地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1170-1186.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.05.008
杨小林1)( ), 杨锦玲2), 苏利娜3), 冯静4), 王军5)
), 杨锦玲2), 苏利娜3), 冯静4), 王军5)
收稿日期:2022-12-22
修回日期:2023-03-18
出版日期:2023-11-23
发布日期:2023-11-23
作者简介:杨小林, 男, 1983年生, 高级工程师, 2021年于中国科学院精密测量科学与技术创新研究院获固体地球物理学博士学位, 主要从事大地测量等方面的工作, E-mail: yang-xiaolin123@163.com。
基金资助:
YANG Xiao-lin1)( ), YANG Jin-ling2), SU Li-na3), FENG Jing4), WANG Jun5)
), YANG Jin-ling2), SU Li-na3), FENG Jing4), WANG Jun5)
Received:2022-12-22
Revised:2023-03-18
Online:2023-11-23
Published:2023-11-23
摘要:
目前中国有60余处四分量钻孔应变测点, 这些测点的观测数据在地球动力学和地震前兆等研究中均发挥着重要作用。但在实际观测中, 不少四分量钻孔应变仪会受到不同周期气压波的干扰。截至目前, 还鲜有关于该类仪器对气压频响效应研究的报道。文中以江宁台为例, 尝试采用传递函数对其进行系统诊断; 在此基础上, 进一步利用双衬套力学模型反演其钻孔围岩的力学参数。结果表明: 1)在0.1~30cpd频带内, 气压和钻孔应变的相干性较好; 2)低频带(0.1~0.5cpd)的气压响应最好, 高频带(>8cpd)次之, 中频带(0.5~8cpd)则略差; 3)若不考虑日波和半日波频段的影响, 在整个频带内, 4个分量的应变和面应变气压系数谱近线性平稳; 4)在高频带, 钻孔应变对气压响应的相位谱呈指数形式上升, 平均滞后约24.2°, 频率依赖性明显; 5)利用面应变低频气压系数均值反演的钻孔围岩弹性模量和泊松比分别为33.9GPa和0.27。以上结果将不仅有助于气压效应的分频改正, 同时还能为钻孔围岩力学参数的定量反演提供新方法。
杨小林, 杨锦玲, 苏利娜, 冯静, 王军. 四分量钻孔应变对气压响应的传递函数及围岩力学参数估算——以江苏江宁台为例[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(5): 1170-1186.
YANG Xiao-lin, YANG Jin-ling, SU Li-na, FENG Jing, WANG Jun. FOUR-COMPONENT BOREHOLE STRAINMETER TRANSFER FUNCTIONS AND ROCK PROPERTIES ESTIMATION: A CASE OF JIANGNING STATION, JIANGSU, CHINA[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(5): 1170-1186.
