地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 710-734.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.03.007
王喜龙1)( ), 罗银花2),*(
), 罗银花2),*( ), 金秀英3), 杨梦尧4), 孔祥瑞1)
), 金秀英3), 杨梦尧4), 孔祥瑞1)
收稿日期:2022-12-26
修回日期:2023-02-15
出版日期:2023-06-20
发布日期:2023-07-18
通讯作者:
* 罗银花, 女, 1983年生, 工程师, 主要从事地质调查与矿产地质等方面的研究, E-mail: 作者简介:王喜龙, 男, 1988年生, 2014年于中国地质大学(北京)获岩石学、 矿物学、 矿床学专业硕士学位, 高级工程师, 目前主要研究方向为构造地球化学, E-mail: 546737333@qq.com。
基金资助:
WANG Xi-long1)( ), LUO Yin-hua2),*(
), LUO Yin-hua2),*( ), JIN Xiu-ying3), YANG Meng-yao4), KONG Xiang-rui1)
), JIN Xiu-ying3), YANG Meng-yao4), KONG Xiang-rui1)
Received:2022-12-26
Revised:2023-02-15
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-07-18
摘要:
辽南地区历史中强地震活动频繁, 尤其是金州断裂与海城河断裂, 近代曾发生多次中强地震。对辽南地区金州断裂不同区段与海城河断裂开展多期次构造地球化学土壤气浓度观测, 可为查明断层活动状态、 区域应力调整与分析地震活动规律及特征起到至关重要的作用。文中对辽南地区2条活动断裂的6条剖面进行了多期跨断层土壤气Rn、 CO2与H2浓度观测。测量结果表明, 同一剖面、 不同期次断层土壤气的浓度变化趋势基本一致, 但断层不同区段的土壤气浓度变化存在一定差异, 分析认为不同区段的断层性质及地质地貌等特征是造成这种差异性的主要原因之一。各剖面土壤气浓度的时空变化特征显示, 金州断裂与海城河断裂土壤气浓度空间变化特征在一定范围内主要受地质构造、 地下介质结构与地壳垂直速率变化等因素控制, 土壤气浓度的时间变化特征主要与断裂活动性质、 地震活动及区域应力调整作用有关。研究结果表明, 多期次构造地球化学观测方法可有效反映断层活动状态, 对区域应力调整具有良好的指示意义, 是进行监视断层活动与地震监测预测的一种有效手段。
王喜龙, 罗银花, 金秀英, 杨梦尧, 孔祥瑞. 辽南地区断裂带的断层土壤气地球化学特征及其对区域应力调整的指示[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 710-734.
WANG Xi-long, LUO Yin-hua, JIN Xiu-ying, YANG Meng-yao, KONG Xiang-rui. GEOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SOIL GAS IN ACTIVE FAULT ZONE AND ITS IMPLICATION TO THE ADJUSTMENT OF REGIONAL STRESS FIELD IN THE SOUTHERN AREA OF LIAONING PROVINCE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(3): 710-734.
