地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 753-771.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.03.009
张文亮1)( ), 李营1),*(
), 李营1),*( ), 刘兆飞1), 胡乐1), 路畅1), 陈志1), 韩晓昆2)
), 刘兆飞1), 胡乐1), 路畅1), 陈志1), 韩晓昆2)
收稿日期:2023-02-20
修回日期:2023-03-13
出版日期:2023-06-20
发布日期:2023-07-18
通讯作者:
* 李营, 男, 1978年生, 研究员, 主要从事与构造、 地震有关的流体地球化学工作, E-mail: 作者简介:张文亮, 男, 1999年生, 现为中国地震局地震预测研究所构造地质学专业在读硕士研究生, 主要研究方向为与构造、 地震有关的流体地球化学工作, E-mail: zhangwli99@163.com。
基金资助:
ZHANG Wen-liang1)( ), LI Ying1),*(
), LI Ying1),*( ), LIU Zhao-fei1), HU Le1), LU Chang1), CHEN Zhi1), HAN Xiao-kun2)
), LIU Zhao-fei1), HU Le1), LU Chang1), CHEN Zhi1), HAN Xiao-kun2)
Received:2023-02-20
Revised:2023-03-13
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-07-18
摘要:
断裂带土壤气体地球化学特征与区域构造演化密切相关。文中为探讨六盘山东麓断裂带土壤气He浓度的空间分布特征及其与构造活动之间的关系, 在六盘山东麓断裂跨断层布设了8条土壤气测量剖面, 沿测线开展土壤气He浓度的测量; 同时, 为进行对比分析, 选择位于六盘山东麓断裂以东14km的小关山断裂布设3条跨断层土壤气测量剖面, 沿测线开展土壤气He浓度的测量。测量结果显示, 六盘山东麓断裂各测量剖面的He浓度平均值为4.983~6.335ppm; 小关山断裂各测量剖面的He浓度平均值为4.784~5.235ppm。2条断裂的He浓度在空间分布上均呈现出断裂北部高于断裂中南段的特征, 这与断裂的区域活动性差异密切相关。结合前人对六盘山东麓断裂活动时代、 闭锁程度、 滑移速率、 构造应力的研究成果, 分析表明六盘山东麓断裂北段的活动性强于断裂中南段。经对比分析认为, 六盘山东麓断裂和小关山断裂的构造演化过程相似, 且断裂性质均为逆冲型, 因此2条断裂土壤气He浓度的空间分布特征一致。
张文亮, 李营, 刘兆飞, 胡乐, 路畅, 陈志, 韩晓昆. 六盘山东麓断裂带土壤气体He浓度的空间分布特征及其与构造活动之间的关系[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 753-771.
ZHANG Wen-liang, LI Ying, LIU Zhao-fei, HU Le, LU Chang, CHEN Zhi, HAN Xiao-kun. SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION CHARACTERISTICS OF SOIL GAS HE CONCENTRATION IN THE EASTERN LIUPANSHAN FAULT ZONE AND ITS RELATIONSHIP WITH TECTONIC ACTIVITY[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(3): 753-771.

图 1 研究区的构造简图、 地质图及地质剖面图 改自文献(邓起东等, 1989; Zhang et al., 1991; 向宏发等, 1998a, b)
Fig. 1 Structural sketch, geological map and geological section of the study area.
