地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 845-858.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.04.002
赵凌强1)( ), 胡亚轩1),*(
), 胡亚轩1),*( ), 王庆良1), 祝意青1), 操聪1), 李仲巍2), 綦伟2), 汶宇龙1)
), 王庆良1), 祝意青1), 操聪1), 李仲巍2), 綦伟2), 汶宇龙1)
收稿日期:2021-03-23
修回日期:2021-08-04
出版日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-09-23
通讯作者:
胡亚轩
作者简介:赵凌强, 男, 1988年生, 2020年于中国地震局地质研究所获固体地球物理学专业博士学位, 高级工程师, 主要从事大地电磁在深部构造中的探测应用研究, E-mail: zhaolingqiang0926@126.com。
基金资助:
ZHAO Ling-qiang1)( ), HU Ya-xuan1),*(
), HU Ya-xuan1),*( ), WANG Qing-liang1), ZHU Yi-qing1), CAO Cong1), LI Zhong-wei2), QI Wei2), WEN Yu-long1)
), WANG Qing-liang1), ZHU Yi-qing1), CAO Cong1), LI Zhong-wei2), QI Wei2), WEN Yu-long1)
Received:2021-03-23
Revised:2021-08-04
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-09-23
Contact:
HU Ya-xuan
摘要:
龙岗火山群是中国主要的活火山之一, 其中的金龙顶子火山在距今约1600a前发生过大规模喷发活动, 具有潜在喷发危险。文中利用一条西起梅河口市、 东至长白山景区西门, 穿过龙岗火山核心区及金龙顶子火山, 长度超过160km的宽频带密集测点的大地电磁剖面数据进行相位张量分解和二维反演计算, 获得沿剖面的深部电性结构特征。分析表明, 龙岗火山群及邻区地壳范围内分布深浅不一的高阻结构, 且在早期形成的火山群下方分布更深, 推测与岩浆的固结作用有关。