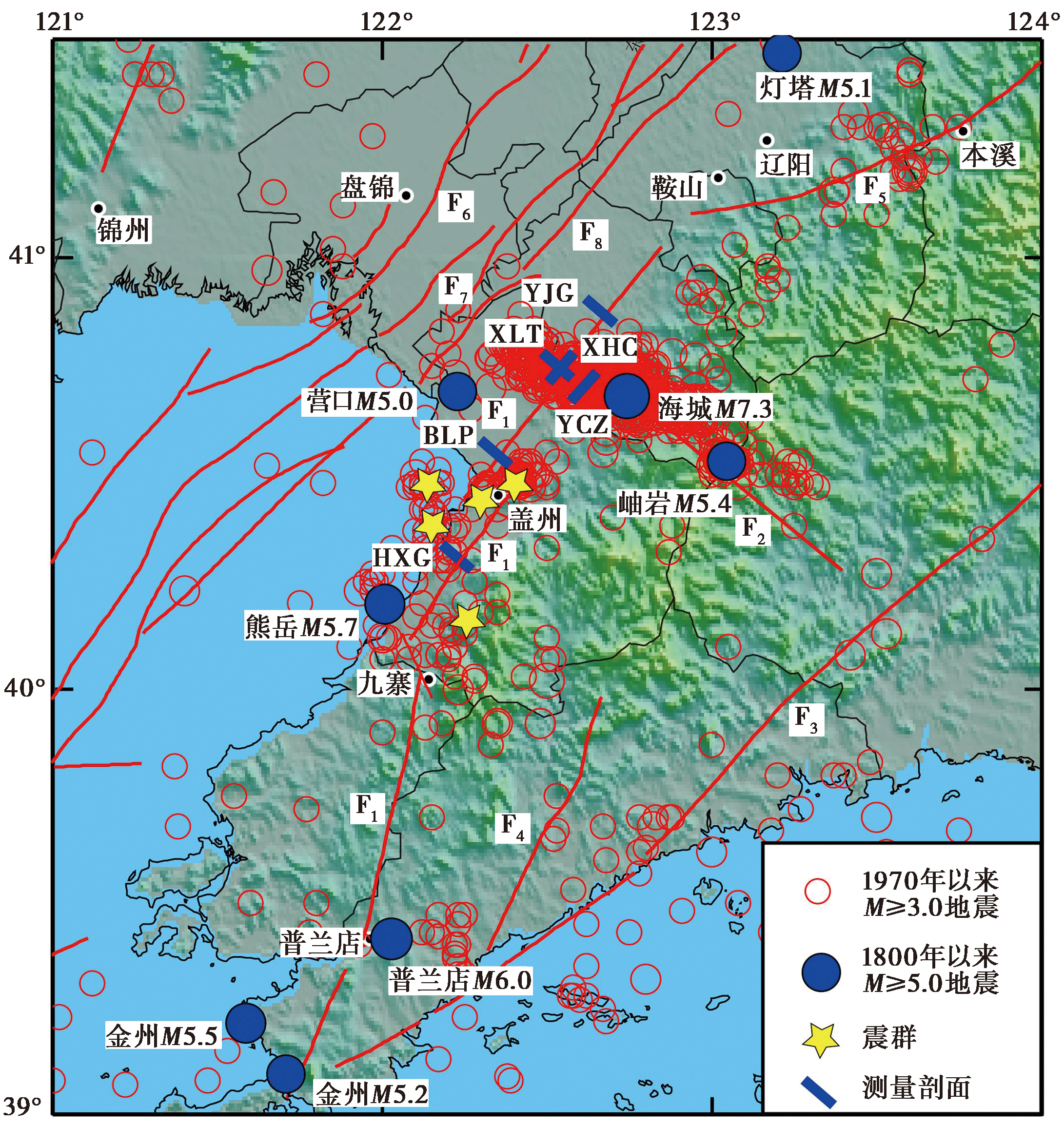
图 1 辽南地区的历史地震和构造简图 F1金州断裂; F2海城河断裂; F3庄河断裂; F4碧流河断裂; F5太子河断裂; F6台安断裂; F7辽中断裂; F8牛居-油燕沟断裂
Fig. 1 Sketch map showing historical earthquakes and tectonic setting in the southern area of Liaoning Province.