| 剖面 | 测点数 | 均值 | 标准差 | 最小值 | 中位数 | 最大值 | Q1 | Q3 | 异常上界 | 异常下界 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 孙永庄 | SZ | 120 | 5.216 | 0.191 | 4.648 | 5.233 | 5.785 | 5.098 | 5.332 | 5.407 | 5.025 |
| 海家庄 | HJZ | 99 | 6.335 | 0.347 | 5.094 | 6.410 | 6.874 | 5.991 | 6.597 | 6.682 | 5.988 |
| 杨岭村 | YLC | 102 | 4.983 | 0.353 | 3.884 | 4.986 | 5.915 | 4.810 | 5.245 | 5.336 | 4.629 |
| 六盘村 | LP | 87 | 5.240 | 0.517 | 4.258 | 5.155 | 7.472 | 4.873 | 5.537 | 5.757 | 4.722 |
| 大庄村 | DZ | 68 | 5.351 | 0.282 | 4.498 | 5.332 | 5.987 | 5.169 | 5.541 | 5.633 | 5.069 |
| 森林公园 | SL | 90 | 5.212 | 0.300 | 4.518 | 5.262 | 5.862 | 4.988 | 5.423 | 5.512 | 4.912 |
| 西贤 | XX | 105 | 5.123 | 0.43 | 3.786 | 5.170 | 5.970 | 4.870 | 5.468 | 5.553 | 4.686 |
| 刘店 | LD | 102 | 5.069 | 0.356 | 4.192 | 5.109 | 5.834 | 4.786 | 5.325 | 5.425 | 4.712 |
| 乃家河 | NJ | 108 | 5.235 | 0.343 | 4.374 | 5.258 | 6.015 | 5.010 | 5.475 | 5.578 | 4.891 |
| 蒿店 | HD | 107 | 4.784 | 0.943 | 2.168 | 4.984 | 7.043 | 4.203 | 5.312 | 5.727 | 3.842 |
| 羊槽村 | YC | 120 | 4.958 | 0.473 | 3.517 | 4.972 | 6.119 | 4.613 | 5.332 | 5.431 | 4.485 |
表 1 土壤气He浓度的测量结果
Table 1 Measurement results of the concentration of soil gas He