高阻体下方存在明显的大规模低阻结构, 推测为中下地壳岩浆系统, 研究区的地壳隆升及地震活动等可能与岩浆活动有关。最新喷发的金龙顶子火山下方(10km以深)可能存在着岩浆通道, 且与中下地壳岩浆系统相连接, 10km以浅的岩浆可能已经固结。在剖面东部发现的中下地壳低阻结构显示出继续向东部的长白山天池火山区延伸, 结合前人的大地电磁及地震学等研究结果推测, 龙岗火山群可能与长白山天池火山在中深部共用岩浆系统。
中图分类号:
赵凌强, 胡亚轩, 王庆良, 祝意青, 操聪, 李仲巍, 綦伟, 汶宇龙. 吉林龙岗火山区深部电性结构特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 845-858.
ZHAO Ling-qiang, HU Ya-xuan, WANG Qing-liang, ZHU Yi-qing, CAO Cong, LI Zhong-wei, QI Wei, WEN Yu-long. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF DEEP ELECTRICAL STRUCTURE IN LONGGANG VOLCANIC AREA, JILIN PROVINCE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(4): 845-858.
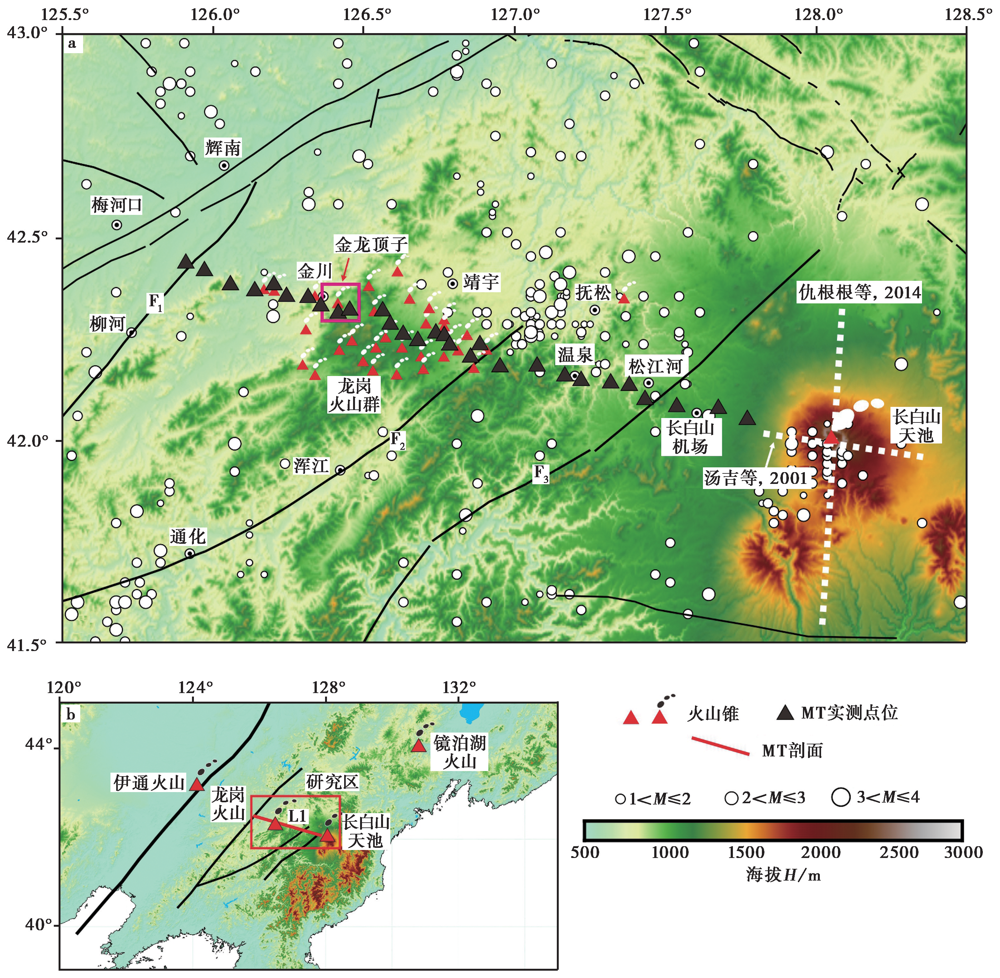
图1 吉林龙岗火山区域构造(邓起东等, 2003) a 大地电磁实测点位; b 研究区周边火山分布图。F1敦化-密山断裂; F2浑江断裂; F3鸭绿江断裂
Fig. 1 Regional structure of Longgang volcano in Jilin Province(DENG Qi-dong et al., 2003).
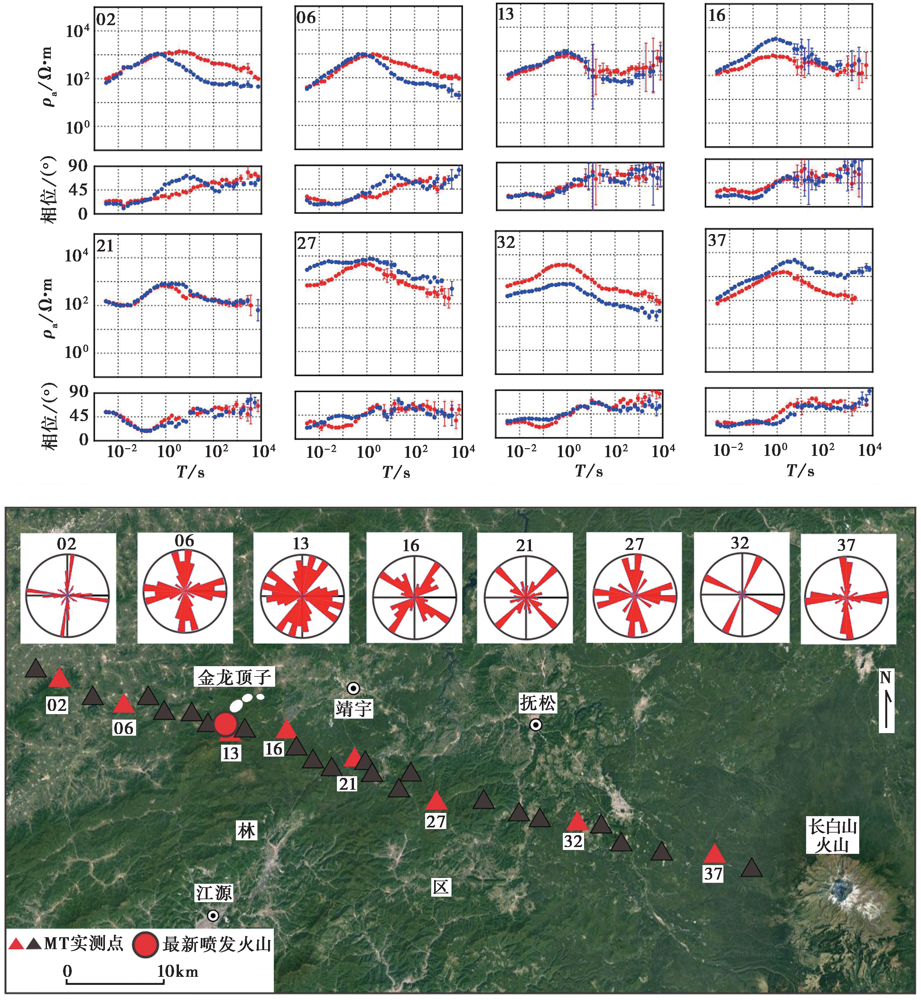
图2 研究区典型测点(红色三角形)的视电阻率相位曲线与地貌分布图
Fig. 2 Apparent resistivity and impedance phase curves of typical measuring points (red triangle)along profile and geomorphic distribution map.
