SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (3): 869-880.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.03.20250044
Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Xiao-fei1,2)( ), MENG Ling-yuan2),*(
), MENG Ling-yuan2),*( )
)
Received:2025-02-05
Revised:2025-02-24
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-08-13
通讯作者:
*孟令媛, 女, 1983年生, 博士, 研究员, 主要从事震源物理、 地震活动性和强地面运动方面的研究, E-mail: menglingyuan@seis.ac.cn。
作者简介:吴晓菲, 女, 2001年生, 现为中国地震局地震预测研究所地球物理学专业在读硕士研究生, 主要从事地震活动性及地震致灾特征研究, E-mail: wuxiaofei96@163.com。
基金资助:WU Xiao-fei, MENG Ling-yuan. COMPARISON OF THE CHARACTERISTICS OF EARTHQUAKE SEQUENCE AND INTENSITY OF THE JANUARY 7, 2025 MS6.8 DINGRI EARTHQUAKE IN XIZANG[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 869-880.
吴晓菲, 孟令媛. 2025年1月7日西藏定日6.8级地震序列特征及烈度比较分析[J]. 地震地质, 2025, 47(3): 869-880.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.dzdz.ac.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.03.20250044
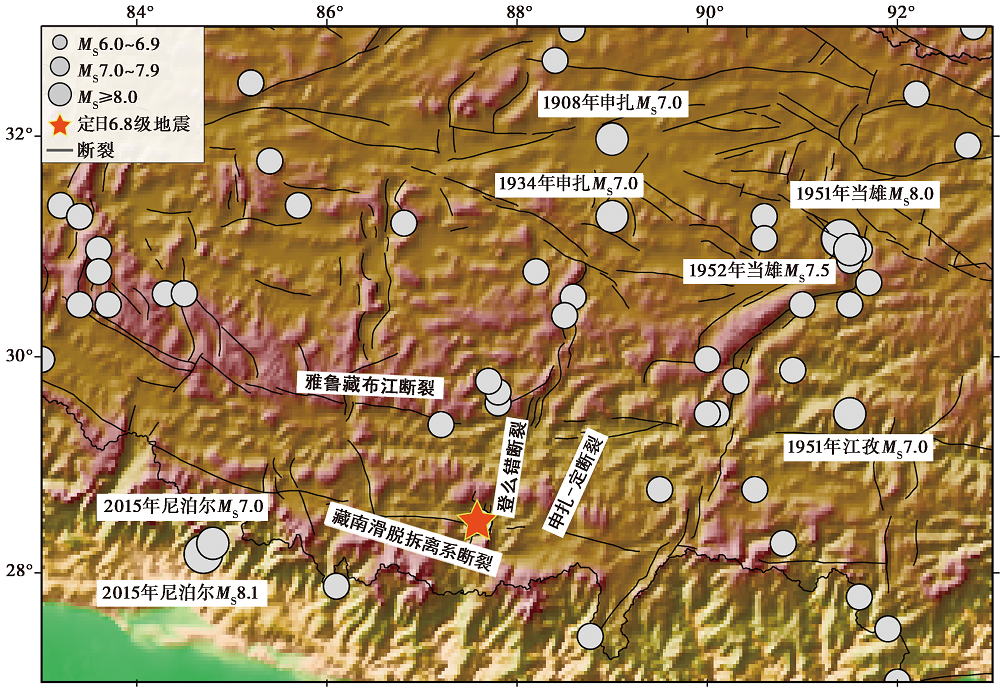
Fig. 2 Map of distribution of historical earthquakes with MS≥6.0 and faults in the vicinity of the epicenter of the 2025 Xizang Dingri MS6.8 earthquake.