| 剖面 | 测点数 | 均值 | 标准差 | 最小值 | 中位数 | 最大值 | Q1 | Q3 | 异常上界 | 异常下界 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 孙永庄 | SZ | 120 | 5.216 | 0.191 | 4.648 | 5.233 | 5.785 | 5.098 | 5.332 | 5.407 | 5.025 |
| 海家庄 | HJZ | 99 | 6.335 | 0.347 | 5.094 | 6.410 | 6.874 | 5.991 | 6.597 | 6.682 | 5.988 |
| 杨岭村 | YLC | 102 | 4.983 | 0.353 | 3.884 | 4.986 | 5.915 | 4.810 | 5.245 | 5.336 | 4.629 |
| 六盘村 | LP | 87 | 5.240 | 0.517 | 4.258 | 5.155 | 7.472 | 4.873 | 5.537 | 5.757 | 4.722 |
| 大庄村 | DZ | 68 | 5.351 | 0.282 | 4.498 | 5.332 | 5.987 | 5.169 | 5.541 | 5.633 | 5.069 |
| 森林公园 | SL | 90 | 5.212 | 0.300 | 4.518 | 5.262 | 5.862 | 4.988 | 5.423 | 5.512 | 4.912 |
| 西贤 | XX | 105 | 5.123 | 0.43 | 3.786 | 5.170 | 5.970 | 4.870 | 5.468 | 5.553 | 4.686 |
| 刘店 | LD | 102 | 5.069 | 0.356 | 4.192 | 5.109 | 5.834 | 4.786 | 5.325 | 5.425 | 4.712 |
| 乃家河 | NJ | 108 | 5.235 | 0.343 | 4.374 | 5.258 | 6.015 | 5.010 | 5.475 | 5.578 | 4.891 |
| 蒿店 | HD | 107 | 4.784 | 0.943 | 2.168 | 4.984 | 7.043 | 4.203 | 5.312 | 5.727 | 3.842 |
| 羊槽村 | YC | 120 | 4.958 | 0.473 | 3.517 | 4.972 | 6.119 | 4.613 | 5.332 | 5.431 | 4.485 |
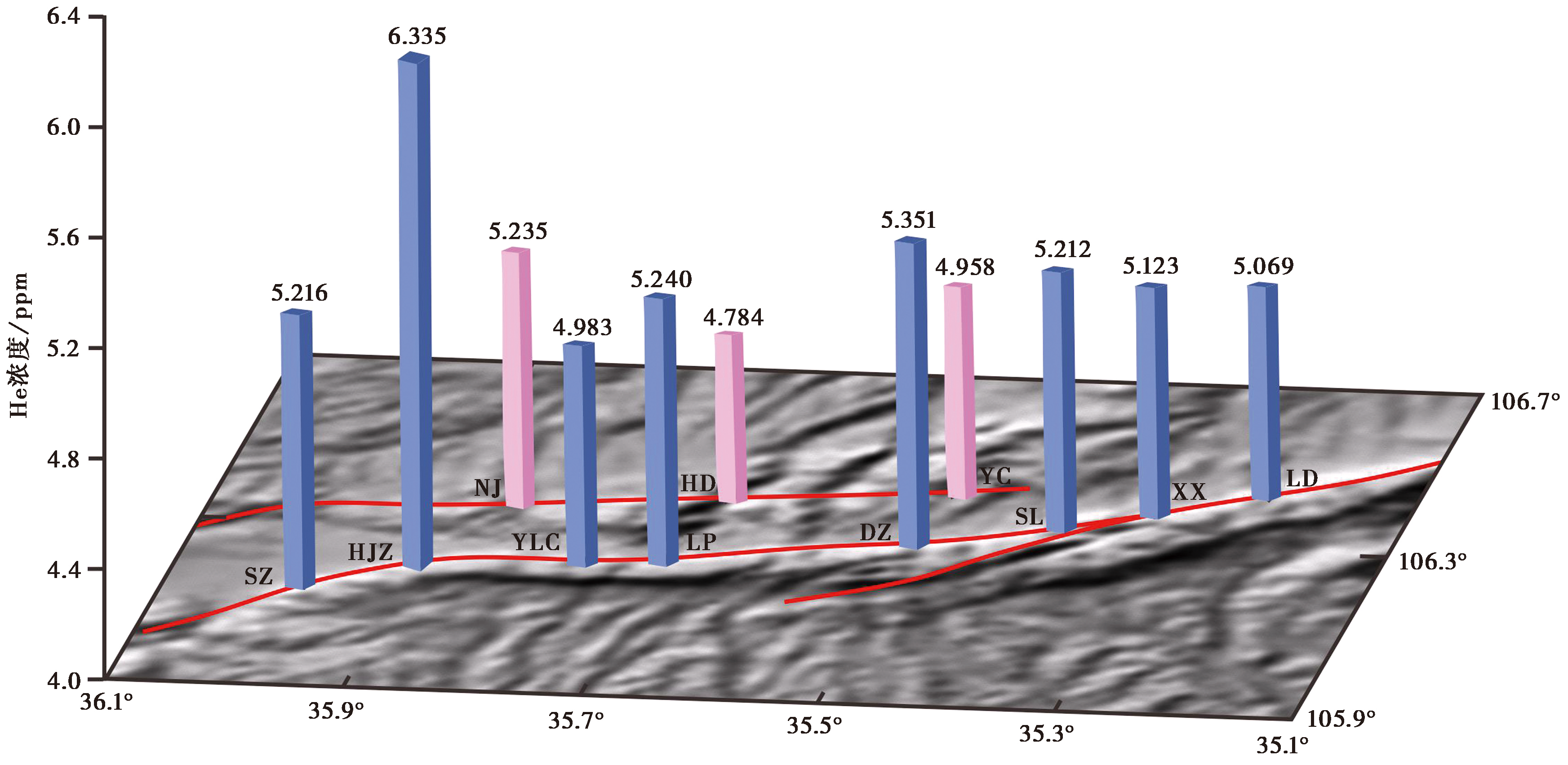
图 4 六盘山东麓断裂和小关山断裂各个剖面的He浓度空间分布
Fig. 4 The spatial distribution of He concentration in each section of the eastern Liupanshan Fault and the Xiaoguanshan Fault.