| 序号 | 测线名称 | 测线代号 | 测线长度/m | 测点数 | 断裂名称 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 于家沟 | YJG | 480 | 16 | 金州断裂 |
| 2 | 兴隆屯 | XLT | 290 | 16 | |
| 3 | 博洛铺 | BLP | 360 | 16 | |
| 4 | 虹溪谷 | HXG | 460 | 16 | |
| 5 | 小河村 | XHC | 590 | 16 | 海城河断裂 |
| 6 | 营城子 | YCZ | 460 | 16 |
表 1 土壤气测线的基本信息表
Table 1 The basic information of the observation lines for soil gas
| 序号 | 测线名称 | 测线代号 | 测线长度/m | 测点数 | 断裂名称 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 于家沟 | YJG | 480 | 16 | 金州断裂 |
| 2 | 兴隆屯 | XLT | 290 | 16 | |
| 3 | 博洛铺 | BLP | 360 | 16 | |
| 4 | 虹溪谷 | HXG | 460 | 16 | |
| 5 | 小河村 | XHC | 590 | 16 | 海城河断裂 |
| 6 | 营城子 | YCZ | 460 | 16 |
| 剖面 | 测点浓度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rn/kBq·m-3 | CO2/% | H2/ppm | |
| YJG | 32.74 | 2.12 | 250.10 |
| XLT | 52.56 | 1.68 | 177.99 |
| XHC | 37.35 | 1.37 | 170.23 |
| YCZ | 26.13 | 0.98 | 179.76 |
| BLP | 26.63 | 1.73 | 133.01 |
| HXG | 15.22 | 0.59 | 201.21 |
表 3 各剖面土壤气的浓度均值
Table 3 The mean concentration of soil gas for each section
| 剖面 | 测点浓度 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rn/kBq·m-3 | CO2/% | H2/ppm | |
| YJG | 32.74 | 2.12 | 250.10 |
| XLT | 52.56 | 1.68 | 177.99 |
| XHC | 37.35 | 1.37 | 170.23 |
| YCZ | 26.13 | 0.98 | 179.76 |
| BLP | 26.63 | 1.73 | 133.01 |
| HXG | 15.22 | 0.59 | 201.21 |
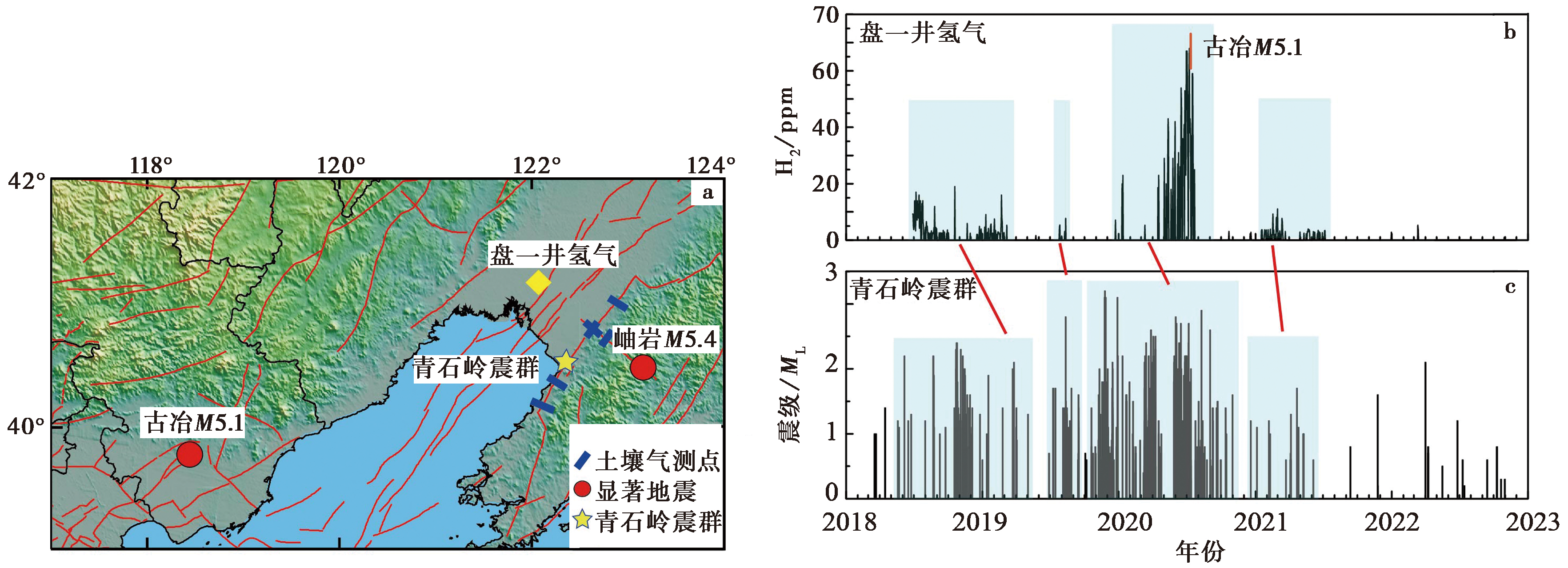
图 8 异常空间分布(a)与盘一井氢气(b)、 青石岭震群(c)变化
Fig. 8 The spatial distribution of anomalies(a)for the hydrogen of Panjin No.1 well(b) and earthquake swarm of Qingshiling(c).