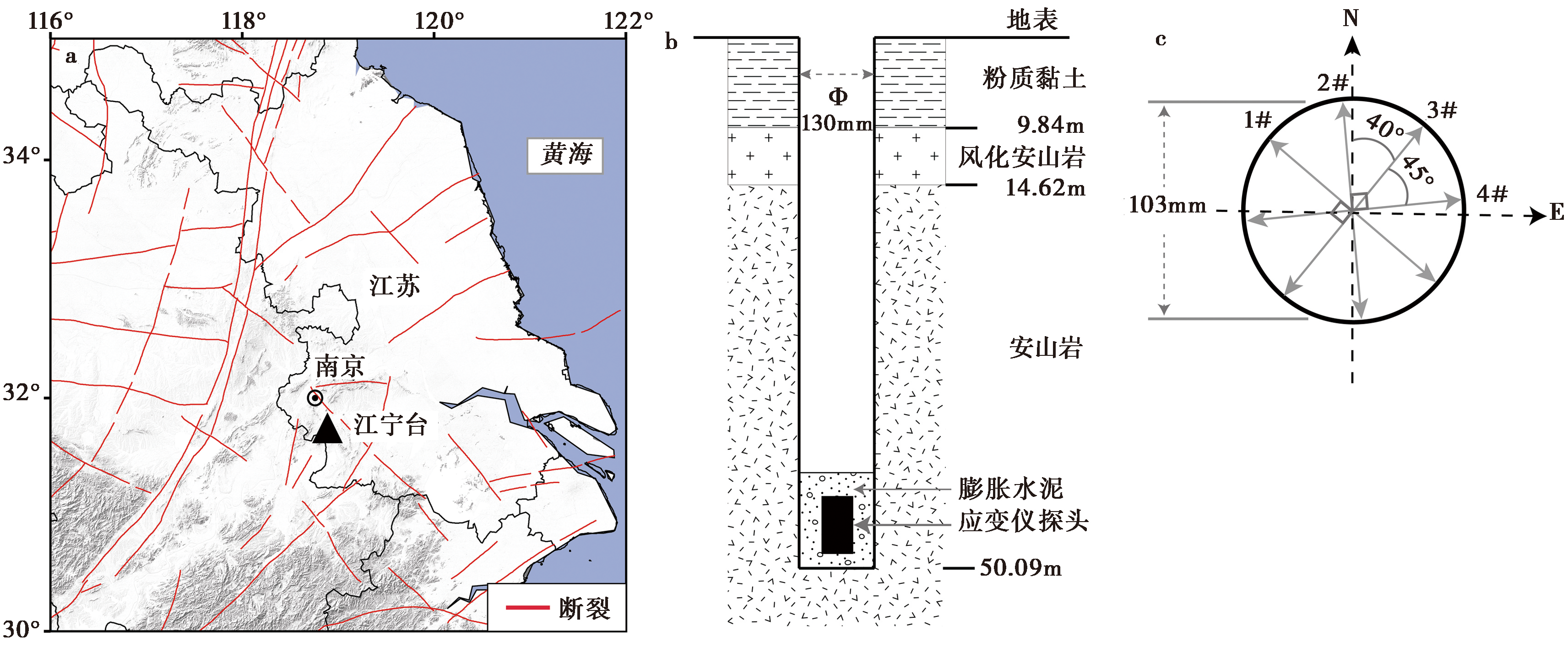
图1 江宁台位置(a)及其钻孔岩性柱状图(b)和探头内传感器方位(c)
Fig. 1 Map showing location of the Jiangning YRY-4 borehole strainmeter(a), borehole lithology log(b), and the plan view of the relative orientations of the four components(c).
| 应变仪类型 | 探头钢筒 | 膨胀水泥 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 内半径 r1/mm | 外半径 r2/mm | 弹性模量 E1/GPa | 泊松比 v1 | 弹性模量 E2/GPa | 泊松比 v2 | |
| YRY-4 | 51.5 | 53.5 | 210 | 0.3 | 30 | 0.25 |
表1 YRY-4型钻孔应变仪探头和膨胀水泥的相关参数