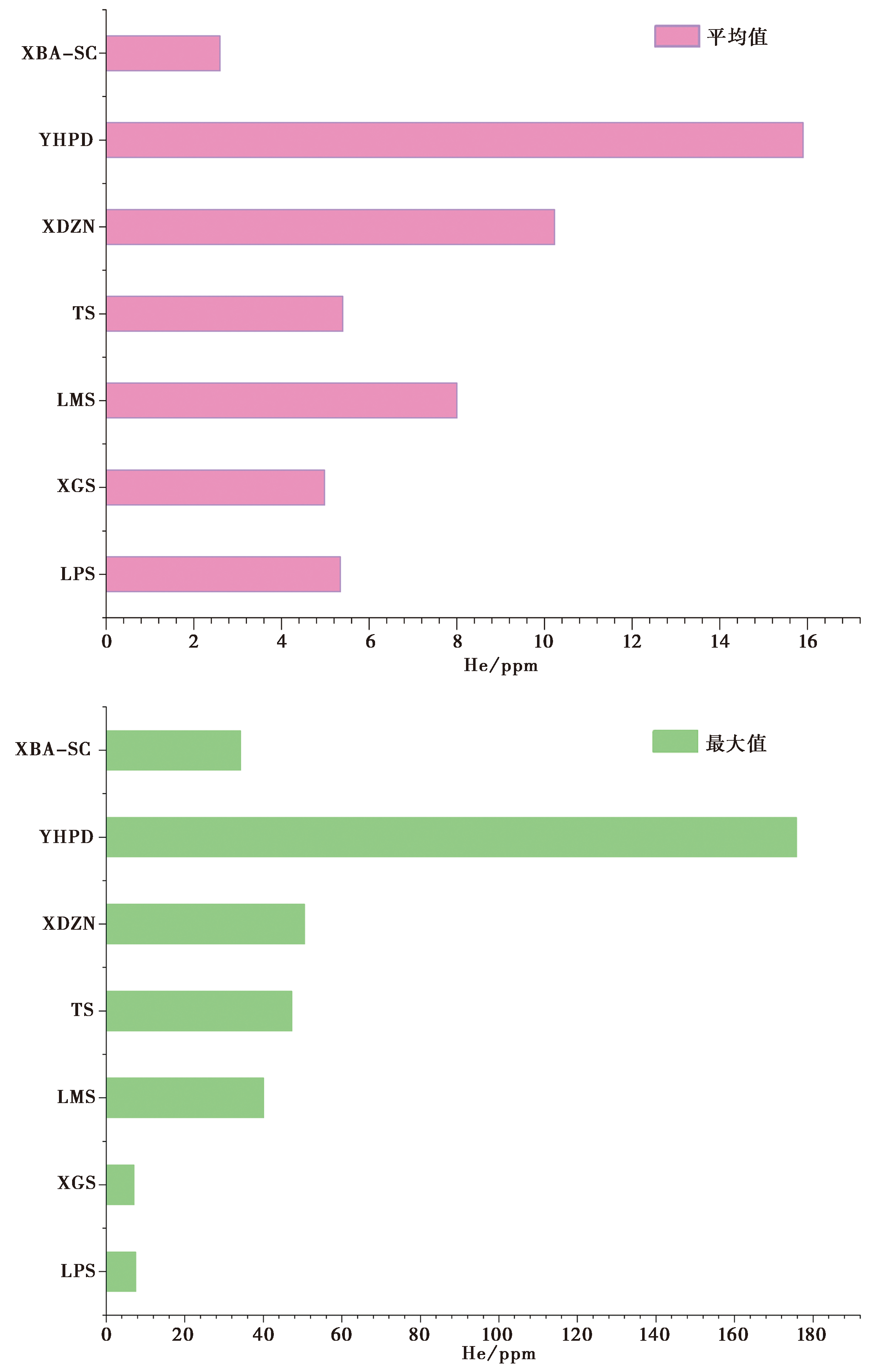
图 5 中国不同断裂带土壤气He浓度的均值和最大值对比图 LPS 六盘山东麓断裂; XGS 小关山断裂; LMS 龙门山断裂带汶川地震地表破裂带; TS 唐山断裂带; XDZN 夏垫断裂中南段; YHPD 延怀盆地; XBA-SC 新保安-沙城断裂。数据引自文献(李营等, 2009; Zhou et al., 2010;韩晓昆等, 2013; Li et al., 2013; 盛艳蕊等, 2015)
Fig. 5 Comparison of mean and maximum values of soil gas He concentration in different fault zones in China.