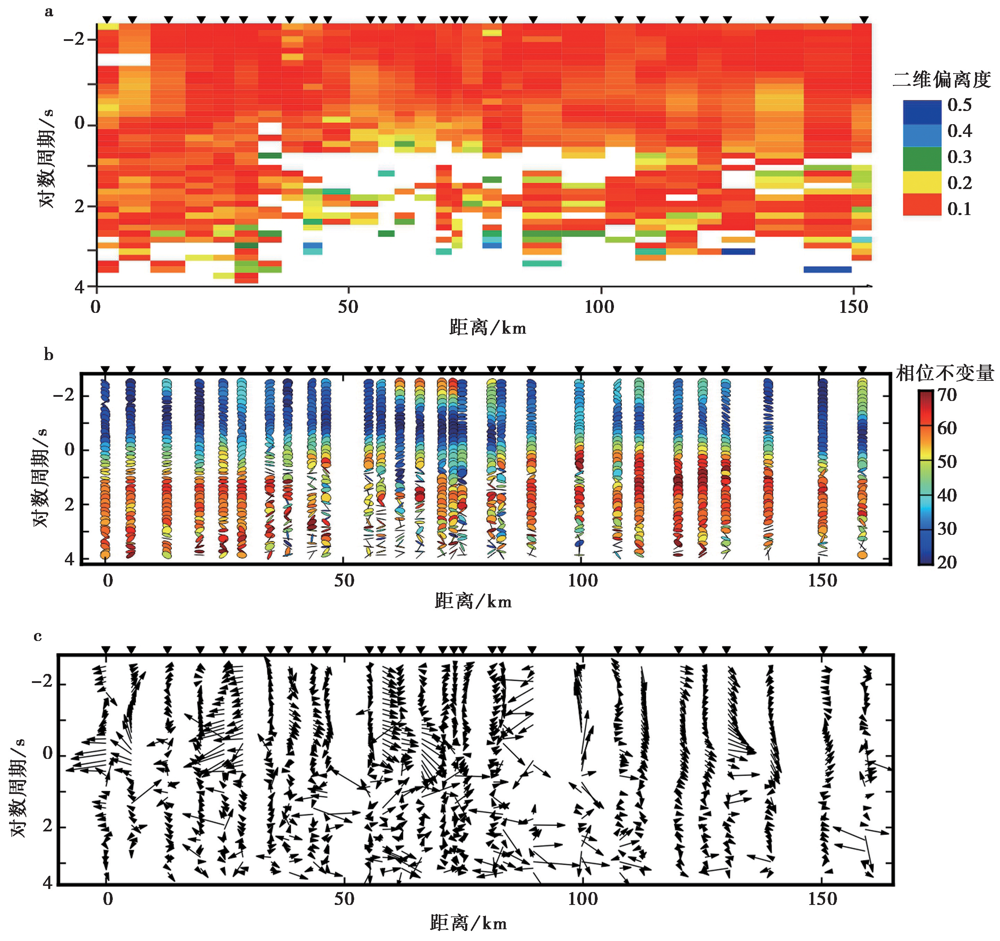
图3 沿剖面不同频率的二维偏离度值(a)、 相位不变量(b)和磁感应矢量分布图(c)
Fig. 3 The phase tensor ellipse(a), phase-tensor data(b)and Schmucker vector(c)of different periods along profile.