Table 1 The relative parameters for the YRY-4 type borehole strainmeter and expansive grout cement
| 应变仪类型 | 探头钢筒 | 膨胀水泥 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 内半径 r1/mm | 外半径 r2/mm | 弹性模量 E1/GPa | 泊松比 v1 | 弹性模量 E2/GPa | 泊松比 v2 | |
| YRY-4 | 51.5 | 53.5 | 210 | 0.3 | 30 | 0.25 |
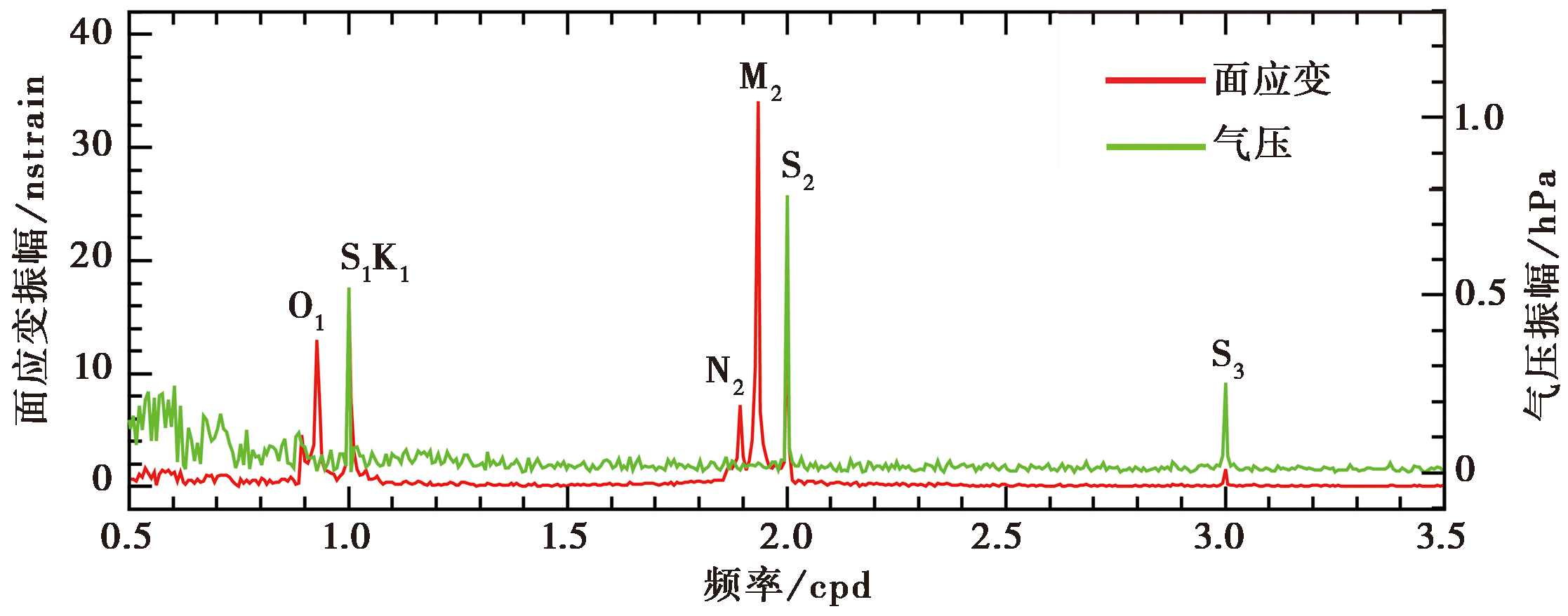
图3 钻孔面应变和气压在日波、 半日波和1/3 日波群频段的振幅谱
Fig. 3 Amplitude spectra of borehole areal strain(red line)and barometric pressure(green line) inside the diurnal, semidiurnal, and ter-diurnal tidal bands, respectively.