| [1] |
毕思文. 1996. 地球内部流体系统科学统一理论[J]. 地学前缘, 3(3-4): 2-9.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
车用太, 刘耀炜, 何钄. 2015. 断层带土壤气中H2观测: 探索地震短临预报的新途径[J]. 地震, 35(4): 1-10.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈为涛, 甘卫军, 肖根如, 等. 2012. 3·11日本大地震对中国东北部地区地壳形变态势的影响[J]. 地震地质, 34(3): 425-439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.03.004.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [4] |
杜建国, 李营, 崔月菊, 等. 2018a. 地震流体地球化学[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
杜建国, 仵柯田, 孙凤霞. 2018b. 地震成因综述[J]. 地学前缘, 25(4): 255-267.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
杜建国, 宇文欣, 李圣强, 等. 1998. 八宝山断裂带逸出氡的地球化学特征及其映震效能[J]. 地震, (2): 155-162.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
杜乐天. 2005. 地球排气作用的重大意义及研究进展[J]. 地质论评, 51(2): 174-180.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
范雪芳, 张磊, 李自红, 等. 2016. 断裂带土壤气高精度氢异常分析[J]. 地震地质, 38(2): 303-315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.02.006.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [9] |
丰成君, 张鹏, 孙炜锋, 等. 2013. 日本 MW9.0 地震对中国华北-东北大陆主要活动断裂带的影响及地震危险性初步探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 20(6): 123-140.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
高常波, 钟以章. 2000. 1999年辽宁海城-岫岩5.6级地震的地质构造背景和发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 22(4): 405-412.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
韩晓昆. 2014. 首都圈地震重点监测区土壤气体地球化学[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地震预测研究所: 10-45.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
姜丽, 崔月菊, 王海燕, 等. 2021. 辽东南地区地下水化学时空变化[J]. 地震, 41(3): 114-130.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
雷清清, 廖旭, 董晓燕, 等. 2008. 辽宁省主要活动断层与地震活动特征分析[J]. 震灾防御技术, 3(2): 111-125.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
李营, 陈志, 胡乐, 等. 2022. 流体地球化学进展及其在地震预测研究中的应用[J]. 科学通报, 67(13): 1404-1420.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
李营, 杜建国, 王富宽, 等. 2009. 延怀盆地土壤气体地球化学特征[J]. 地震学报, 31(1): 82-91.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
林元武, 刘五洲, 王基华, 等. 1998. 张北-尚义地震现场CO2测量与震后趋势判断[J]. 地震地质, 20(2): 117-121.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
林元武, 翟盛华, 范树全, 等. 1994. 华北隐伏活动断裂H2异常特征及其异常机制研究[J]. 地震地质, 16(3): 264-268.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
刘耀炜, 范世宏, 曹玲玲. 1999. 地下流体中短期异常与地震活动性指标[J]. 地震, 19(1): 19-25.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
路畅, 李营, 胡乐, 等. 2022. 唐山地区土壤气Rn通量及其与地震活动的关系[J]. 地震研究, 45(2): 241-248.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
孙凤霞, 崔月菊, 王海燕, 等. 2020. 辽宁省地震监测站地下水化学类型及成因分析[J]. 地震学报, 42(1): 79-90.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