| 序号 | 时间 | 北纬/(°) | 东经/(°) | 震级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2025-01-07, 09:09 | 28.90 | 87.48 | MS4.6,— |
| 2 | 2025-01-07,09:14 | 28.52 | 87.52 | ML5.1,— |
| 3 | 2025-01-07, 09:24 | 28.35 | 87.37 | ML4.2, MS4.4 |
| 4 | 2025-01-07, 09:37 | 28.36 | 87.67 | ML4.3, MS4.2 |
| 5 | 2025-01-07, 09:43 | 28.22 | 87.63 | ML4.2, MS4.1 |
| 6 | 2025-01-08, 11:51 | 28.42 | 87.44 | ML4.3, MS4.0 |
| 7 | 2025-01-13, 20:57 | 28.42 | 87.50 | ML4.8, MS4.9 |
| 8 | 2025-01-13, 20:58 | 28.45 | 87.52 | ML5.0, MS5.0 |
| 9 | 2025-01-13, 23:44 | 28.45 | 87.46 | ML4.6, MS4.2 |
| 10 | 2025-01-16, 11:19 | 28.47 | 87.50 | ML4.5, MS4.4 |
| 11 | 2025-01-18, 23:36 | 28.35 | 87.57 | ML5.0, MS4.6 |
| 12 | 2025-01-19, 00:26 | 28.36 | 87.57 | ML4.2, MS4.2 |
| 13 | 2025-01-21, 05:03 | 28.20 | 87.56 | ML4.6, MS4.6 |
| 14 | 2025-01-21, 08:14 | 28.28 | 87.54 | ML4.2, MS4.1 |
| 15 | 2025-01-27, 17:33 | 28.55 | 87.42 | ML4.5, MS4.1 |
Table 1 Information of aftershocks with MS≥4.0 from January 7, 2025 to January 27, 2025 for the 2025 Xizang Dingri MS6.8 Earthquake
| 序号 | 时间 | 北纬/(°) | 东经/(°) | 震级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2025-01-07, 09:09 | 28.90 | 87.48 | MS4.6,— |
| 2 | 2025-01-07,09:14 | 28.52 | 87.52 | ML5.1,— |
| 3 | 2025-01-07, 09:24 | 28.35 | 87.37 | ML4.2, MS4.4 |
| 4 | 2025-01-07, 09:37 | 28.36 | 87.67 | ML4.3, MS4.2 |
| 5 | 2025-01-07, 09:43 | 28.22 | 87.63 | ML4.2, MS4.1 |
| 6 | 2025-01-08, 11:51 | 28.42 | 87.44 | ML4.3, MS4.0 |
| 7 | 2025-01-13, 20:57 | 28.42 | 87.50 | ML4.8, MS4.9 |
| 8 | 2025-01-13, 20:58 | 28.45 | 87.52 | ML5.0, MS5.0 |
| 9 | 2025-01-13, 23:44 | 28.45 | 87.46 | ML4.6, MS4.2 |
| 10 | 2025-01-16, 11:19 | 28.47 | 87.50 | ML4.5, MS4.4 |
| 11 | 2025-01-18, 23:36 | 28.35 | 87.57 | ML5.0, MS4.6 |
| 12 | 2025-01-19, 00:26 | 28.36 | 87.57 | ML4.2, MS4.2 |
| 13 | 2025-01-21, 05:03 | 28.20 | 87.56 | ML4.6, MS4.6 |
| 14 | 2025-01-21, 08:14 | 28.28 | 87.54 | ML4.2, MS4.1 |
| 15 | 2025-01-27, 17:33 | 28.55 | 87.42 | ML4.5, MS4.1 |
| [1] |
黄婷, 吴中海, 韩帅, 等. 2024. 西藏日喀则地区的活断层基本特征及地震灾害潜在风险评估[J]. 地震科学进展, 54(10): 696-711.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
梁明剑, 董芸希, 左洪, 等. 2025. 2025年西藏定日6.8级地震登么错段地表变形特征及其成因[J]. 地震地质, 47(1): 80-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.01.006.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [3] |
刘婷, 何骁慧, 计婷婷, 等. 2025. 2017年8月8日九寨沟地震的余震序列特征与地震灾害效应[J]. 灾害学, 40(1): 220-226.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
孟令媛, 史保平. 2012. 2010年墨西哥BajaMW7.2地震与中国玉树 MW6.9 地震强地震动特征的对比研究[J]. 地震学报, 34(1): 1-19.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
孟令媛, 解孟雨, 臧阳. 2022. 2022年门源 MS6.9 和2016年门源 MS6.4 地震序列比较分析[J]. 中国地震, 38(1): 1-11.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
潘章容, 周扬, 苗在鹏, 等. 2023. 2022年1月8日青海门源6.9级地震仪器烈度与宏观烈度对比分析[J]. 高原地震, 35(3): 8-15.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
石峰, 梁明剑, 罗全星, 等. 2025. 2025年1月7日西藏定日6.8级地震发震构造与同震地表破裂特征[J]. 地震地质, 47(1): 1-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.01.001.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [8] |