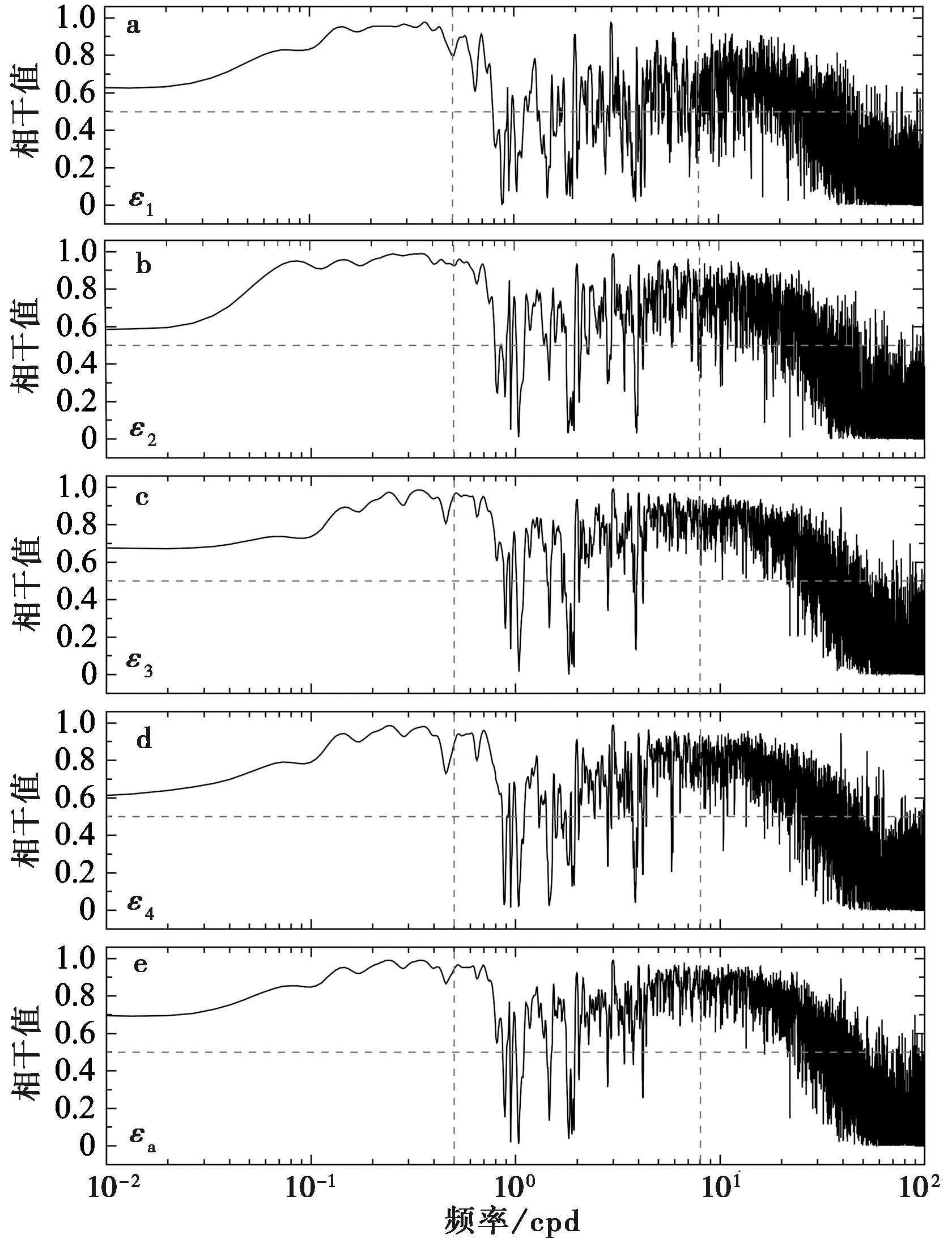
图4 气压与不同应变分量间的相干谱曲线 水平灰色虚线表示相干值=0.5, 左、 右垂直灰色虚线依次表示0.5cpd和8cpd频点
Fig. 4 Spectral coherence between individual strain component and barometric pressure.