| [1] |
鲍志诚, 赵爱平, 吕坚, 等. 2022. 瑞昌-武宁活动断裂带土壤气地球化学特征[J]. 地震研究, 45(2): 249-256.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
柴炽章, 马禾青, 金春华. 2003. 祁连山-六盘山地震带中强地震活动特点及震前异常特征[J]. 西北地震学报, 25(4): 67-71.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
车用太, 刘成龙, 鱼金子, 等. 2008. 汶川 MS8.0 地震的地下流体与宏观异常及地震预测问题的思考[J]. 地震地质, 30(4): 828-838.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
陈绍绪, 张跃刚, 乔子云, 等. 2003. 晋冀蒙交界地区主要断裂的现今活动[J]. 华北地震科学, 21(2): 16-22.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
邓起东, 张维岐, 张培震, 等. 1989. 海原走滑断裂带及其尾端挤压构造[J]. 地震地质, 11(1): 1-14.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
杜方, 闻学泽, 冯建刚, 等. 2018. 六盘山断裂带的地震构造特征与强震危险背景[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(2): 545-559.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
付碧宏, 王萍, 孔屏, 等. 2008. 四川汶川5·12大地震同震滑动断层泥的发现及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 24(10): 2237-2243.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
高小其, 蓝陵, 许秋龙, 等. 2002. 乌鲁木齐10号泉He含量变化的映震特征[J]. 四川地震, (3): 27-31.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
郭正府, 郑国东, 孙玉涛, 等. 2017. 中国大陆地质源温室气体释放[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 36(2): 204-212, 183.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
韩晓昆, 李营, 杜建国, 等. 2013. 夏垫断裂中南段土壤气体地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 37(6): 976-982.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
郝明, 李煜航, 秦姗兰. 2017. 基于GPS数据的海原-六盘山断裂带滑动速率亏损时空分布[J]. 地震地质, 39(3): 471-484. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.03.003.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [12] |
蒋锋云, 季灵运, 赵强. 2021. 海原-六盘山断裂带现今地震危险性的数值模拟分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 230-240.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
江娃利, 侯治华, 肖振敏, 等. 2000. 北京平原夏垫断裂齐心庄探槽古地震事件分析[J]. 地震地质, 22(4): 413-422.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
孔令昌, 陈文寄. 1986. 氦及其同位素比值与断层和地震活动的关系[J]. 地震地质译丛, (5): 40-42.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
李海兵, 王宗秀, 付小方, 等. 2008. 2008年5月12日汶川地震(MS8.0)地表破裂带的分布特征[J]. 中国地质, 35(5): 803-813.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
李强, 江在森, 武艳强, 等. 2013. 海原-六盘山断裂带现今构造变形特征[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 33(2): 18-22.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
李营, 陈志, 胡乐, 等. 2022. 流体地球化学进展及其在地震预测研究中的应用[J]. 科学通报, 67(13): 1404-1420.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
李营, 杜建国, 王富宽, 等. 2009. 延怀盆地土壤气体地球化学特征[J]. 地震学报, 31(1): 82-91, 117.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
林茂炳, 吴山. 1991. 龙门山推覆构造变形特征[J]. 成都地质学院学报, 18(1): 46-55.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
刘亢, 曲国胜, 房立华, 等. 2015. 唐山古冶、 滦县地区中小地震活动与构造关系研究[J]. 地震, 35(2): 111-120.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
刘兆飞, 李营, 陈志, 等. 2019. 吉兰泰断陷盆地周缘断裂带气体释放及其对断层活动性的指示意义[J]. 地震学报, 41(5): 613-632, 680.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
庞亚瑾, 杨少华, 李海兵, 等. 2019. 青藏高原东北缘海原-六盘山断裂带现今地壳应力环境的数值分析[J]. 岩石学报, 35(6): 1848-1856.