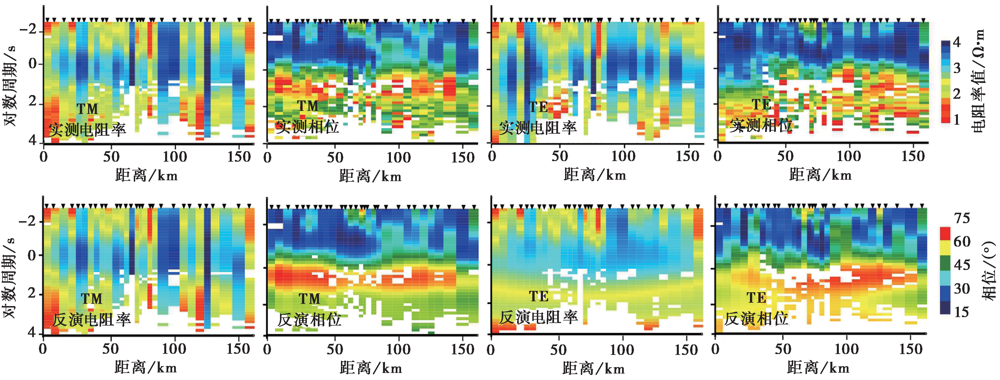
图4 剖面实测与2D模型理论计算的TE和TM极化模式的视电阻率和阻抗相位柱状图 上图为实测数据, 下图为理论模型数据
Fig. 4 Comparison of TE and TM apparent resistivity and impedance phase of measured values and calculated values from 2-D theoretical response along the profile.
| [1] | 白登海, 廖志杰, 赵国泽, 等. 1994. 从MT探测结果推论腾冲热海热田的岩浆热源[J]. 科学通报, 39(4): 344-347. |
| BAI Deng-hai, LIAO Zhi-jie, ZHAO Guo-ze, et al. 1994. The inference of magmatic heat source beneath the Rehai field of Tengchong from the result of magnetotelluric sounding[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 39(4): 344-347. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 白志达, 徐德斌, 张秉良, 等. 2006. 龙岗火山群第四纪爆破式火山作用类型与期次研究[J]. 岩石学报, 22(6): 1473-1480. |
| BAI Zhi-da, XU De-bin, ZHANG Bing-liang, et al. 2006. Study on type and phase of Quaternary explosive volcanism in Longgang volcanic cluster[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(6): 1473-1480. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 蔡军涛, 陈小斌. 2010a. 大地电磁资料精细处理和二维反演解释技术研究(二): 反演数据极化模式选择[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(11): 2703-2714. |
| CAI Jun-tao, CHEN Xiao-bin. 2010a. Refined techniques for data processing and two-dimensional inversion in magnetotelluric Ⅱ: Which data polarization mode should be used in 2D inversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(11): 2703-2714. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 蔡军涛, 陈小斌, 赵国泽. 2010b. 大地电磁资料精细处理和二维反演解释技术研究(一): 阻抗张量分解与构造维性分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(10): 2516-2526. |
| CAI Jun-tao, CHEN Xiao-bin, ZHAO Guo-ze. 2010b. Refined techniques for data processing and two-dimensional inversion in magnetotelluric Ⅰ: Tensor decomposition and dimensionality analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(10): 2516-2526. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 陈小斌, 赵国泽, 詹艳. 2004a. MT资料处理与解释的Windows可视化集成系统[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 39(S1): 11-16. |
| CHEN Xiao-bin, ZHAO Guo-ze, ZHAN Yan. 2004a. A visual integrated windows system for MT data processing and interpretation[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 39(S1): 11-16. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 陈小斌, 赵国泽, 詹艳, 等. 2004b. 磁倾子矢量的图示分析及其应用研究[J]. 地学前缘, 11(4): 626-636. |
| CHEN Xiao-bin, ZHAO Guo-ze, ZHAN Yan, et al. 2004b. Analysis of tipper visual vectors and its application[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(4): 626-636. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2003. 中国活动构造与地震活动[J]. 地学前缘, 10(S1): 66-73. |
| DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Pei-zhen, RAN Yong-kang, et al. 2003. Active tectonics and earthquake activities in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(S1): 66-73. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 樊祺诚, 刘若新, 魏海泉, 等. 1999. 龙岗金垅顶子近代活动火山的岩石学与地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 15(4): 584-589. |
| FAN Qi-cheng, LIU Ruo-xin, WEI Hai-quan, et al. 1999. The petrology and geochemistry of Jinlongdingzi modern active volcano in Longgang area[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(4): 584-589. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 樊祺诚, 隋建立, 刘若新, 等. 2002. 吉林龙岗第四纪火山活动分期[J]. 岩石学报, 18(4): 495-500. |
| FAN Qi-cheng, SUI Jian-li, LIU Ruo-xin, et al. 2002. Periods of Quaternary volcanic activity in Longgang area, Jilin Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 18(4): 495-500. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 范兴利, 陈棋福, 郭震. 2020. 长白山火山区高精度Rayleigh 面波相速度结构与岩浆系统[J]. 岩石学报, 36(7): 2081-2091. |
|
FAN Xing-li, CHEN Qi-fu, GUO Zhen. 2020. High-resolution Rayleigh-wave phase velocity structure beneath the Changbaishan volcanic field associated with its magmatic system[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(7): 2081-2091. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [11] |
韩江涛, 王天琪, 刘文玉, 等. 2018. 阿尔山火山群深部“拱桥式”岩浆系统及其稳定性分析[J]. 地震地质, 40(3): 590-610. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.03.007.