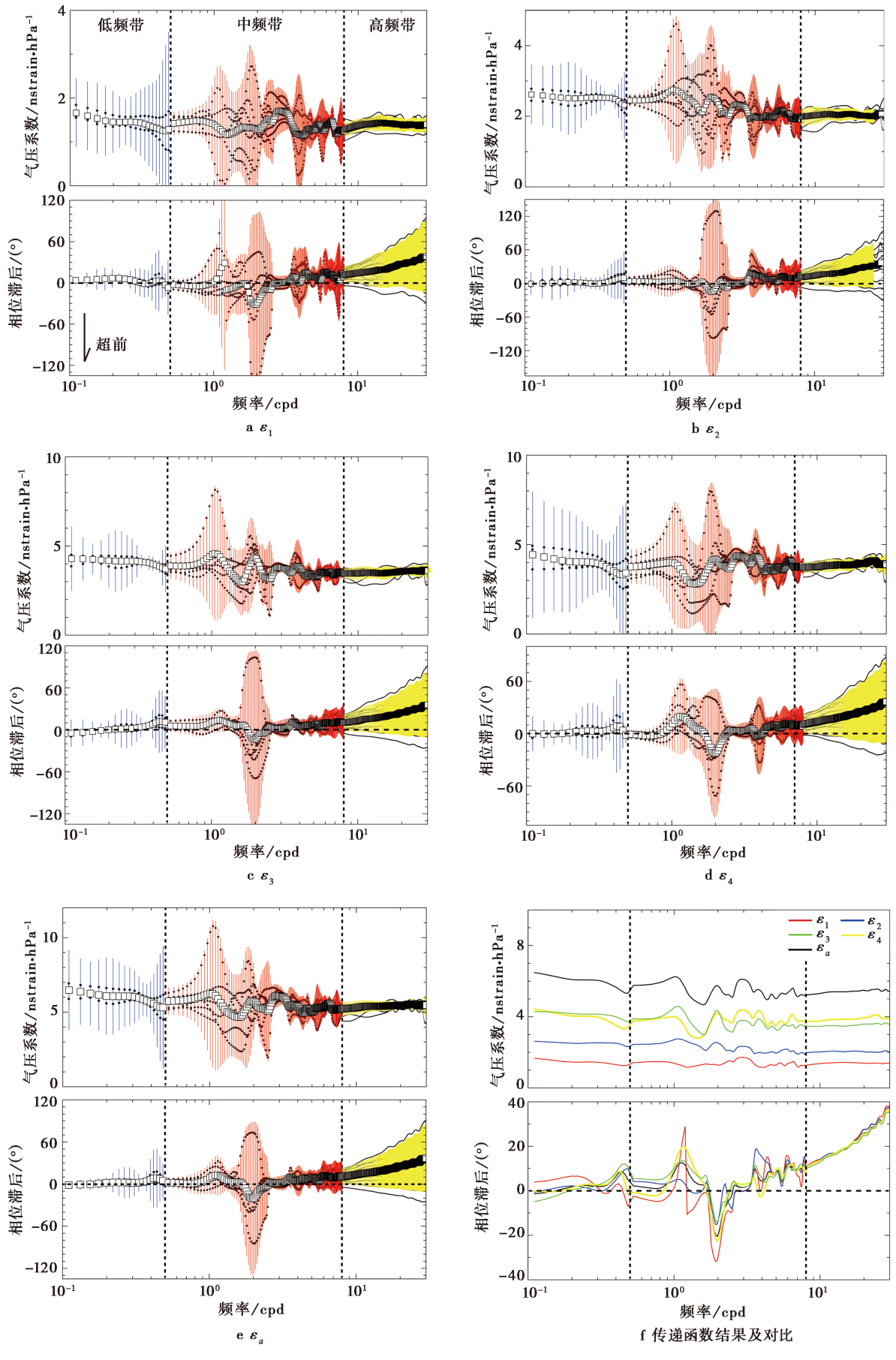
图5 4个分量和面应变对气压响应的传递函数及对比 黑色圆点表示气压系数和相移; 黑色空心方格分别为同一频点处各传递函数的均值, 蓝色、 红色和黄色竖线分别为低、 中和高频带传递函数均值的95%置信区间, 黑色水平虚线表示零相移, 黑色垂直虚线分别表示0.5cpd和8cpd频点; 图f为4个分量应变和面应变对气压响应的传递函数的均值曲线, 其中, 相位滞后为正, 表示钻孔应变滞后于气压波动, 反之则为超前
Fig. 5 Barometric pressure response coefficients and phase shifts(black dots)in the low-, intermediate-, and high-frequency bands retrieved by transfer functions for the four strain components and areal strain, respectively.