|
|
DOI URL |
|
| [23] |
盛艳蕊, 张子广, 周晓成, 等. 2015. 新保安-沙城断裂带土壤气地球化学特征分析[J]. 地震, 35(4): 90-98.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
史志刚, 李廷栋, 袁道阳, 等. 2014. 六盘山东麓断裂南段断裂沟槽韵律沉积特征对最新活动时代的限定[J]. 地球学报, 35(1): 31-37.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
王登红, 毛景文. 1996. 氦同位素地质研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 15(2): 51-56.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
王广才, 张作辰, 汪民, 等. 2003. 延怀盆地地下热水与稀有气体的地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质, 25(3): 421-429.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
王喜龙, 李营, 杜建国, 等. 2017. 首都圈地区土壤气Rn, Hg, CO2地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 地震学报, 39(1): 85-101, 155.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
王小娟, 韩晓昆, 陈志, 等. 2016. 六盘山东麓断裂带逸出气氡浓度特征分析[J]. 地震工程学报, 38(S2): 276-281.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
王永才, 孙香荣. 1992. 河北及邻近地区地下水溶解二氧化碳、 氢和氦分布的地震地质特征[J]. 华北地震科学, 10(2): 58-66.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
吴玉涛, 杨为民, 谭成轩, 等. 2018. 延怀盆地隐伏断裂第四纪活动性研究[J]. 华北地震科学, 36(4): 1-9.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
向宏发, 方仲景, 徐杰, 等. 1988. 三河-平谷8级地震区的构造背景与大震重复性研究[J]. 地震地质, 10(1): 15-28.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
向宏发, 虢顺民, 张秉良, 等. 1998a. 六盘山东麓地区活动构造研究[J]. 国际地震动态, (7): 24-27.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
向宏发, 虢顺民, 张秉良, 等. 1998b. 六盘山东麓活动逆断裂构造带晚第四纪以来的活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 20(4): 321-327.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
谢富仁, 舒塞兵, 窦素芹, 等. 2000. 海原-六盘山断裂带至银川断陷第四纪构造应力场分析[J]. 地震地质, 22(2): 139-146.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
谢富仁, 张红艳, 崔效锋, 等. 2007. 延怀盆地活动断裂运动与现代构造应力场[J]. 地震地质, 29(4): 693-705.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 叶建青, 等. 2008. 汶川 MS8.0 地震地表破裂带及其发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 597-629.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
杨江, 李营, 陈志, 等. 2019. 唐山断裂带南西段和北东段土壤气Rn和CO2浓度特征[J]. 地震, 39(3): 61-70.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
詹艳, 赵国泽, 王继军, 等. 2005. 青藏高原东北缘海原弧形构造区地壳电性结构探测研究[J]. 地震学报, 27(4): 431-440, 466.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
张秉良, 向宏发, 虢顺民, 等. 2000. 六盘山东麓断裂断层泥的组构特征及其意义[J]. 地震地质, 22(1): 47-52.
|
|
|
|
| [40] |
张宏志, 刁桂苓, 陈祺福, 等. 2008. 1976年唐山7.8级地震震区现今地震震源机制分析[J]. 地震研究, 31(1): 1-6, 99.
|
|
|
|
| [41] |
张慧, 张新基, 苏鹤军, 等. 2010. 兰州市活动断层土壤气汞、 氡地球化学特征场地试验[J]. 西北地震学报, 32(3): 273-278.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
张培震, 郑德文, 尹功明, 等. 2006. 有关青藏高原东北缘晚新生代扩展与隆升的讨论[J]. 第四纪研究, 25(1): 5-13.
|
|
|
|
| [43] |
张晓亮, 师昭梦, 蒋锋云, 等. 2011. 海原-六盘山弧型断裂及其附近最新构造变形演化分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 31(3): 20-24.
|
|
|
|
| [44] |
赵元鑫, 李营, 陈志, 等. 2022. 唐山断裂带气体组分变异函数空间分布特征[J]. 地震, 42(1): 18-32.
|
|
|
|
| [45] |
周晓成, 杜建国, 陈志, 等. 2012. 地震地球化学研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 31(4): 340-346.
|
|
|
|
| [46] |
周晓成, 郭文生, 杜建国, 等. 2007. 呼和浩特地区隐伏断层土壤气氡、 汞地球化学特征[J]. 地震, 27(1): 70-76.