孙启凯, 池国民, 畅柳, 等. 2017. 辽宁地区地壳垂直形变特征与地震危险性分析[J]. 地震学报, 39(6): 891-898.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
万波. 2000. 岫岩-海城5.6级地震地震地质背景及其发震构造[J]. 东北地震研究, 16(2): 27-32.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
万波, 贾丽华, 戴盈磊, 等. 2013. 辽东半岛中强地震活动及其与构造相关性[J]. 地震地质, 35(2): 300-314.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
万波, 靳超宇, 索锐. 2017. 辽宁省及邻近地区主要地震构造及其危险性判定[J]. 防灾减灾学报, 33(1): 1-11.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
万波, 钟以章. 1997. 东北地区的新构造运动特征分析及新构造运动分区[J]. 东北地震研究, 13(4): 64-75.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
王博, 周永胜, 钟骏, 等. 2022. 滇西北断裂带土壤气地球化学特征及对断层活动性的启示[J]. 地震地质, 44(2): 428-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.02.010.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [27] |
王广才, 王基华, 刘成龙, 等. 2002. 福州市隐伏断层地球化学试验探测及研究[J]. 地震地质, 24(4): 593-600.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
王基华, 林元武, 高松升. 1998. 怀来断层气CO2监测及张北-尚义地震的短临预报[J]. 地震地质, 20(2): 113-116.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
王江, 陈志, 张帆, 等. 2022. 基于土壤气体地球化学的雄安新区活动断裂空间展布及活动性探讨[J]. 地震研究, 45(2): 264-274.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
王亮, 焦明若, 钱蕊, 等. 2022. 利用双差地震成像方法反演辽南地区地壳速度结构[J]. 地震地质, 44(2): 378-394.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
王敏, 李强, 王凡, 等. 2011. 全球定位系统测定的2011年日本宫城 MW9.0 地震远场同震位移[J]. 科学通报, 56(20): 1593-1596.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
王喜龙, 贾晓东, 杨梦尧. 2021. 辽宁金州断裂断层土壤气地球化学调查[J]. 中国地震, 37(4): 767-779.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
王喜龙, 焦明若, 王海燕, 等. 2016. 中强震前辽宁地区流体异常特征与地震预测研究[J]. 地震, 36(4): 131-143.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
王喜龙, 李营, 杜建国, 等. 2017. 首都圈地区土壤气Rn, Hg, CO2地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 地震学报, 39(1): 85-101.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
王喜龙, 王海燕, 李彤霞, 等. 2018. 盘一井水氡映震效能及Rn值迁移机理分析[J]. 防灾减灾学报, 34(4): 26-33.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
王喜龙, 杨梦尧, 郭红霞, 等. 2022. 辽宁盘一井氢气浓度异常特征及预报效能分析[J]. 地震研究, 45(2): 275-283.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
仵柯田, 崔月菊, 孙凤霞, 等. 2019. 鞍山-海城地区地震地下水地球化学研究[J]. 中国地震, 35(4): 629-642.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
杨秋野, 张艳, 符力耘, 等. 2020. 应力变化与流体(水位、 水温、 水化学、 土壤气等)变化的耦合机理及其在川滇地区地震前兆研究中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 35(6): 2124-2133.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
赵元鑫, 李营, 陈志, 等. 2022. 唐山断裂带气体组分变异函数空间分布特征[J]. 地震, 42(1): 18-32.
|
|
|
|
| [40] |
郑国东, 郭正府, 王云鹏, 等. 2018. 气体地球化学新进展: 纪念著名气体地球化学专家David R. Hilton教授[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 37(4): 796-799.