| 钻孔应变 | 平均气压系数/nstrain·hPa-1 | 平均相位滞后/(°) | 平均变异系数/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低频带 | 中频带 | 高频带 | 低频带 | 中频带 | 高频带 | 低频带 | 中频带 | 高频带 | |
| ε1 | 1.42 | 1.35 | 1.39 | 2.32 | 3.42 | 25.09 | 14.07 | 21.56 | 8.26 |
| ε2 | 2.5 | 2.15 | 2.04 | 2.93 | 6.35 | 24.73 | 5 | 6.53 | 15.09 |
| ε3 | 4.08 | 3.58 | 3.55 | 3.57 | 6.14 | 23.27 | 4.81 | 12.35 | 5.98 |
| ε4 | 3.86 | 3.81 | 3.9 | 2.83 | 5.06 | 23.93 | 13.16 | 15.44 | 6.2 |
| εa | 5.92 | 5.39 | 5.44 | 3.11 | 5.23 | 24.01 | 7.56 | 12.11 | 4.45 |
表 2 钻孔应变对不同频带气压响应的导纳和相移均值及对应的平均变异系数
Table 2 The averaged barometric pressure response coefficients, phase lags, and averaged coefficients of variation for the individual strain component and areal strain in different frequency bands
| 钻孔应变 | 平均气压系数/nstrain·hPa-1 | 平均相位滞后/(°) | 平均变异系数/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低频带 | 中频带 | 高频带 | 低频带 | 中频带 | 高频带 | 低频带 | 中频带 | 高频带 | |
| ε1 | 1.42 | 1.35 | 1.39 | 2.32 | 3.42 | 25.09 | 14.07 | 21.56 | 8.26 |
| ε2 | 2.5 | 2.15 | 2.04 | 2.93 | 6.35 | 24.73 | 5 | 6.53 | 15.09 |
| ε3 | 4.08 | 3.58 | 3.55 | 3.57 | 6.14 | 23.27 | 4.81 | 12.35 | 5.98 |
| ε4 | 3.86 | 3.81 | 3.9 | 2.83 | 5.06 | 23.93 | 13.16 | 15.44 | 6.2 |
| εa | 5.92 | 5.39 | 5.44 | 3.11 | 5.23 | 24.01 | 7.56 | 12.11 | 4.45 |
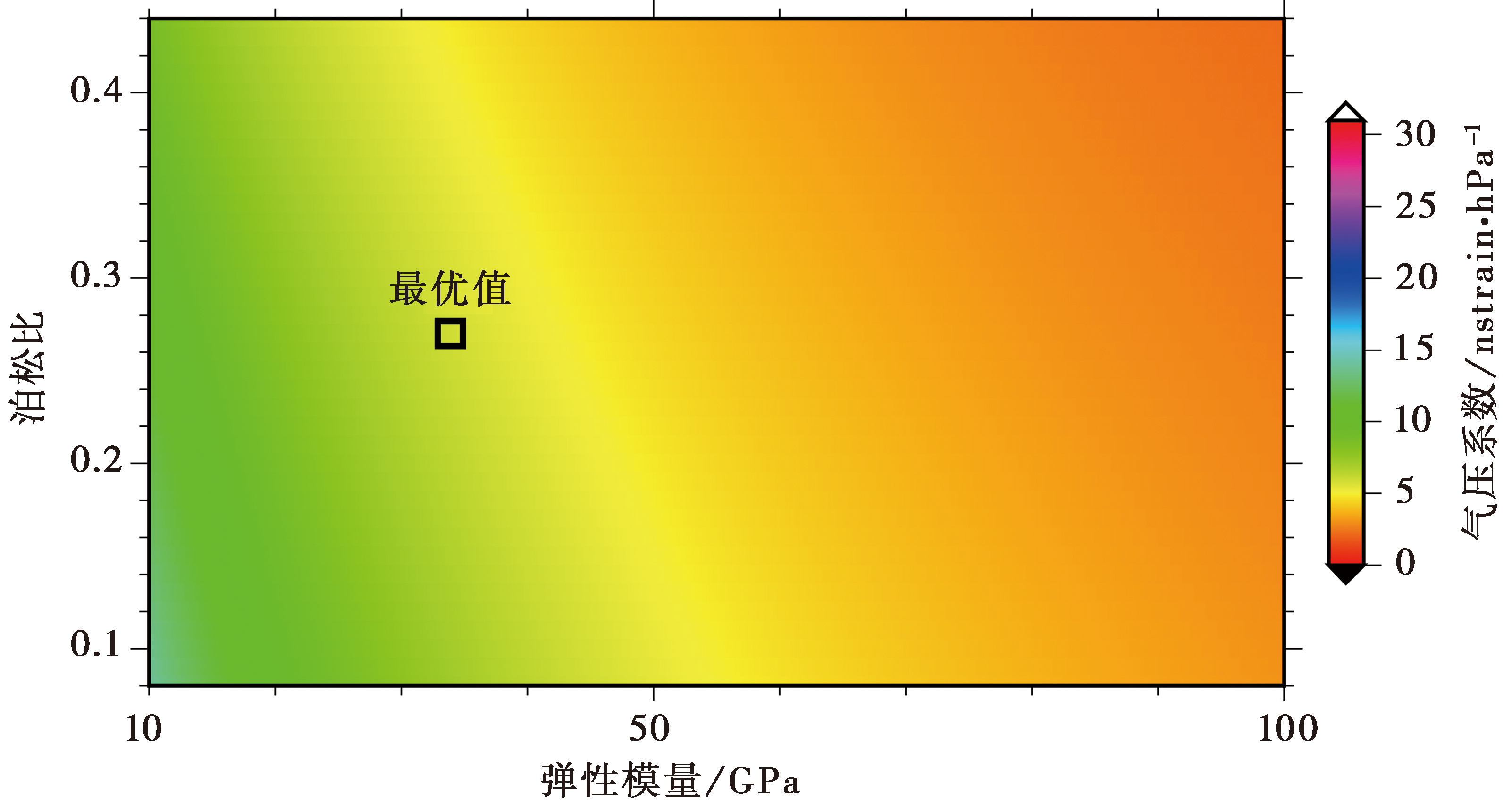
图6 钻孔围岩力学参数的折中反演
Fig. 6 The barometric coefficients are modeled to illustrate the trade-off inversion for the mechanical properties of borehole surrounding rock.
| [1] |
薄万举, 徐树心, 池顺良. 1993. 滦县台YRY-2型钻孔应变仪两井孔固体潮观测的对比分析[J]. 地震, 13(2): 47—54.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈丽君, 苏小芸, 周卫东, 等. 2020. 临夏台钻孔应变观测资料浅析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 40(S2): 70—73.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
池顺良. 1977. 连续自记压容地应力仪[C]// 《全国地应力专业会议论文选编(下)》. 北京: 地质出版社: 369—373.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
池顺良. 1993. 一种浅孔安装的YRY-2型钻孔应变仪在中国华北地区8个台站试验观测的结果[J]. 地震学报, 15(2): 224—231.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