|
|
|
|
| [47] |
周晓成, 孙凤霞, 陈志, 等. 2017. 汶川 MS8.0 地震破裂带CO2、 CH4、 Rn和Hg脱气强度[J]. 岩石学报, 33(1): 291-303.
|
|
|
|
| [48] |
DOI URL |
| [49] |
DOI URL |
| [50] |
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
DOI URL |
| [53] |
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
DOI URL |
| [55] |
DOI URL |
| [56] |
DOI URL |
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
DOI URL |
| [59] |
DOI URL |
| [60] |
DOI URL |
| [61] |
DOI URL |
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
DOI URL |
| [67] |
DOI |
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
DOI PMID |
| [70] |
DOI URL |
| [71] |
DOI PMID |
| [72] |
DOI URL |
| [73] |
DOI |
| [74] |
DOI PMID |
| [75] |
DOI URL |
| [76] |
DOI URL |
| [77] |
DOI URL |
| [78] |
DOI URL |
| [79] |
DOI URL |
| [80] |
DOI URL |
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
DOI URL |
| [83] |
DOI |
| [84] |
DOI URL |
| [1] | 李营, 方震, 张晨蕾, 李继业, 鲍志诚, 张翔, 刘兆飞, 周晓成, 陈志, 杜建国. 地震流体地球化学短临预测研究进展与展望[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 593-621. |
| [2] | 蒋雨函, 王子思, 刘佳琪, 梁卉, 周启超, 高小其. 中国地震断裂带氢气观测研究现状[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 622-637. |
| [3] | 申华梁, 杨耀, 周志华, 芮雪莲, 廖晓峰, 赵德杨, 梁明剑, 陈梦蝶, 官致君, 任宏微. 川西理塘毛垭温泉群的成因及深部地热过程[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 689-709. |
| [4] | 王喜龙, 罗银花, 金秀英, 杨梦尧, 孔祥瑞. 辽南地区断裂带的断层土壤气地球化学特征及其对区域应力调整的指示[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 710-734. |
| [5] | 王江, 陈志, 张帆, 张志相, 张素欣. 雄安新区主要断裂带土壤气体的Rn与CO2脱气特征[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 735-752. |
| [6] | 王博, 崔凤珍, 刘静, 周永胜, 徐胜, 邵延秀. 玛多 MS7.4地震断层土壤气特征与地表破裂的相关性[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 772-794. |
| [7] | 朱治国, 祝意青, 王东振, 艾力夏提·玉山. 2020年伽师MS6.4地震重力与地壳形变综合分析[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 269-285. |
| [8] | 李昭, 付碧宏. 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段晚第四纪构造活动特征的地貌响应定量研究[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1421-1447. |
| [9] | 蒋雨函, 高小其, 杨朋涛, 刘冬英, 孙小龙, 向阳, 朱成英, 汪成国. 新疆北天山地区断裂带断层土壤气的地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1597-1614. |
| [10] | 朱成英, 闫玮, 麻荣, 李志海, 汪成国, 黄建明, 周晓成. 2017年8月9日精河MS6.6地震宏观烈度及其余震分布的断层气体地球化学表征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1225-1239. |
| [11] | 周秉锐, 潘波, 尹成孝, 张哲宇, 颜丽丽. 基于MELTS模型的长白山天池火山岩浆演化过程的新认识[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 831-844. |
| [12] | 王博, 周永胜, 钟骏, 胡小静, 张翔, 周青云, 李旭茂. 滇西北断裂带土壤气地球化学特征及对断层活动性的启示[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 428-447. |
| [13] | 路畅, 周晓成, 李营, 刘磊, 颜玉聪, 徐岳仁. 玛多MS7.4 地表破裂带与东昆仑断裂温泉的水文地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1101-1126. |
| [14] | 文翔, 周斌, 史水平, 覃坚, 李家宁, 何衍, 阎春恒, 罗远鹏. 桂西北地区近期重力与地壳形变综合分析[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(4): 927-943. |
| [15] | 熊诚, 谢祖军, 郑勇, 熊熊, 艾三喜, 谢仁先. 大别—郯庐造山带地壳上地幔Rayleigh面波层析成像[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(1): 1-20. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||