田婷婷, 吴中海. 2023. 西藏申扎-定结裂谷南段丁木错正断层的最新史前大地震事件及其地震地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 69(S1): 53-55.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
王海云. 2011. 渭河盆地中土层场地对地震动的放大作用[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(1): 137-150.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
吴中海, 叶培盛, 王成敏, 等. 2015. 藏南安岗地堑的史前大地震遗迹、 年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 40(10): 1621-1642.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
吴中海, 赵根模, 刘杰. 2016. 2015年尼泊尔 MS8.1 地震构造成因及对青藏高原及邻区未来强震趋势的影响[J]. 地质学报, 90(6): 1062-1085.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
张晁军. 2021. 云南大理 MS6.4 地震与意大利拉奎拉 MW6.3 地震序列的比较研究和危险性分析启示[J]. 地震科学进展, 51(8): 345-351, 361.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
张建龙, 尼玛, 司金罗布, 等. 2021. 西藏定日 MS5.9 地震烈度评定及震害特征分析[J]. 西藏科技, (1): 48-49, 59.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
张进江, 丁林. 2003. 青藏高原EW向伸展及其地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 38(2): 179-189.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
张培震, 邓起东, 张竹琪, 等. 2013. 中国大陆的活动断裂、 地震灾害及其动力过程[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 43(10): 1607-1620.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
张培震, 王伟涛, 甘卫军, 等. 2022. 青藏高原的现今构造变形与地球动力过程[J]. 地质学报, 96(10): 3297-3313.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
赵伟华, 许强, 吉锋, 等. 2025. 2025年1月7日西藏定日 MS6.8 地震形变场特征及场地效应分析[J/OL]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 52: 1-12.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
USGS(US Geological Survey). 2017. Advanced National Seismic System-Current Status, Development Opportunities, and Priorities for 2017-2027[M]. US Geological Survey, Circular, 1429, 32 p. doi: 10.3133/cir1429.
|
| [1] | GUO Zhao-wu, LU Ren-qi, ZHANG Jin-yu, FANG Li-hua, LIU Guan-shen, WU Xi-yan, SUN Xiao, QI Shi-miao. THREE-DIMENSIONAL MODEL OF SEISMOGENIC FAULT AND SEISMIC ENVIRONMENT OF XIZANG DINGRI MS6.8 EARTHQUAKE OF JANUARY 7, 2025 [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 671-688. |
| [2] | GAO Yang, WU Zhong-hai, HAN Shuai, TIAN Ting-ting. LATE QUATERNARY THROW RATE OF THE SEISMOGENIC FAULT(DENGMECUO FAULT)OF THE 2025 MS6.8 DINGRI EARTHQUAKE IN SHIGATSE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 689-706. |
| [3] | WANG Duo, CHEN Li-chun, LI Yan-bao, WANG Hu, JIA Yong-shun, GAO Yin-yi, XUE Ke-yi. LATE QUATERNARY ACTIVITY OF THE XIETONGMEN TO DENGMECUO SEGMENT ALONG THE XAINZA-DINGGYE RIFT IN SOUTHERN QINGHAI-XIZANG PLATEAU [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 718-733. |
| [4] | XU Yue-yi, XU Bei-bei, XU Chen-yu, SHAO Zhi-gang, HU Chao-zhong. JOINT INVERSION OF THE 2025 DINGRI MS6.8 EARTHQUAKE RUPTURE PROCESS BASED ON TELESEISMIC P WAVES, STRONG-MOTION AND INSAR DATA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 734-746. |
| [5] | QIAO Jun-xiang, SHI Feng, LI An, LI Tao, ZHANG Da, WANG Xin, Gesangdanzhen, SUN Hao-yue. COSEISMIC SURFACE RUPTURE OF THE MS6.8 DINGRI EARTHQUAKE IN XIZANG, CHINA, BASED ON GF IMAGERY INTERPRETATION [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 789-805. |