|
|
|
|
| [41] |
周晓成. 2011. 汶川 MS8.0 地震后川西地区的气体地球化学[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学地球和空间科学学院: 10-78.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
周志华, 王海燕, 薛艳. 2014. 辽宁中南部地下井泉水化学组成特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(6): 1601-1605.
|
|
|
|
| [43] |
DOI URL |
| [44] |
DOI URL |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
DOI |
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
DOI URL |
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
DOI URL |
| [53] |
DOI URL |
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
DOI URL |
| [56] |
DOI URL |
| [57] |
DOI URL |
| [58] |
DOI URL |
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
DOI URL |
| [61] |
DOI URL |
| [62] |
DOI URL |
| [63] |
DOI URL |
| [64] |
DOI URL |
| [65] |
DOI URL |
| [66] |
DOI URL |
| [67] |
DOI URL |
| [68] |
DOI URL |
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
DOI |
| [71] |
DOI URL |
| [72] |
DOI |
| [73] |
DOI URL |
| [1] | 蒋雨函, 王子思, 刘佳琪, 梁卉, 周启超, 高小其. 中国地震断裂带氢气观测研究现状[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 622-637. |
| [2] | 王博, 崔凤珍, 刘静, 周永胜, 徐胜, 邵延秀. 玛多 MS7.4地震断层土壤气特征与地表破裂的相关性[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 772-794. |
| [3] | 蒋雨函, 高小其, 杨朋涛, 刘冬英, 孙小龙, 向阳, 朱成英, 汪成国. 新疆北天山地区断裂带断层土壤气的地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1597-1614. |
| [4] | 朱成英, 闫玮, 麻荣, 李志海, 汪成国, 黄建明, 周晓成. 2017年8月9日精河MS6.6地震宏观烈度及其余震分布的断层气体地球化学表征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1225-1239. |
| [5] | 王博, 周永胜, 钟骏, 胡小静, 张翔, 周青云, 李旭茂. 滇西北断裂带土壤气地球化学特征及对断层活动性的启示[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 428-447. |
| [6] | 吴果, 冉洪流, 周庆, 谢卓娟. 中国海域及邻区自适应空间平滑地震活动模型[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 150-169. |
| [7] | 张致伟, 龙锋, 赵小艳, 王迪. 川滇地区的震源机制解及应力场特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 170-187. |
| [8] | 王志伟, 马胜利, 雷兴林, 王凯英. 基于加密地震观测讨论红河断裂带北段维西-乔后断层的地震活动性特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1524-1536. |
| [9] | 张盛峰, 张永仙, 范晓易. 基于时-空ETAS模型的新疆伽师地区背景及触发地震活动的探讨[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(2): 297-310. |
| [10] | 邵志刚, 冯蔚, 王芃, 尹晓菲. 中国大陆活动地块边界带的地震活动特征研究综述[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(2): 271-282. |
| [11] | 张磊, 高小其, 包创, 李静, 李旭茂. 呼图壁地下储气库构造气体地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(5): 1059-1071. |
| [12] | 朱成林, 甘卫军, 贾媛, 李杰, 殷海涛, 孔向阳. 沂沭断裂带两侧地区地震能量释放与块体相对运动的关系[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(2): 299-309. |
| [13] | 祁玉萍, 张致伟, 龙锋, 肖本夫, 梁明剑, 路茜, 江鹏. 大凉山次级块体及邻区震源机制解与区域应力场特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(2): 377-395. |
| [14] | 谢超, 周本刚, 李正芳. 东喜马拉雅构造结地貌形态及其构造指示意义[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(2): 276-286. |
| [15] | 朱艾斓, 徐锡伟, 任烨, 孙冬军, 王鹏, 于海英, 宋秀青, 刘芳. 中国东南部地区背景地震重新定位及隐伏活动构造初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(1): 67-80. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||