DOI |
| HAN Jiang-tao, WANG Tian-qi, LIU Wen-yu, et al. 2018. Deep “arch-bridge” magmatic system of the Aershan volcanic group and its stability analysis[J]. Seismology and Geology, 40(3): 590-610. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 胡亚轩, 王庆良, 王雄. 2009. 利用垂直形变资料分析龙岗火山的活动性[J]. 地震研究, 32(3): 289-294. |
| HU Ya-xuan, WANG Qing-liang, WANG Xiong. 2009. Analysis of activity of Longgang volcano based on vertical deformation[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 32(3): 289-294. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 李世文, 翁爱华, 李建平, 等. 2020. 三维电性结构揭示的中国东北地区新生代火山深部起源[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 50(4): 538-552. |
| LI Shi-wen, WENG Ai-hua, LI Jian-ping, et al. 2020. Deep origin of Cenozoic volcanoes in Northeast China revealed by 3D electrical structure[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 50(4): 538-552. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 李智, 韩松, 邓亚平, 等. 2006. 吉林金龙顶子火山空降堆积物体积估算及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 28(1): 28-31. |
| LI Zhi, HAN Song, DENG Ya-ping, et al. 2006. Calculation of fallout tephra volumes in Sihai phase of Jinlongdingzi volcano of Longgang volcanic swarm in Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 28(1): 28-31. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 刘俊清, 丁广, 张晨侠, 等. 2013. 吉林省龙岗火山群现今活动性研究[J]. 华北地震科学, 31(1): 31-33. |
| LIU Jun-qing, DING Guang, ZHANG Chen-xia, et al. 2013. Study on present activity of Longgang volcano in Jilin Province[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 31(1): 31-33. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 刘若新. 2000. 中国的活火山[M]. 北京: 地震出版社:67-74. |
| LIU Ruo-xin. 2000. Active Volcanoes in China[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing: 67-74. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 刘祥, 张成梁. 1997. 龙岗火山群四海火山渣层: 来自金龙顶子火山亚普林尼式火山爆发[J]. 吉林地质, 16(3): 1-8. |
| LIU Xiang, ZHANG Cheng-liang. 1997. Sihai basaltic scoria deposits in the Longgang volcanic swarm belong to the sub-Plinian eruption of Jinlongdingzi volcano[J]. Jilin Geology, 16(3): 1-8. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 綦伟, 刘俊清, 李仲巍, 等. 2013. 龙岗火山喷发危险性初探[J]. 防灾减灾学报, 29(4): 70-73. |
| QI Wei, LIU Jun-qing, LI Zhong-wei, et al. 2013. Preliminary discussion on the risk of volcano eruption in Longgang area[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Reduction, 29(4): 70-73. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 仇根根, 裴发根, 方慧, 等. 2014. 长白山天池火山岩浆系统分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(10): 3466-3477. |
| QIU Gen-gen, PEI Fa-gen, FANG Hui, et al. 2014. Analysis of magma chamber at the Tianchi volcano area in Changbai Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(10): 3466-3477. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] |
阮帅, 汤吉, 董泽义, 等. 2020. 基于三维大地电磁AR-QN反演的长白山天池火山区电性结构[J]. 地震地质, 42(6): 1282-1230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.06.002.