| [6] | WANG Peng, DAI Zong-hui, KONG Xue, LI Bo, XU Chang-peng, ZHANG Meng-xin. ANALYSIS ON THE EVOLUTION CHARACTERISTICS OF LOCAL STRESS FIELD IN THE MAGNITUDE 6.8 EARTHQUAKE SEQUENCE IN DINGRI, XIZANG [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 881-896. |
| [7] | YIN Xiao-fei, QIANG Sheng-yin, ZHANG Wei, SHAO Zhi-gang, WANG Wu-xing, YUAN Xiao-xiang, LI Yong-sheng, LIU Hao. RESEARCH ON GROUND MOTION SIMULATION OF THE DINGRI MS6.8 EARTHQUAKE IN XIZANG BASED ON DIFFERENT SOURCE MODELS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 897-916. |
| [8] | JI Zhi-wei, YU Hou-yun, LI Zong-chao, JU Chang-hui, SUN Yao-chong, ZHANG Yong-xian, CHEN Xiao-fei. PRELIMINARY SIMULATION OF LONG-PERIOD GROUND MOTION OF THE DINGRI MS6.8 EARTHQUAKE ON JANUARY 7, 2025 [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 917-931. |
| [9] | DU Hao-guo, ZUO Xiao-qing, LIN Xu-chuan, XIAO Ben-fu, LU Yong-kun, HE Shi-fang, ZHANG Fang-hao, YUAN Xiao-xiang, TAO Tian-yan, YE Yang, DENG Shu-rong, ZHAO Zheng-xian, XU Jun-zu, BAI Xian-fu, ZHANG Yuan-shuo, ZHANG Lu-lu. TEXTURE FEATURE DAMAGE DETECTION OF SINGLE BUILD-ING BASED ON DRONE IMAGES AFTER EARTHQUAKE: A CASE STUDY OF 2025 DINGRI MS6.8 EARTHQUAKE IN XIZANG, CHINA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 949-968. |
| [10] | ZHANG Li-feng, ZHONG Mei-jiao, PAN Yu-hang, GUO Ying-xia, SUN Xi-hao, ZHANG Yuan-sheng. STUDY ON THERMAL INFRARED ANOMALIES OF THE 2025 DINGRI MS6.8 EARTHQUAKE AND SEVERAL EARTHQUAKE CASES IN SOUTHERN XIZANG [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(3): 984-998. |
| [11] | WANG Xue-zhu, WU Chuan-yong, LIU Jian-ming, ZANG Ke-zhi, YUAN Hai-yang, GAO Zhan, ZHANG Jin-shuo, MA Yun-xiao. EARTHQUAKE SEQUENCE RELOCATION AND SEISMOGENIC STRUCTURE OF THE 2024 MS7.1 WUSHI EARTHQUAKE ON JANUARY 23, 2024, XINJIANG [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(2): 488-506. |
| [12] | ZOU Jun-jie, SHAO Zhi-gang, HE Hong-lin, GAO Lu, XU Yue-yi, DOU Ai-xia, LIANG Ze-yu. SURFACE RUPTURE INTERPRETATION AND BUILDING DAMAGE ASSESSMENT OF XIZANG DINGRI MS6.8 EARTHQUAKE ON JANUARY 7, 2025 [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(1): 16-35. |
| [13] | SHI Feng, LIANG Ming-jian, LUO Quan-xing, QIAO Jun-xiang, ZHANG Da, WANG Xin, YI Wen-xing, ZHANG Jia-wei, ZHANG Ying-feng, ZHANG Hui-ping, LI Tao, LI An. SEISMOGENIC FAULT AND COSEISMIC SURFACE DEFORMATION OF THE DINGRI MS6.8 EARTHQUAKE IN XIZANG, CHINA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(1): 1-15. |
| [14] | YANG Jian-wen, JIN Ming-pei, YE Beng, LI Zhen-ling, LI Qing. SOURCE RUPTURE MECHANISM AND STRESS CHANGES TO THE ADJACENT AREA OF JANUARY 7, 2025, MS6.8 DINGRI EARTHQUAKE, XIZANG, CHINA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(1): 36-48. |
| [15] | WEI Ben-yong, ZHANG Yu-man, SHI Feng, QIAO Jun-xiang, WANG Xin, ZHANG Da. ANALYSIS OF BUILDING DAMAGE AND CASUALTIES OF THE 2025 DINGRI MS6.8 EARTHQUAKE IN XIZANG BASED ON FIELD INVESTIGATION [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(1): 64-79. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||