenozoic basalts from Weizhou Island, Guangxi, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(7): 2092-2110. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [26] | 于红梅. 2011. 火山喷发物的显微构造研究及其地质意义[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所:1-40. |
| YU Hong-mei. 2011. Microstructural study on volcanic products and its geological implications[D]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing: 1-40. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 曾广策. 1984. 海南岛北部第四纪玄武岩岩石学[J]. 地球科学, (1): 63-72. |
| ZENG Guang-ce. 1984. Petrology of Quaternary basalt in the north of Hainan Island[J]. Earth Science, (1): 63-72. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 张仲英, 刘瑞华. 1989. 海南岛第四系火山岩的分期[J]. 地质科学, (1): 67-76. |
| ZHANG Zhong-ying, LIU Rui-hua. 1989. The stage-division of Quaternary volcanic rocks in Hainan Island[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, (1): 67-76. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 赵波, 许建东, 潘波, 等. 2008. 吉林龙岗龙泉龙湾火山火口基浪堆积物粒度特征及搬运机制分析[J]. 岩石学报, 24(11): 2631-2637. |
| ZHAO Bo, XU Jian-dong, PAN Bo, et al. 2008. Preliminary study on grain size distribution and transportation characteristics of the base-surge deposits near Longquanlongwan volcano crater, Jilin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(11): 2631-2637. (in Chinese) | |
| [30] |
赵波, 许建东, 于红梅. 2010. 长白山地区火山碎屑粒度特征研究[J]. 地震地质, 32(2): 233-243.. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2010.02.006.
DOI |
| ZHAO Bo,XU Jian-dong,YU Hong-mei. 2010. Grain size characteristics of pyroclasts in Changbaishan Mountain area[J]. Seismology and Geology, 32(2): 233-243. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 赵勇伟, 樊祺诚, 白志达, 等. 2008. 大兴安岭哈拉哈河-淖尔河地区第四纪火山活动初步研究[J]. 岩石学报, 24(11): 2569-2575. |
| ZHAO Yong-wei, FAN Qi-cheng, BAI Zhi-da, et al. 2008. Preliminary study on Quaternary volcanoes in the Halaha River and Chaoer River area in Daxing’an Mountain range[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(11): 2569-2575. (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 赵勇伟, 樊祺诚, 白志达, 等. 2013. 大兴安岭诺敏河-奎勒河地区第四纪火山活动研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 43(9): 1464-1473. |
| ZHAO Yong-wei, FAN Qi-cheng, BAI Zhi-da, et al. 2013. Quaternary volcanism in the Nuomin River and Kuile River area of the Greater Hinggan Mountains[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 43(9): 1464-1473. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | 朱炳泉, 王慧芬. 1989. 雷琼地区MORB-OIB过渡型地幔源火山作用的Nd-Sr-Pb同位素证据[J]. 地球化学, (3): 193-201. |
| ZHU Bing-quan, WANG Hui-fen. 1989. Nd-Sr-Pb isotopic and chemical evidence for the volcanism with MORB-OIB source characteristics in the Leiqiong area, China[J]. Geochimica, (3): 193-201. (in Chinese) | |
| [34] | Briais A, Patriat P, Tapponnier P. 1993. Updated interpretation of magnetic anomalies and seafloor spreading stages in the South China Sea: Implications for the Tertiary tectonics of Southeast Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 98(B4): 6299-6328. |
| [35] |
Gu X Y, Wang P Y, Kuritani T, et al. 2019. Low water content in the mantle source of the Hainan plume as a factor inhibiting the formation of a large igneous province[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 515: 221-230.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Ho K S, Chen J C, Juang W S. 2000. Geochronology and geochemistry of late Cenozoic basalts from the Leiqiong area, southern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18(3): 307-324.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Le Bas M J, Le Maitre R W, Streckeisen A, et al. 1986. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 27(3): 745-750.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Lebedev S, Nolet G. 2003. Upper mantle beneath Southeast Asia from S velocity tomography[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(B1): ESE21-1-ESE21-26. |
| [39] | Lei J S, Zhao D P, Steinberger B, et al. 2009. New seismic constraints on the upper mantle structure of the Hainan plume[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 173(1-2): 33-50. |
| [40] |
Liu J Q, Ren Z Y, Nichols A R L, et al. 2015. Petrogenesis of Late Cenozoic basalts from North Hainan Island: Constraints from melt inclusions and their host olivines[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 152: 89-121.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Sigurdsson H. 2015. The History of Volcanology [M]∥ Sigurdsson H, Houghton B, McNutt S R, et al (eds). The Encyclopedia of Volcanoes(Second Edition). Academic Press, London: 13-32. |
| [42] |
Wang X C, Li Z X, Li X H, et al. 2012. Temperature, pressure, and composition of the mantle source region of late Cenozoic basalts in Hainan Island, SE Asia: A consequence of a young thermal mantle plume close to subduction zones?[J]. Journal of Petrology, 53(1): 177-233.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Wang X C, Li Z X, Li X H, et al. 2013. Identification of an ancient mantle reservoir and young recycled materials in the source region of a young mantle plume: Implications for potential linkages between plume and plate tectonics[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 377-378: 248-259. |
| [44] |
Wei W, Xu J D, Zhao D P, et al. 2012. East Asia mantle tomography: New insight into plate subduction and intraplate volcanism[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 60: 88-103.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Wei W, Zhao D P. 2020. Intraplate volcanism and mantle dynamics of Mainland China: New constraints from shear-wave tomography[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 188: 104103. |
| [46] |
Xia S H, Zhao D P, Sun J L, et al. 2016. Teleseismic imaging of the mantle beneath southernmost China: New insights into the Hainan plume[J]. Gondwana Research, 36: 46-56.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Zhao B, Xu D B, Bai Z D, et al. 2021. Volcanism in the Longgang volcanic field of NE China: Insights from eruption history, volcano types and geochemical characteristics[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 510(1): 27-39.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Zou H B, Fan Q C. 2010. U-Th isotopes in Hainan basalts: Implications for sub-asthenospheric origin of EM2 mantle endmember and the dynamics of melting beneath Hainan Island[J]. Lithos, 116(1-2): 145-152.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 杨列坤, 王非, 贺怀宇, 桑海清, 王英兰. 年轻火山岩氩同位素体系定年技术最新进展及问题[J]. 地震地质, 2009, 31(1): 174-185. |
| [2] | 孙谦, 樊祺诚. 琼北射气岩浆喷发力学机制探讨[J]. 地震地质, 2005, 27(1): 63-72. |
| [3] | 白志达, 徐德斌, 魏海泉, 胡久常. 琼北马鞍岭地区第四纪火山活动期次划分[J]. 地震地质, 2003, 25(s1): 12-20. |
| [4] | 陈孝德, 史兰斌, 林传勇. 华北第四纪火山作用研究[J]. 地震地质, 2001, 23(4): 564-573. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||