DOI |
| RUAN Shuai, TANG Ji, DONG Ze-yi, et al. 2020. Electric structure model of Tianchi volcano in Changbai Mountains based on three-dimensional AR-QN magnetotelluric inversion[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(6): 1282-1230. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 隋建立, 樊祺诚, 曹杰. 1999. 龙岗火山喷发特征与火山岩化学初步研究[J]. 地质论评, 45(S1): 319-324. |
| SUI Jian-li, FAN Qi-cheng, CAO Jie. 1999. A preliminary study of eruption features and petrochemistry of volcanic rocks from the Longgang volcanoes[J]. Geological Review, 45(S1): 319-324. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] |
孙翔宇, 詹艳, 赵国泽, 等. 2020. 琼东北马鞍岭-雷虎岭火山区深部岩浆系统大地电磁三维探测[J]. 地震地质, 42(3): 640-653. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.03.007.
DOI |
| SUN Xiang-yu, ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Guo-ze, et al. 2020. Magnetotelluric imaging of magma distribution beneath Ma’anling and Leihuling volcanoes of northeastern Hainan, China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(3): 640-653. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 汤吉, 邓前辉, 赵国泽, 等. 2001. 长白山天池火山区电性结构和岩浆系统[J]. 地震地质, 23(2): 191-200. |
| TANG Ji, DENG Qian-hui, ZHAO Guo-ze, et al. 2001. Electric conductivity and magma chamber at the Tianchi volcano area in Changbaishan Mountains[J]. Seismology and Geology, 23(2): 191-200. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 汤吉, 晋光文, 赵国泽, 等. 1999. 感应矢量及其在长白山天池火山区的应用[J]. 地质论评, 45(S1): 294-303. |
| TANG Ji, JIN Guang-wen, ZHAO Guo-ze, et al. 1999. Induction arrow and its application in Tianchi volcano, Changbaishan Mountains[J]. Geological Review, 45(S1): 294-303. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 詹艳, 赵国泽, 王继军, 等. 2006. 黑龙江5大连池火山群地壳电性结构[J]. 岩石学报, 22(6): 1494-1502. |
| ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Guo-ze, WANG Ji-jun, et al. 2006. Crustal electric conductivity structure for Wudalianchi volcanic cluster in Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(6): 1494-1502. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 张炯, 黄少鹏, 傅饶, 等. 2017. 大地电磁测深在火山区地热研究中的应用[J]. 岩石学报, 33(1): 279-290. |
| ZHANG Jiong, HUANG Shao-peng, FU Rao, et al. 2017. Application of magnetotellurics in geothermal exploration and research in volcano areas[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(1): 279-290. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] |
赵波, 张焘, 徐德斌, 等. 2017. 吉林龙岗火山群金龙顶子火山机构及灾害区划[J]. 地震地质, 39(2): 423-435. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.02.011.
DOI |
| ZHAO Bo, ZHANG Tao, XU De-bin, et al. 2017. Preliminary volcanic hazard zonation in Jinlongdingzi volcano, Longgang volcano area, Jilin Province, China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(2): 423-435. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] |
Bibby H M, Caldwell T G, Brown C. 2005. Determinable and non-determinable parameters of galvanic distortion in magnetotellurics[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 163(3): 915-930.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Caldwell T G, Bibbly H M, Brown C. 2004. The magnetotelluric phase tensor[J]. Geophysical Journal international, 158(2): 457-469.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Chave A D, Thomson D J, Ander M E. 1987. On the robust estimation of power spectra, coherences and transfer functions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 92(B1): 633-648.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Comeau M J, Unsworth M J, Ticona F, et al. 2015. Magnetotelluric images of magma distribution beneath Volcán Uturuncu, Bolivia: Implications for magma dynamics[J]. Geology, 43(3): 243-246.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Egbert G D, Booker J R. 1986. Robust estimation of geomagnetic transfer functions[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 87(1): 173-194. |