池顺良, 池毅, 邓涛, 等. 2009. 从5·12汶川地震前后分量应变仪观测到的应变异常看建设密集应变观测网络的必要性[J]. 国际地震动态, (1): 1—13.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
方功先, 钟华昱, 闻昕. 2022. 1951—2020年南京市降水量变化特征分析[J]. 江苏水利, 25(11): 50—53.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
何斌, 江昊琳, 章东, 等. 2020. 基于单轴压缩试验的钻孔应变仪岩心力学性质的研究[J]. 地震学报, 42(6): 697—706.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
侯跃伟, 刘孝峰, 赵庆福. 2020. 江宁地震台YRY-4型四分量钻孔应变仪可靠性检验[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 41(3): 111—117.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李富珍, 张怀, 唐磊, 等. 2021. 基于钻孔应变地震波记录确定地震面波应变震级[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(5): 1620—1631.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
李涛, 陈群策, 欧阳祖熙, 等. 2011. RZB型钻孔应变仪在青藏高原东缘地应力监测中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 47(4): 677—683.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
刘序俨, 杨锦玲, 陈超贤, 等. 2016. 临夏台钻孔系统性质的论证[J]. 地球物理学报, 59(9): 3343—3353.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
欧阳祖熙. 1977. RZB-1型电容式地应变计[C]// 全国地应力专业会议论文选编(下). 北京: 地质出版社: 337—348.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
邱泽华, 张宝红, 池顺良, 等. 2010. 汶川地震前姑咱台观测的异常应变变化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 40(8): 1040—1047.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
邱泽华, 张国宏, 张宝红, 等. 2013. 用高密度电法勘探预判钻孔应变观测点岩石完整性[J]. 地震地质, 35(4): 805—816.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
石耀霖, 范桃园. 2000. 地应力观测井中元件标定及应力场计算方法[J]. 地震, 20(2): 101—106.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
苏恺之. 2018. 四分量钻孔应变仪计算式梳理及震例应用[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 39(5): 101—111.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
苏恺之. 2020. 中国四分量钻孔应变仪风雨历程四十年[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 41(2): 172—180.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
席道瑛, 陈运平, 陶月赞, 等. 2006. 岩石的非线性弹性滞后特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 25(6): 1086—1093.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
谢仁海, 渠天祥, 钱光谟. 2007. 构造地质学[M]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