| [33] |
Heise W T, Caldwell G, Bibby H M, et al. 2008. Three-dimensional modelling of magnetotelluric data from the Rotokawa geothermal field, Taupo volcanic zone, New Zealand[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 173: 740-750.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Liu J Q, Chu G Q, Han J T, et al. 2009. Volcanic eruptions in the Longgang volcanic field, northeastern China, during the past 15, 000 years[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34(5): 645-654.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Rodi W, Mackie R L. 2001. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion[J]. Geophysics, 66(1): 174-187.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Song J L, Hetland E A, Wu F T, et al. 2007. P-wave velocity structure under the Changbaishan volcanic region, NE China, from wide-angle reflection and refraction data[J]. Tectonophysics, 433(1-4): 127-139.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Ye T, Huang Q H, Chen X B, et al. 2018. Magma chamber and crustal channel flow structures in the Tengchong volcano area from 3-D MT inversion at the intracontinental block boundary southeast of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(12): 11112-11126.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Zhang H Q, Huang Q H, Zhao G Z, et al. 2016. Three-dimensional conductivity model of crust and uppermost mantle at the northern Trans-North China Orogen: Evidence for a mantle source of Datong volcanoes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 453: 182-192.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王明亮, 张扬, 徐顺强, 徐志萍. 华北坳陷中南部深部结构大地电磁探测[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 536-552. |
| [2] | 董泽义, 汤吉, 赵国泽, 陈小斌, 崔腾发, 韩冰, 姜峰, 王立凤. 首都圈极低频电磁台网区地下电性结构探测[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 649-668. |
| [3] | 赵凌强, 詹艳, 王庆良, 孙翔宇, 韩静, 操聪, 张松, 蔡妍. 大地电磁数据揭示的1303年洪洞8级地震区精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 686-700. |
| [4] | 韩静, 詹艳, 孙翔宇, 赵国泽, 刘雪华, 包雨鑫, 孙建宝, 彭远黔. 强电磁干扰环境下的大地电磁数据特征及处理[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 736-752. |
| [5] | 张赟昀, 王培杰, 陈小斌, 詹艳, 韩冰, 王立凤, 赵国泽. 强干扰环境下的大地电磁时间序列处理过程[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 786-801. |
| [6] | 刘钟尹, 陈小斌, 蔡军涛, 崔腾发, 赵国泽, 汤吉, 欧阳飚. 大地电磁三维反演云计算系统toPeak的设计与实现[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 802-820. |
| [7] | 阮帅, 汤吉, 董泽义, 王立凤, 邓琰, 韩冰. 基于三维大地电磁AR-QN反演的长白山天池火山区电性结构[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(6): 1282-1300. |
| [8] | 孙翔宇, 詹艳, 赵国泽, 赵凌强, 邓琰, 胡亚轩, 胡久常, 向小娟. 琼东北马鞍岭-雷虎岭火山区深部岩浆系统大地电磁三维探测[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(3): 640-653. |
| [9] | 孙翔宇, 詹艳, 赵凌强, 陈小斌, 李陈侠, 孙建宝, 韩静, 崔腾发. 东昆仑断裂带东端和2017年九寨沟7.0级地震区深部电性结构探测[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(1): 182-197. |
| [10] | 姜峰, 陈小斌, 董泽义, 崔腾发, 刘钟尹, 王培杰. 利用单剖面大地电磁三维反演识别沙德和玉农希断裂[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(6): 1444-1463. |
| [11] | 张继红, 赵国泽, 董泽义, 王立凤, 韩冰, 王庆林, 唐廷梅, 王梅. 郯庐断裂带安丘、莒县电磁台地壳电性结构研究[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(5): 1239-1253. |
| [12] | 赵凌强, 詹艳, 王庆良, 孙翔宇, 杨皓, 陈小斌. 1954年甘肃民勤7级地震区深部电性结构特征及地震构造环境研究[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(3): 552-565. |
| [13] | 韩江涛, 王天琪, 刘文玉, 刘国兴, 韩松, 刘立家. 阿尔山火山群深部“拱桥式”岩浆系统及其稳定性分析[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(3): 590-610. |
| [14] | 周耀明, 朱文斌, 陈正乐, 朱炳玉, 薛峰. 准噶尔盆地克-百断裂带火山岩分布特征的重磁资料解释[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(3): 641-655. |
| [15] | 翁爱华, 李建平, 范小平, 李斯睿, 韩江涛, 李大俊, 李亚彬, 赵祥阳, 唐裕. 大地电磁测深揭示的1668年郯城8.5级地震震中地壳精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(2): 396-409. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||