杨小林, 储日升, 危自根, 等. 2021. 钻孔体应变对气压和固体潮响应的传递函数: 以陕西地区为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(8): 2749—2765.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
岳龙, 徐清风, 刘云, 等. 2019. 短周期气压波对青岛台体应变的影响分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 39(9): 977—981.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
张宝松, 邸兵叶, 黄宁, 等. 2021. 溧水火山岩盆地地球物理场特征及火山机构圈定[J]. 华北地质, 44(1): 39—44, 60.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
张晶, 曹建玲, 刘琦. 2014. 钻孔剪应变观测与构造有关的介质各向异性研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 29(5): 2461—2465.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
张凌空, 牛安福. 2013a. 分量式钻孔应变观测耦合系数的计算[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(9): 3029—3037.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
张凌空, 牛安福. 2013b. 钻孔体应变与面应变观测参数k的计算[J]. 中国地震, 29(3): 335—346.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
张凌空, 牛安福. 2019. 周期气压波对地壳岩石应变测量影响的理论解[J]. 地球物理学进展, 34(4): 1366—1370.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
张少琴, 王丽娟, 杨颍鹤. 2015. 长江中下游溧水盆地火山岩的时代、 地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 21(1): 15—30.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
DOI URL |
| [31] |
DOI URL |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
DOI URL |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
DOI |
| [37] |
DOI URL |
| [38] |
DOI URL |
| [39] |
DOI URL |
| [40] |
DOI URL |
| [41] |
DOI URL |
| [42] |
DOI URL |
| [43] |
DOI URL |
| [44] |
DOI URL |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
DOI |
| [49] |
|
| [1] | 刘伟, 白细民, 吕少杰, 史浙明, 齐之钰, 何冠儒. 基于井水位气压效应计算含水层的水力参数[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 652-667. |
| [2] | 雷生学, 刘建波, 闫伟, 宋田, 李昊, 李恩健, 朱冰清, 李颖楠. 岩体完整性对载荷干扰定量分析的影响——以天津小辛庄应变为例[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1600-1613. |
| [3] | 张大维, 田竹君, 朱清钟. 北京塔院井水位短临预报指标的研究[J]. 地震地质, 1994, 16(2): 179-187. |
| [4] | 杜品仁. 北京塔院井水位微动态资料的分析和应用[J]. 地震地质, 1987, 9(1): 85-90. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||